Thyroid Gland Hormones and Disorders Explained
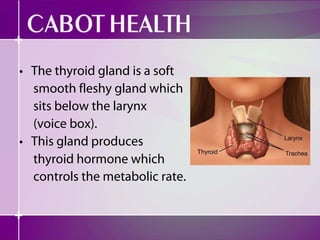
- 1. • The thyroid gland is a soft smooth fleshy gland which sits below the larynx (voice box). • This gland produces thyroid hormone which controls the metabolic rate.
- 2. • The thyroid gland produces the hormone called Thyroxine (T4) – this contains 4 molecules of iodine • T4 is converted into the much more active form of thyroid hormone called Triiodothyronine (T3) – this contains 3 molecules of iodine • T4 is converted into T3 in the liver, muscle, kidney and to a lesser degree in all other body tissues
- 3. Disorders of the thyroid • Hypothyroidism (underactive) • Hyperthyroidism (overactive) • Thyroiditis (inflammation of thyroid tissue) • Goiter (enlargement of thyroid gland) • Thyroid nodules (lumps within the thyroid) • Thyroid cancer (malignant growth in the thyroid)
- 4. Hypothyroidism Underactive = inadequate thyroid hormone Causes include: • Auto-immune disease (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) • Poor nutrition • Environmental toxins – petrochemicals, fluoride, bromide • Radiation • Hereditary factors • Some prescribed medications e.g. Lithium • Ageing
- 5. Symptoms of hypothyroidism • Weight gain • Low body temperature • Constipation • Hair loss • Dry flaky skin • Fluid retention • Slow reflexes • Fatigue • Muscle weakness
- 6. Symptoms of hypothyroidism • Rapid ageing • Slowness of thought • Depression • Increased sensitivity to the cold • Loss of interest in sex • Puffiness around the eyes • Heavy or irregular menstrual periods • Infertility
- 7. Myxoedema is a sign of severe hypothyroidism
- 8. Hyperthyroidism Over production of thyroid hormone Causes include: • Stress & lack of rest • Autoimmune disease • Hot nodule • Over dose of thyroid hormone • Amiodarone (heart medication) • Iodine toxicity (rare)
- 9. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism • Rapid heart beat • Shortness of breath • Increased appetite • Weight loss • Intolerance of heat • Irregularity of menstrual cycle • Irritability • Anxiety • Insomnia
- 10. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism • Tremor • Malaise • Muscle weakness • Diarrhea • Infertility • Exophthalmos – eye disease – not always
- 11. Blood tests for thyroid function • Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) • Free T3 • Free T4 • Reverse T3 • Thyroid antibody levels Feedback circuit
- 12. Thyroid hormones - normal ranges • Free T3 2.5 – 6.0 • Free T4 8.0 – 22.0 • TSH 0.30 – 2.5 Auto-immune antibodies against the thyroid • Anti-thyroglobulin = negative ....... (< 100) • Anti-microsomal = negative .......... (< 100) • TSH receptor antibodies Genetic test for gluten intolerance Serum vitamin D blood test: a healthy serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D value is between 75 nmol/L and 125 nmol/L (30 ng/mL and 50 ng/mL)
- 13. Thyroid antibodies are like missiles. They travel through the blood & find the thyroid gland and attack its cells
- 14. • Men should take their basal body temperature for four consecutive days • Women should take their basal body temperature for first 10 days of your menstrual cycle; this avoids confusion with the normal spike in body temperature which occurs after healthy ovulation • If your temperature is below 36.0º C or 96.8º F, your thyroid gland function is less than desirable; this should be confirmed with a blood test
- 15. Other thyroid tests • Urinary spot iodine test • Basal body temperature • Ultrasound of thyroid • Nuclear scan of thyroid • Needle biopsy of nodule
- 16. Goiter = Enlarged thyroid Causes include: • Iodine deficiency • Selenium deficiency • Auto-immune inflammation • Nodules within the thyroid • Tumours – benign & malignant • Physiological – During pregnancy & puberty • Goiters can compress the trachea or esophagus causing difficulty breathing or swallowing
- 17. Thyroid Nodules (lumps) • Single nodules • Multiple nodules • Hot nodules (functioning) • Cold nodules (non-functioning) • Often no symptoms
- 18. Toxic Multinodular Goiter • Multinodular goiter – one or more hot nodules, which produce excess thyroid hormone, resulting in symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
- 19. Thyroid hormone replacement may be required; • Thyroxine (T4) tablets eg. Synthroid or Oroxine • Cytomel or Tertroxin (T3) tablets • Porcine desiccated thyroid capsules • Thyroid cream
- 20. Treatment for hypothyroidism Selenium (100-200mcg) • Vitamin D3 (1000-2000IU) • Iodine (160-320mcg) • Zinc (5-10mg) • Tyrosine – maybe useful in high doses (500mg-3000mg) • Omega 3 fatty acids – fish, flaxseed, hempseed oil daily doses given
