Data Structures used in Linux kernel
•Transferir como PPTX, PDF•
3 gostaram•6,007 visualizações
Brief view of Linux kernel data structures and APis.
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Recomendados
Recomendados
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
Mais procurados (20)
writing self-modifying code and utilizing advanced assembly techniques

writing self-modifying code and utilizing advanced assembly techniques
Injection on Steroids: Codeless code injection and 0-day techniques

Injection on Steroids: Codeless code injection and 0-day techniques
introduction to linux kernel tcp/ip ptocotol stack 

introduction to linux kernel tcp/ip ptocotol stack
Destaque
Destaque (20)
Uma visão do mundo rails campus party 2011 - fabio akita

Uma visão do mundo rails campus party 2011 - fabio akita
The Linux Kernel Implementation of Pipes and FIFOs

The Linux Kernel Implementation of Pipes and FIFOs
Linux Performance Analysis: New Tools and Old Secrets

Linux Performance Analysis: New Tools and Old Secrets
Semelhante a Data Structures used in Linux kernel
Semelhante a Data Structures used in Linux kernel (20)
Write a Java Class to Implement a Generic Linked ListYour list mus.pdf

Write a Java Class to Implement a Generic Linked ListYour list mus.pdf
For each task, submit your source java code file.(1) Objective Im.pdf

For each task, submit your source java code file.(1) Objective Im.pdf
Process Address Space: The way to create virtual address (page table) of user...

Process Address Space: The way to create virtual address (page table) of user...
Exploitation of counter overflows in the Linux kernel

Exploitation of counter overflows in the Linux kernel
1) Create a function called reverselist that will take a simple list.pdf

1) Create a function called reverselist that will take a simple list.pdf
Linked List, Types of Linked LIst, Various Operations, Applications of Linked...

Linked List, Types of Linked LIst, Various Operations, Applications of Linked...
write recursive function that calculates and returns the length of a.pdf

write recursive function that calculates and returns the length of a.pdf
Complete a C++ class implementation for a linked-list of sorted (asc.pdf

Complete a C++ class implementation for a linked-list of sorted (asc.pdf
Mais de assinha
Mais de assinha (10)
Nwe Embodiment (Naba Kalebara) of Lord Jagannath of PURI - The Greatest and B...

Nwe Embodiment (Naba Kalebara) of Lord Jagannath of PURI - The Greatest and B...
Architectural Patterns - Interactive and Event Handling Patterns

Architectural Patterns - Interactive and Event Handling Patterns
Último
God is a creative God Gen 1:1. All that He created was “good”, could also be translated “beautiful”. God created man in His own image Gen 1:27. Maths helps us discover the beauty that God has created in His world and, in turn, create beautiful designs to serve and enrich the lives of others.
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...christianmathematics
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Último (20)
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
Asian American Pacific Islander Month DDSD 2024.pptx

