6 electrochemistry
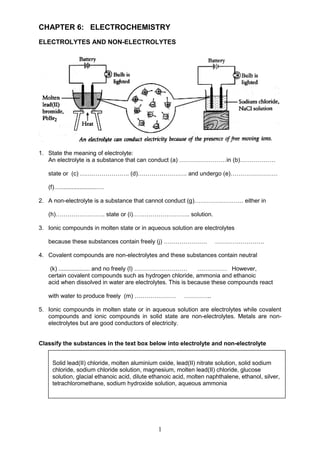
- 1. 1 CHAPTER 6: ELECTROCHEMISTRY ELECTROLYTES AND NON-ELECTROLYTES 1. State the meaning of electrolyte: An electrolyte is a substance that can conduct (a) ……………………in (b)……………… state or (c) ……………………. (d)……………………. and undergo (e)…………………… (f)…......................…. 2. A non-electrolyte is a substance that cannot conduct (g)……………………. either in (h)……………………. state or (i)……………………….. solution. 3. Ionic compounds in molten state or in aqueous solution are electrolytes because these substances contain freely (j) …………………. ……………………. 4. Covalent compounds are non-electrolytes and these substances contain neutral (k) ................... and no freely (l) ……………………… …………… However, certain covalent compounds such as hydrogen chloride, ammonia and ethanoic acid when dissolved in water are electrolytes. This is because these compounds react with water to produce freely (m) ………………… ………….. 5. Ionic compounds in molten state or in aqueous solution are electrolytes while covalent compounds and ionic compounds in solid state are non-electrolytes. Metals are non- electrolytes but are good conductors of electricity. Classify the substances in the text box below into electrolyte and non-electrolyte Solid lead(II) chloride, molten aluminium oxide, lead(II) nitrate solution, solid sodium chloride, sodium chloride solution, magnesium, molten lead(II) chloride, glucose solution, glacial ethanoic acid, dilute ethanoic acid, molten naphthalene, ethanol, silver, tetrachloromethane, sodium hydroxide solution, aqueous ammonia
- 2. 2 Electrolyte Non-electrolyte ELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN COMPOUNDS 1. What do you understand by the term electrolysis? Electrolysis is a process whereby compounds in (a) .................... or (b) ..…………… states are broken down (or decomposed) into their constituent (c) …………………… by passing (d) ……………………. through them. 2. Anode is the electrode which is connected to the (e) …………………. terminal of a battery. 3. Cathode is the electrode which is connected to the (f) ……………………… terminal of a battery. 4. Carbon or platinum is chosen as electrodes as they are chemically inert or unreactive. 5. The diagram below shows the set-up of apparatus of electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide. Name the main apparatus and materials in the diagram.
- 3. 3 6. Diagram 3.1 shows the relationship between the presence of freely moving ions and electrical conductivity. The box below shows a list of statements that explain the why ionic compound in solid state do not conduct electricity but will conduct electricity in aqueous solution. The statements are arranged in random order. Choose the correct statement from the box below and write it into the correct text box in Diagram 3.1. Diagram 3.1 During electrolysis cations are attracted to the cathode and anions are attracted to the anode. Solid sodium chloride contains sodium ions and chloride ions which are in fixed position and not freely moving. In solid state, sodium ions and chloride ions are strongly attracted by electrostatic forces in a lattice. Electric circuit is complete due to the flow of electrons along the connecting wires and movement of ions in the solution. If the electrodes are placed further apart, the ammeter reading will decrease because there will be an increase in internal resistance. Aqueous sodium chloride contains freely moving ions to conduct electricity.
