Regular expressions-Theory of computation
•Transferir como PPT, PDF•
6 gostaram•6,182 visualizações
Theory of computation regular expressions re to dfa dfa to re regular expressions to nfa
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Recomendados
Recomendados
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
Mais procurados (20)
Type Checking(Compiler Design) #ShareThisIfYouLike

Type Checking(Compiler Design) #ShareThisIfYouLike
Push Down Automata (PDA) | TOC (Theory of Computation) | NPDA | DPDA

Push Down Automata (PDA) | TOC (Theory of Computation) | NPDA | DPDA
Destaque
Destaque (17)
Quiz1 | Theory of Computation | Akash Anand | MTH 401A | IIT Kanpur

Quiz1 | Theory of Computation | Akash Anand | MTH 401A | IIT Kanpur
Xin Yao: "What can evolutionary computation do for you?"

Xin Yao: "What can evolutionary computation do for you?"
Lecture: Regular Expressions and Regular Languages

Lecture: Regular Expressions and Regular Languages
Semelhante a Regular expressions-Theory of computation
Semelhante a Regular expressions-Theory of computation (20)
Theory of Computation Regular Expressions, Minimisation & Pumping Lemma

Theory of Computation Regular Expressions, Minimisation & Pumping Lemma
Mais de Bipul Roy Bpl
Mais de Bipul Roy Bpl (7)
Software engineering quality assurance and testing

Software engineering quality assurance and testing
Último
Foundation models are machine learning models which are easily capable of performing variable tasks on large and huge datasets. FMs have managed to get a lot of attention due to this feature of handling large datasets. It can do text generation, video editing to protein folding and robotics.
In case we believe that FMs can help the hospitals and patients in any way, we need to perform some important evaluations, tests to test these assumptions. In this review, we take a walk through Fms and their evaluation regimes assumed clinical value.
To clarify on this topic, we reviewed no less than 80 clinical FMs built from the EMR data. We added all the models trained on structured and unstructured data. We are referring to this combination of structured and unstructured EMR data or clinical data.
Reassessing the Bedrock of Clinical Function Models: An Examination of Large ...

Reassessing the Bedrock of Clinical Function Models: An Examination of Large ...harshavardhanraghave
Vip Call Girls Noida ➡️ Delhi ➡️ 9999965857 No Advance 24HRS Live
Booking Contact Details :-
WhatsApp Chat :- [+91-9999965857 ]
The Best Call Girls Delhi At Your Service
Russian Call Girls Delhi Doing anything intimate with can be a wonderful way to unwind from life's stresses, while having some fun. These girls specialize in providing sexual pleasure that will satisfy your fetishes; from tease and seduce their clients to keeping it all confidential - these services are also available both install and outcall, making them great additions for parties or business events alike. Their expert sex skills include deep penetration, oral sex, cum eating and cum eating - always respecting your wishes as part of the experience
(29-April-2024(PSS)Vip Call Girls Noida ➡️ Delhi ➡️ 9999965857 No Advance 24HRS Live

Vip Call Girls Noida ➡️ Delhi ➡️ 9999965857 No Advance 24HRS LiveCall Girls In Delhi Whatsup 9873940964 Enjoy Unlimited Pleasure
Último (20)
Reassessing the Bedrock of Clinical Function Models: An Examination of Large ...

Reassessing the Bedrock of Clinical Function Models: An Examination of Large ...
The Ultimate Test Automation Guide_ Best Practices and Tips.pdf

The Ultimate Test Automation Guide_ Best Practices and Tips.pdf
Right Money Management App For Your Financial Goals

Right Money Management App For Your Financial Goals
Unveiling the Tech Salsa of LAMs with Janus in Real-Time Applications

Unveiling the Tech Salsa of LAMs with Janus in Real-Time Applications
call girls in Vaishali (Ghaziabad) 🔝 >༒8448380779 🔝 genuine Escort Service 🔝✔️✔️

call girls in Vaishali (Ghaziabad) 🔝 >༒8448380779 🔝 genuine Escort Service 🔝✔️✔️
W01_panagenda_Navigating-the-Future-with-The-Hitchhikers-Guide-to-Notes-and-D...

W01_panagenda_Navigating-the-Future-with-The-Hitchhikers-Guide-to-Notes-and-D...
Introducing Microsoft’s new Enterprise Work Management (EWM) Solution

Introducing Microsoft’s new Enterprise Work Management (EWM) Solution
How To Troubleshoot Collaboration Apps for the Modern Connected Worker

How To Troubleshoot Collaboration Apps for the Modern Connected Worker
+971565801893>>SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHAB...

+971565801893>>SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHAB...
Azure_Native_Qumulo_High_Performance_Compute_Benchmarks.pdf

Azure_Native_Qumulo_High_Performance_Compute_Benchmarks.pdf
A Secure and Reliable Document Management System is Essential.docx

A Secure and Reliable Document Management System is Essential.docx
Vip Call Girls Noida ➡️ Delhi ➡️ 9999965857 No Advance 24HRS Live

Vip Call Girls Noida ➡️ Delhi ➡️ 9999965857 No Advance 24HRS Live
The Guide to Integrating Generative AI into Unified Continuous Testing Platfo...

The Guide to Integrating Generative AI into Unified Continuous Testing Platfo...
Optimizing AI for immediate response in Smart CCTV

Optimizing AI for immediate response in Smart CCTV
Shapes for Sharing between Graph Data Spaces - and Epistemic Querying of RDF-...