Asian American Pacific Islander Month DDSD 2024.pptx
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
Data Structures used in Linux kernel
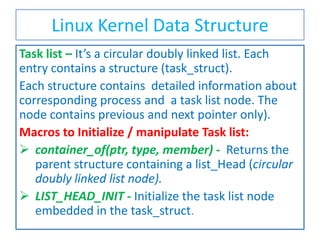
- 1. Linux Kernel Data Structure Task list – It’s a circular doubly linked list. Each entry contains a structure (task_struct). Each structure contains detailed information about corresponding process and a task list node. The node contains previous and next pointer only). Macros to Initialize / manipulate Task list: container_of(ptr, type, member) - Returns the parent structure containing a list_Head (circular doubly linked list node). LIST_HEAD_INIT - Initialize the task list node embedded in the task_struct.
- 2. Linux Kernel Data Structure Macros to Initialize / manipulate Task list: list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) – Traverse given list list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) – safe against entry removal while traversing the list list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) – Traverse given list backward list_for_each_entry_reverse_safe(pos, n, head, member) safe against entry removal while traversing the list backward list_for_each_entry_safe_continue (pos, n, head, member) - safe against entry removal while continuing after current point pos: pointer type to use as a loop cursor. n: pointer type to store next pointer. head: the head for your list (struct list_head *head) member: the name of the list_struct (struct list_head *list)
- 3. Linux Kernel Data Structure Functions to Initialize/manipulate Task list: list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) - add a node to given list list_add_tail( struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) - add the new node to the list immediately before the head node list_del(struct list_head *entry) – delete a node from the list list_del_init(struct list_head *entry) – delete a node from a linked list and reinitialize the given list head
- 4. Linux Kernel Data Structure Functions to Initialize/manipulate Task list: list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) – Remove the node from the list and add the node after head node in the given list. list_move_tail list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) ) – Remove the node from the list and add the node add the node before head node in the given list. list_empty(struct list_head *head) – verify if list is empty list_splice(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) – Join two lists list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) – Join two lists and initialize first list
- 5. Linux Kernel Data Structure Kfifo - Generic Queue used by Linux kernel Functions to Initialize/manipulate Queue: int kfifo_alloc(struct kfifo *fifo, unsigned int size, gfp_t gfp_mask) – creates a queue and initializes with “size” bytes void kfifo_init(struct kfifo *fifo, void *buffer, unsigned int size)- creates a queue and initializes with “size” bytes from the memory pointed by buffer static inline bool kfifo_initialized(struct kfifo *fifo) – verify if queue is initialized unsigned int kfifo_in(struct kfifo *fifo, const void *from, unsigned int len) – add data of size “len” from memory pointed to by “from pointer” to queue
- 6. Linux Kernel Data Structure Functions to Initialize/manipulate Queue: unsigned unsigned int kfifo_out(struct kfifo *fifo, void *to, unsigned int len)– remove from queue data of size “len” and copy to memory pointed by “to pointer” from queue unsigned int kfifo_out_peek(struct kfifo *fifo, void *to, unsigned int len, unsigned offset) – peek data within the queue without removing it static inline void kfifo_reset(struct kfifo *fifo) – remove entire contents of queue static inline void kfifo_reset_out(struct kfifo *fifo) – does not remove entire contents of queue
- 7. Linux Kernel Data Structure Functions to Initialize/manipulate Queue: int kfifo_is_empty(struct kfifo *fifo) – verify if queue is empty int kfifo_is_full (struct kfifo *fifo) - verify if queue is full static inline unsigned int kfifo_len(struct kfifo *fifo) – returns queue size unsigned int kfifo_avail(struct kfifo *fifo) – returns no of bytes available in the queue void kfifo_free(struct kfifo *fifo) – free memory allocated to queue using kfifo_alloc()
- 8. Linux Kernel Data Structure IDR – It is the map implementation of Linux . Struct idr is used for mapping user-space UIDs to their associated kernel data structure Functions to Initialize/manipulate IDR: void idr_init(struct idr *idp)- initialize Map (idr) Allocating a new UID (create a new map entry) 2 steps: 1. int idr_pre_get(struct idr *idp, gfp_t gfp_mask) Resizes the backing tree 2. int idr_get_new(struct idr *idp, void *ptr, int *id)Uses the idr pointed at by idp to allocate a new UID and associate it with the pointer ptr
- 9. Linux Kernel Data Structure Functions to Initialize/manipulate Queue: void *idr_find(struct idr *idp, int id)– look up a UID void idr_remove(struct idr *idp, int id) Remove a UID from an idr void idr_remove_all(struct idr *idp) – remove all entries from idr void idr_destroy(struct idr *idp) - Destroy entire idr
- 10. Linux Kernel Data Structure Rbtree (red-black tree) – It is the Linux’s implementation of (semi) Balanced Binary search tree. It is useful for inserting and searching efficiently. prio_tree (PST) - It is the Linux’s implementation of radix priority search tree which is a mix of heap and radix trees. It is useful for storing intervals. e.g. consider a vma as a closed interval of file pages [offset_begin, offset_end], and store all vmas that map a file in a PST.
- 11. Thank You • Your suggestions and comments are always welcome. • Please send me your feedback at a_s_sinha@yahoo.com