The DNA base code that corresponds to the mRNA codon AUG recognized by the tRNA with anticodon UAC would be TAC. This is because:- DNA and mRNA are complementary, with T pairing with A and C pairing with G.- The tRNA anticodon pairs with the mRNA codon through complementary base pairing. So if the tRNA anticodon is UAC, it will pair with the mRNA codon AUG. And the corresponding DNA sequence would be the complementary base pair TAC
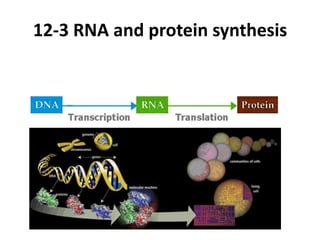
- 1. 12-3 RNA and protein synthesis The Central Dogma
- 2. RNA and DNA DNA RNA Strands • Double helix strands • One strand Sugar • Deoxyribose • Ribose Base • A,T,C,G • A,U (uracil), C,G Location • Nucleus • Cytoplasm & nucleus
- 3. DNA ( A T C G) RNA (A U C G)
- 4. Three types of RNA A. messenger RNA (mRNA) B. transfer RNA (tRNA) C. ribosome RNA (rRNA)
- 5. Steps from DNA to Proteins A cooking book in French Sequence of nucleotides A cooking book in Chinese Sequence of nucleotides Sequence of amino acids The Central Dogma
- 6. Steps from DNA to Proteins Nuclear DNA membrane Transcription Pre-mRNA RNA Processing mRNA Ribosome Translation Protein
- 7. Transcription • Synthesize a mRNA molecule along one template strand of DNA – In nucleus – Starts at promoter (TATA region of DNA) – Ends at terminator – Need enzyme RNA polymerase – When complete, pre-mRNA is released.
- 8. DNA A T C G T A C G A A G T C T A C G G G A C T A T C G 5 3 A C G A A G U C T A G C G A T A G C A T G C T T C A G A T G C C C T mRNA RNA polymerase Direction of transcription
- 9. Transcription • Steps – DNA unzipped by RNA polymerase – RNA polymerase builds RNA by base paring RNA nucleotides to one strand of DNA – U is used instead of T – RNA is released and leaves the nucleus
- 12. Question • What would be the complementary RNA strand for the following DNA sequence? • DNA: GCGTATG RNA: CGCAUAC
- 13. Question • What is the enzyme responsible for the production of the RNA molecule? • RNA Polymerase – Separates the DNA molecule by breaking the H- bonds between the bases. – Then moves along one of the DNA strands and links RNA nucleotides together.
- 15. RNA processing
- 16. RNA processing Part of a DNA strand exon intron exon intron exon 3’ 5’ transcription into pre-mRNA poly-A tail cap 5’ 3’ snipped out intron snipped out intron 5’ 3’ mature mRNA transcript
- 17. Translation • Synthesize a polypeptide chain using the genetic code on mRNA
- 18. Translation • Key characters – 1) mRNA : provide code – 2) tRNA : bring building blocks – 3) Ribosome (rRNA) : provide site
- 19. 1) mRNA • A linear sequence of nucleotides • Three nucleotides make a codon – Codon : the genetic code for a amino acid – 64 codons – AUG: start – UAA, UAG, UGA: stop
- 21. 1) mRNA start codon mRNA A U G G G C U C C A U C G G C G C A U A A codon 1 codon 2 codon 3 codon 4 codon 5 codon 6 codon 7 protein methionine glycine serine isoleucine glycine alanine stop codon Primary structure of a protein aa1 aa2 aa3 aa4 aa5 aa6 peptide bonds
- 22. 2) tRNA • Delivers amino acids to ribosomes • One side attached with amino acid • Another side with anticodon – Anticodon: 3 nucleotides that can pair with a codon – 20 different types of amino acids
- 23. 2) tRNA amino acid attachment site methionine amino acid U A C anticodon
- 24. 3) rRNA • Major component of ribosomes • Ribosome • Place where amino acids are made into proteins • Small subunit + large subunit • Large subunit has 2 sites for tRNA
- 25. 3) rRNA Ribosome Large subunit P A Site Site mRNA A U G C U A C U U C G Small subunit
- 26. Translation • Three Steps 1. initiation: start codon (AUG) 2. elongation: 3. termination: stop codon (UAG, UAA, UGA) • Let’s make a PROTEIN!!!!.
- 28. 1) Initiation aa1 Large subunit P A Site Site 1-tRNA anticodon U A C mRNA A U G C U A C U U C G codon Small subunit
- 29. aa2 aa1 2-tRNA 1-tRNA G A U anticodon U A C hydrogen A U G C U A C U U C G A bonds codon mRNA
- 30. 2) Elongation peptide bond aa3 aa1 aa2 3-tRNA 1-tRNA 2-tRNA G A A anticodon U A C G A U hydrogen A U G C U A C U U C G A bonds codon mRNA
- 31. aa1 peptide bond aa3 aa2 1-tRNA U A C 3-tRNA (leaves) 2-tRNA G A A G A U A U G C U A C U U C G A mRNA Ribosomes move over one codon
- 32. peptide bonds aa1 aa4 aa2 aa3 4-tRNA 2-tRNA 3-tRNA G C U G A U G A A A U G C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA
- 33. peptide bonds aa1 aa4 aa2 aa3 2-tRNA 4-tRNA G A U (leaves) 3-tRNA G C U G A A A U G C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA Ribosomes move over one codon
- 34. peptide bonds aa5 aa1 aa2 aa4 aa3 5-tRNA U G A 3-tRNA 4-tRNA G A A G C U G C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA
- 35. aa1 peptide bonds aa5 aa2 aa3 aa4 5-tRNA 3-tRNA U G A G A A 4-tRNA G C U G C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA Ribosomes move over one codon
- 36. 3) Termination aa5 aa4 aa199 aa3 primary aa200 structure aa2 of a protein aa1 terminator 200-tRNA or stop codon A C U C A U G U U U A G mRNA
- 37. 4) End Product • The end products of protein synthesis is a primary structure of a protein. – A sequence of amino acid bonded together by peptide bonds. aa5 aa3 aa4 aa2 aa199 aa1 aa200
- 40. Question: • The anticodon UAC belongs to a tRNA that recognizes and binds to a particular amino acid. • What would be the DNA base code for this amino acid?
- 41. Answer: • tRNA - UAC (anticodon) • mRNA - AUG (codon) • DNA - TAC