Shapes for Sharing between Graph Data Spaces - and Epistemic Querying of RDF-...
Regular expressions-Theory of computation
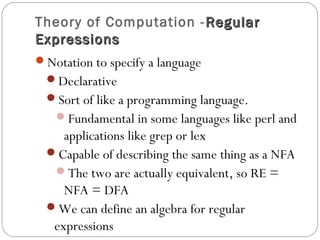
- 1. Theory of Computation - RegularRegular ExpressionsExpressions Notation to specify a language Declarative Sort of like a programming language. Fundamental in some languages like perl and applications like grep or lex Capable of describing the same thing as a NFA The two are actually equivalent, so RE = NFA = DFA We can define an algebra for regular expressions
- 2. Algebra for LanguagesAlgebra for Languages Previously we discussed these operators: Union (+) Concatenation (.) Kleene Star/Closure (*)
- 3. Definition of a Regular Expression R is a regular expression if it is: 1. a for some a in the alphabet ∑, standing for the language {a} 2. , standing for the language { }ε ε 3. Ø, standing for the empty language 4. R1+R2where R1 and R2 are regular expressions, and + signifies union (sometimes | is used) 5. R1R2 where R1 and R2 are regular expressions and this signifies concatenation 6. R* where R is a regular expression and signifies closure 7. (R) where R is a regular expression, then a parenthesized R is also a regular expression
- 4. RE Examples:RE Examples: L(001) = {001} L(0+10*) = { 0, 1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, … } L(0*10*) = {1, 01, 10, 010, 0010, …} i.e. {w | w has exactly a single 1} L(∑∑)* = {w | w is a string of even length} L((0(0+1))*) = { , 00, 01, 0000, 0001, 0100, 0101, …}ε L((0+ )(1+ε ε)) = { , 0, 1, 01}ε L(1Ø) = Ø ; concatenating the empty set to any set yields the empty set. R = Rε R+Ø = R
- 5. Equivalence of FA andEquivalence of FA and RERE Finite Automata and Regular Expressions are equivalent. To show this: Show we can express a DFA as an equivalent RE Show we can express a RE as an NFA.
- 6. Turning a DFA into a RETurning a DFA into a RE Theorem: If L=L(A) for some DFA , then there is a regular expression R such that L=L(R). State Elimination We’ll see how to do this next, easier than inductive construction, there is no exponential number of expressions
- 7. DFA to RE: StateDFA to RE: State EliminationElimination Eliminates states of the automaton and replaces the edges with regular expressions that includes the behavior of the eliminated states. Eventually we get down to the situation with just a start and final node, and this is easy to express as a RE
- 8. DFA to RE via StateDFA to RE via State Elimination (1)Elimination (1) 1. Starting with intermediate states and then moving to accepting states, apply the state elimination process to produce an equivalent automaton with regular expression labels on the edges. • The result will be a one or two state automaton with a start state and accepting state.
- 9. DFA to RE StateDFA to RE State Elimination (2):Elimination (2): 2. If the two states are different, we will have an automaton that looks like the following: Start S R T U We can describe this automaton as: (R+SU*T)*SU*
- 10. DFA to RE StateDFA to RE State Elimination (3)Elimination (3) 3. If the start state is also an accepting state, then we must also perform a state elimination from the original automaton that gets rid of every state but the start state. This leaves the following: Start R We can describe this automaton as simply R*.
- 11. DFA to RE State EliminationDFA to RE State Elimination (4)(4) 4. If there are n accepting states, we must repeat the above steps for each accepting states to get n different regular expressions, R1, R2, … Rn. For each repeat we turn any other accepting state to non-accepting. The desired regular expression for the automaton is then the union of each of the n regular expressions: R1∪ R2… ∪ RN
- 12. DFARE Example Convert the following to a RE First convert the edges to RE’s: 3Start 1 2 1 1 0 0 0,1 3Start 1 2 1 1 0 0 0+1
- 13. DFADFA RE Example (2)RE Example (2) Eliminate State 1: 3Start 1 2 1 1 0 0 0+1 3Start 2 11 0+10 0+1 Answer: (0+10)*11(0+1)*
- 14. Converting a RE to anConverting a RE to an AutomataAutomata We have shown we can convert an automata to a RE. To show equivalence we must also go the other direction, convert a RE to an automaton. We can do this easiest by converting a RE to an NFA Inductive construction Start with a simple basis, use that to build more complex parts of the NFA
- 15. RE toRE to NFA:NFA: Basis: R=a R=ε a ε R=Ø
- 17. RE to NFA Example Convert R= (ab+a)* to an NFA We proceed in stages, starting from simple elements and working our way up a a b b ab a bε
- 18. RE toRE to NFANFA Example (2):Example (2): ab+a a bε a ε ε ε ε (ab+a)* a bε a ε ε ε ε εε ε ε
- 19. Algebraic Laws for RE’s Just like we have an algebra for arithmetic, we also have an algebra for regular expressions. While there are some similarities to arithmetic algebra, it is a bit different with regular expressions.
- 20. Algebra for RE’s:Algebra for RE’s: Commutative law for union: L + M = M + L Associative law for union: (L + M) + N = L + (M + N) Associative law for concatenation: (LM)N = L(MN) Note that there is no commutative law for concatenation, i.e. LM ≠ ML
- 21. Algebra for RE’s (2):Algebra for RE’s (2): The identity for union is: L + Ø = Ø + L = L The identity for concatenation is: L = L = Lε ε The annihilator for concatenation is: ØL = LØ = Ø Left distributive law: L(M + N) = LM + LN Right distributive law: (M + N)L = LM + LN Idempotent law: L + L = L
- 22. Laws Involving Closure:Laws Involving Closure: (L*)* = L* i.e. closing an already closed expression does not change the language Ø* = ε *ε = ε L+ = LL* = L*L L* = L+ + ε
- 23. 23 End of SlidesEnd of Slides