- 4. 4 7. Colour all the cations red and the anions blue in solid sodium chloride and in the electrolyte in Diagram 3.1 above. 8. Given below is a list of ionic compounds in molten state. Identify the cation and anion in each electrolyte. Electrolyte (Molten) Cation Anion Name Formula Name Formula Sodium chloride Lead(II) oxide Potassium bromide 9. Given below is a list of electrolytes and products discharged at both electrodes. Based on the given substance discharged at the electrode, write a half equation to represent the reaction occurring at the electrode. Electrolyte (molten) Substance discharged at the electrodes and the half equation Anode Cathode (i) Aluminium oxide Oxygen gas Half equation: …………………………………….. Aluminium Half equation: …………………………………….. (ii) Potassium iodide Iodine Half equation: …………………………………… Potassium Half equation: ……………………………..……… (iii) Sodium chloride Chlorine gas Half equation: …………………………………..… Sodium Half equation: ………….………………………… (iv) Zinc bromide Bromine gas Half equation: ………………………………..…… Zinc Half equation: …………….………………………
- 5. 5 10. The flow chart below is used to predict the products formed at the electrodes during the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide. 11. In the spaces below, draw a similar flow chart (as in question 1) to predict the products formed at the electrodes from the electrolysis of molten zinc chloride, ZnCl2. d Molten lead(II) bromide a gf e cb Consists of (Ions that are present) ( Movement of ions) To anode To cathode (Half equation) At Anode At Cathode (Products formed) At Anode At Cathode
- 6. 6 ELECTROLYSIS OF AQUEOUS SOLUTION 1. State three factors that may influence the selective discharge of ions during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution. (a) ………………………………………………………………………………………………… (b) …………………………………………………………………………………………………. (c) …………………………………………………………………………………………………. 2. In an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, apart from sodium ions, Na+ and chloride ions, Cl-- , ………………………ions, ……… and ……………………………….ions, …… from the slight dissociation of water are also present. 3. List the electrochemistry series (cations and anions) in order of increasing ease of discharge. Ease of discharge increases Cation: ……………………………………………………………………………………………. Anion: …………………………………………………………………………………………….. 4. The following statements refer to the factors that affect the electrolysis of an aqueous solution. Fill in the blanks. (a) The ions that are placed …………………… in the electrochemical series will be ……………….. discharged. (b) If the concentration of a particular ion is …………………, the ion is …………….. ……………………… (c) In the electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate, CuSO4 ……………..using copper electrodes, no ions are discharged at the anode. Instead, the copper anode …………………… and ………………………… in the electrolyte. 5. The diagram below shows the set-up of apparatus of an electrolytic cell containing concentrated copper(II) sulphate solution. Two test tubes filled with copper(II) sulphate solution were placed over the electrodes J and K to collect any gas evolved. The switch is then turned on so that electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate solution can occur.
- 7. 7 (a) Identify the cations and the anions present in the aqueous solution. Cations: …………………………………….. Anions: …………………..……………………… (b) Identify which electrode ( J or K ) is the anode and the cathode: Anode ……………………………….. Cathode ………………………………………. (c) (i) Which ion is selectively discharge at the anode? ……………………………………… (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i). ………………………………………………….. …..……………………………………………………………………………………………. (iii) What do you observe at the anode? ……………………………………………………… (iv) Give one test to confirm the gas released at K. ………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………. (v) Write a half equation to represent the discharge of ions at anode. …….…………………………………………………………………………………………… (d) (i) Which ion is selectively discharge at the cathode? ………………………………………… (ii) Give a reason for your answer in (d) (i) …………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………… (iii) Which do you observe at the cathode? ………………………………………………… (iv) Write a half equation to represent the discharge of ions at the cathode. …………………………………. …………………………………………………………. (e) What do you observe about the copper(II) sulphate solution? …………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- 8. 8 6. The table below shows three electrolytic cells with different electrolytes and different electrodes. You are required to answer each section by writing your answer in the spaces provided. 1. In the diagrams, label the cathode with the symbol “” and the anode with the symbol “+”. 2. Show the direction of the flow of the electrons with arrowheads, “ > “ 3. Write the formula of all ions in the electrolyte. 4. Write the formula of ions which are attracted to the cathode. Underline the formula of ion which is selectively discharged. 5. Write the half equation to represent the reaction at the cathode. 6. What will you observe at the cathode? 7. Write the formula of ions which are attracted to the anode. Underline the formula of ion which is selectively discharged. 8. Write the half equation to represent the reaction at the anode. 9. What will you observe at the anode?