- 21. Treatment for thyroid problems • Bowel and liver detox plan • Gluten free diet if thyroid antibodies present • Gluten is found in wheat, rye, barley, oats, spelt, kamut and many processed foods • A reduction of dairy products may be required if thyroid nodules contain a mucus secretion called colloid
- 22. Treatment for thyroid problems • Magnesium supplement • Fish oil – 1 tablespoon daily before food • Selenium - 100-200mcg daily • Vitamin D3 – 1000-2000IU daily • Zinc – 5-10mg daily • Iodine (maybe required but needs to be tested) • Good quality sleep & more rest • Stress management
- 23. Natural progesterone cream • Can help women who have stubborn or hard to help thyroid problems • Unfortunately this is often completely overlooked and is not considered to be significant • However it can make the difference between success or failure • Daily doses vary from 25-100mg
- 24. Capsules for thyroid health • Must contain Iodine, Selenium, Vitamin D and Zinc • Easy to swallow capsules
- 25. Iodine • 70 – 80% of the iodine in your body is stored in your thyroid gland • Required for healthy thyroid tissue • Required for production of thyroid hormones • Required for healthy breast tissue • Reduces thyroid & breast cancer • Iodine deficiency is common worldwide
- 26. Dietary sources of Iodine • Seafood and seaweed (Such as Kelp or Nori) • Iodised salt • Plant & animal foods Contain variable amounts
- 27. • Iodine and/or selenium deficiency is a common cause of under active thyroid gland • Long term iodine deficiency, particularly in conjunction with selenium deficiency, can cause the thyroid to enlarge and form a swelling called a goiter. • Selenium and/or iodine deficiency increases the risk of thyroid and breast cancer. • Obtaining adequate iodine during pregnancy is vital for the healthy intellectual development of the infant. Iodine deficiency in infancy can lead to reduced IQ
- 28. Selenium • Essential for the conversion of T4 to T3 • Essential for healthy thyroid tissue • Anti-tumor effect and helps to shrink nodules, most types of warts & some types of skin tags • Has been shown to stimulate cell death (apoptosis) in tumor cells • Reduces anti-thyroid antibody levels – essential for autoimmune disease • Geographic studies have shown that people who live in areas with selenium deficient soils have higher cancer mortality rates
- 29. Dietary sources of Selenium Many areas of the world have selenium deficient soils Brazil nuts are the best dietary source of selenium
- 30. • The incidence of thyroid cancer has more than doubled in the USA since the 1970s • Regular checkups from your local doctor of your thyroid are essential – the most important being a physical exam of your gland (palpation)
- 31. Vitamin D • Promotes a healthy immune system • Helps cell differentiate (become specialized) and inhibits cell proliferation (growing in an out of control way) • It is thought that these are the reasons why Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of at least 17 different types of cancer, including breast colon and prostrate cancer • Vitamin D works with the parathyroid glands to control calcium metabolism and bone strength
- 32. Sources of Vitamin D • Skin exposure to Sunlight • Sardines, Tuna, salmon, mackerel, herring and catfish • Eggs • Fortified dairy products
- 33. Statistics • Vitamin D deficiency is a common problem in those that work indoors • Vitamin D deficiency affects more than 1 in 3 women during summer, and 1 in 2 during winter • Sunscreen stops manufacture of vitamin D • Prolonged sun exposure can be hazardous and inconvenient and vitamin D is found in very few foods; therefore supplementing with vitamin D may be the best option
- 34. Zinc • Helps maintain a healthy immune system • Required for binding of thyroid hormones to receptors inside cells, therefore zinc is essential to activate thyroid hormones and enable them to carry out their functions.
- 35. Dietary sources of Zinc • Seafood, esp. Oysters • Beans, lentils, yeast, nuts, seeds and wholegrain cereals. • Pumpkin seeds (one of the most concentrated vegetarian food sources of zinc)
- 36. Capsules for Thyroid Health Herbal extract equivalent to dry: 533mg Fucus vesiculosus whole plant (Kelp) providing 160mcg of iodine Nutrients: Selenium (as selenomethionine) 100mcg Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) 1000IU Zinc 5mg
- 37. For additional technical support, please call our Health Advisory team on (1623 334-3232) or email us from www.liverdoctor.com