- 9. 9 ELECTROLYSIS IN INDUSTRIES 1. Fill in the blanks. The application of electrolysis in industries are (a) ………………………………………. (b) ……………………………………………… and (c) …………………………………… In the extraction of aluminium from its ore, (d) ….……………… electrodes are used and (e) ……..………………. is added to aluminium oxide to lower its melting point. In purification of metals, the pure metal is made the (f) ….………………. and the impure metal is made the (g) ……….……………. The electrolyte used is an aqueous salt solution of the metal ions. In electroplating of metals, the (h) ………..…………….is made the anode and the (i) ……………… to be (j) ..…..………………….. is made the cathode. The electrolyte used is an aqueous salt solution of the electroplating metal. The purposes of electroplating metals are to make the electroplated object more (k) ………………………………….. and (l) …………………..……………… to corrosion. 2. Below are shown the three uses of electrolysis in industries. Fill in the blanks. Extraction of aluminium from bauxites Purification of copper from impure mined copper Electroplating of iron spoon with silver 1. Substance usedascathode andanode Cathode: Anode: Cathode: Anode: Cathode: Anode 2. Electrolyte used 3. Half equation representing the process. Cathode: Anode: Cathode: Anode: Cathode: Anode: VOLTAIC CELLS 1. A simple voltaic cell can be constructed by immersing two ………………………. metals in an ………………………. connected by ………………… 2. In a voltaic cell, ……………………… energy is converted to ……………………. energy.
- 10. 10 3. THE ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES is an arrangement of metals based on the tendency of each metal atom to donate electrons. Complete the table below. Electrochemical series of metals Cation formed and number of electron(s) released during the process K K+ + e Al Al3+ + 3e * Note: Hydrogen is not a metal, but it is included in the Electrochemical Series. 4. The diagram below shows an example of a simple voltaic cell. In the text box below are sentences explaining the production of electricity from a simple voltaic cell. The sentences are listed in random order. You are required to arrange these sentences in the best possible order so as to give a clear description of the reactions occurring in a simple voltaic cell. Tendency of metal atoms to donate electrons to form ions increases
- 11. 11 [If you have any problem, you can refer to page 104 of the text book for guidance.] Answer: (a) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… (b) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… (c) …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… (d) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… (e) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… (f) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (g) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. An example of a simple voltaic cell is a magnesium strip and a copper strip immersed in dilute sodium chloride solution. The electrons then flows from the magnesium ribbon to the copper plate through the wire and this results in the flow of electrical current. Hence magnesium atom releases electrons more easily than a copper atom and the magnesium act as the negative terminal of the cell. The overall equation for the reaction is given as follows. Mg(s) + 2H+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + H2(g) Magnesium is placed higher than copper in the electrochemical series. At the negative terminal, each magnesium atom releases two electrons and the Mg2+ formed moved into the solution. Mg(s) Mg2+ (aq) + 2e At the positive terminal which is the copper plate, the electrons are accepted by the H+ ions in sodium chloride solution. 2H+ + 2e H2 (g)
- 12. 12 5. (a) Draw and label the set-up of apparatus of a Daniell cell consisting of a salt bridge. (b) (i) Which metal in the Daniell cell is the negative terminal? ………………………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) Give reason for your answer in (b)(i). ………………………………………………………………………………………………… (iii) Write a half equation to represent the reaction occurring at the negative terminal. …………………………………………………………………………………………………. (c) Write a half equation to represent reaction at positive terminal. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… (d) What do you observe at (i) negative terminal ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (ii) positive terminal ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (e) State two functions of the salt bridge. 1. ……………..……………………………………………………………………………… 2. …………………………………… …………………………………… …………………… 2. The table below listed are five types of voltaic cells commonly used in our daily lives. Each voltaic cell has its advantages and disadvantages. Complete the table by stating the advantages and disadvantages of each voltaic cell. Voltaic cell Advantages Disadvantages 1. Lead-acid accumulator
- 13. 13 2. Dry cell 3. Mercury cell 4. Alkaline cell 5. Nickel-cadmium cell 6. What are the differences between an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell? Table 12.1 are statements showing differences between an electrolytic cell and a voltaic cell. Complete Table 12.2 by choosing the correct matching statements. It does not require a source of electric current It requires a source of electric current The electrical energy causes chemical reactions to occur at the electrodes. Electrical energy chemical energy The chemical reaction that occur at the electrodes produces electric current. Chemical energy electrical energy The electrodes must be of two different metals The electrodes may be of the same material such as carbon Electrons flow from the positive electrode (anode) to the negative electrode (cathode). Electrons flow from the more electropositive metal (negative terminal) to the less electropositive metal (positive terminal). Ions receive electrons at the positive terminal. (Reduction) Ions donate electrons at the positive terminal. (Oxidation) Ions receive electrons at the negative terminal. (Reduction) Ions donate electrons at the negative terminal. (Oxidation) Table 12.1
- 14. 14 DIFFERENCES Electrolytic cell Aspect Chemical cell Source of electric current Conversion of energy Type of electrodes Direction of flow of electrons Type of reaction at positive terminal Type of reaction at negative terminal Table 12.2
- 15. 15 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES 1. Three experiments were conducted to investigate the potential differences between three pairs of metals in a voltaic cell. An electrochemical series for four metals P, Q, S and T is then constructed based on the potential difference obtained. Three pair of metals used as electrodes in different voltaic cells are: P and Q, Q and S and S and T. All the metals are cleaned with sandpaper before used. 50 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium nitrate solution is poured into a beaker as electrolyte. Experiment I The electrodes P and Q are immersed into the solution. The two electrodes are connected to a voltmeter using copper wires. Electrode Q is the positive terminal. The voltmeter reading is recorded. Experiment II The electrodes Q and S are immersed into the solution. The two electrodes are connected to a voltmeter using copper wire. Electrode Q is the positive terminal. The voltmeter reading is recorded. Experiment III The electrodes S and T are immersed into the solution. The two electrodes are connected to a voltmeter using copper wire. Electrode T is the positive terminal. The voltmeter reading is recorded. Based on Experiment I, II and III, answer the questions below. (a) Record the voltmeter reading of each experiment in the spaces provided. Experiment 1 Experiment II Experiment III Voltmeter reading: …………. Voltmeter reading: …………… Voltmeter reading: ….…….. (b) Construct a table to record the data from the above experiments. (c) List the apparatus and materials that you will need to carry out this experiment. Apparatus: ………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Materials: ……………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 V 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 V 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 V
- 16. 16 (d) State all the variables: 1. Manipulated variable: ………………………………………………………………….. 2. Responding variable: ……………………………………………………………………. 3. Controlled variable: ……………………………………………………………………… (e) State the hypothesis: ………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (f) Based on the information obtained in Experiment I, what can you infer about metal P and Q? …………………………………………………………………………………………………… (g) Write a half equation for the reaction occurring in negative of Experiment I, assuming the cation has a +2 charge. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (h) Arrange the metals P, Q, S and T in descending order of their tendency to donate electrons. ...…………………………………………………………………………………………………… (i) Another voltaic cell is set-up using metals T and Q as electrodes. Predict the potential difference produced in the cell. …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (j) Given that metal X is placed between metal S and metal Q in the electrochemical series, can metal X displace metal S from its salt solution? Give an explanation for your answer ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (k) Given that copper is more electropositive than metal T, a displacement reaction will occur when copper is immersed into a salt solution of metal T, TNO3. Write the chemical equation for this reaction. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (l) State three important uses of the electrochemical series …………………………………………………………………..………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
