How Web Pages Are Created With HTML, CSS & JavaScript
- 2. How Web Page Creates? HTML (Structure) Css (Style) Javascript (Behavior) ◦ HTML tags create objects. In other words……Document Object Model(DOM) ◦ <SCRIPT></SCRIPT> Once page found this tag – Start download the javascript. ◦ JavaScript lets you manipulate the DOM. ◦ Css – do the styles.
- 3. What is DOM? The Document Object Model (DOM) is an application programming interface (API) for valid HTML and well-formed XML documents. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated.
- 6. What is Angularjs? A JavaScript framework for creating dynamic web applications Open Source ◦ GitHub: https://github.com/angular/angular.js ◦ MIT License Uses jQuery ◦ jQuery 1.7.1 or above ◦ jQLite
- 7. MVC or MVW…. Model ◦ The data View ◦ The interface ◦ How the data is presented to the user Whatever (Controller/Services/Directives/Filters) ◦ The behavior ◦ Modifying / updating the models
- 8. How Angularjs works? bindJQuery() : Either one of jQuery or jqLite is bound to angular. angularInit(document, bootstrap) : method which checks for ng-app module bootstrap(element) : method which is invoked once an ng-app module is found ◦ Invoke createInjector() method which returns dependency injector ◦ The dependency injector invokes the compilation and linking process with some of the following key parameters: Scope object – Reference to rootScope Reference to element with ng-app Compile service Reference to dependency injector
- 9. How Angularjs works? Cont… compile(element): bind events to the element compile(element)(scope): bind element to the scope ◦ At this phase compiler will look for every directive and creates the watchers ($watch) that are needed. scope.$apply(function{}): Finally, the $apply method is invoked on the scope object As a result of execution of $apply method, the view appears……
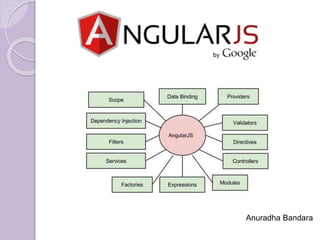
- 10. How Angularjs works? Cont…
- 11. Reusable components with directives…. A directive is an extension of the HTML vocabulary that allows us to create new behaviours. This technology lets the developers create reusable components that can be used within the whole application. The directive can be applied as an ◦ Attribute ◦ Element ◦ Class ◦ Comment we can use ng-model, ng:model, ng_model,data-ng-model, and x-ng-model in the HTML markup.
- 12. AngularJS built-in directives... ngApp - defines the root of an AngularJS application ngController - attach any controller to the view ◦ Nested Controllers ngBind – act as same as {{expression}} ngBindHtml – bind plain html
- 13. AngularJS built-in directives... ngRepeat - iterate over arrays and objects. ngModel - attaches the element to a property in the scope ngClick – bind any custom behavior to the click event of the element ngDisable – disable elements based on the Boolean value of an expression. ngClass – dynamically apply a class to an element ngOptions – create the options of a select element ngStyle – apply the dynamic style configuration demand
- 14. AngularJS built-in directives... ngShow/ngHide – apply visibility of an element based on its display property. ngIf - prevents the rendering of an element in our template ngClick – bind any custom behavior to the click event of the element ngInclude – include other external HTML fragments in to pages
- 15. Create own Directory Directive properties
- 16. Dependency Injection and Services… Services ◦ Use to isolating the business logic in the application Lazily instantiated – Angular only instantiates a service when an application component depends on it. Singletons – Each component dependent on a service gets a reference to the single instance generated by the service factory. No UI Dependency Injection ◦ A software design pattern that deals with how components get hold of their dependencies. ◦ eg :
- 17. Dependency Injection and Services… Custom Services ◦ We can define our own custom services in different ways in angular js app and use them wherever required Service() Factory() Provider()
- 18. Dependency Injection and Services… Creating services with the factory ◦ You give angular a function ◦ Angular create an object ◦ add properties to it ◦ return that same object
- 19. Dependency Injection and Services… Creating services with the Service ◦ You give angular a function ◦ Angular will instantiated with the ‘new’ keyword ◦ add properties to “this” ◦ return “this”
- 20. Dependency Injection and Services… Creating services with the Provider ◦ You give angular a function ◦ angular will call its $get function ◦ return value from the $get function
- 21. Data handling… Expressions Filters Form validations
- 22. Data handling… Expressions ◦ An expression is a simple piece of code that will be evaluated by the framework and can be written between double curly brackets eg : {{car.plate}}
- 23. Data handling… Filters ◦ perfect solution to easily perform any data manipulation. Eg : {{expression | filter}} {{expression | filter1 | filter2}} ◦ Currency {{ 10 | currency}} => $10.00 (take locale currency) {{ 10 | currency:'R$'}} => R$ 10.00 ◦ Date {{ car.entrance | date }} => Dec 10, 2014 {{ car.entrance | date:'MMMM dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss' }} => December 10/12/2013 21:42:10.
- 24. Data handling… Filters ◦ Filter ◦ Json {{ car | json }} =>
- 25. Data handling… Filters ◦ limitTo – limit size to 10 {{ expression | limitTo:10 }} ◦ Lowercase – convert to lowercase {{ expression | lowercase }} ◦ Number – limit two decimal places {{ 10 | number:2 }} => 10.00 ◦ Orderby – orderby String/Array {{ expression | orderBy:predicate:reverse }}
- 26. Data handling… Creating custom filters
- 27. Data handling… Form validations $pristine =>form is not modified $dirty => form is modified
- 28. Data handling… Form validations $error => It accumulates the detailed list of everything that happens with the form
- 29. Data Binding – Two way Data-binding in Angular apps is the automatic synchronization of data between the model and view components. The view is a projection of the model at all times. When the model changes, the view reflects the change, and vice versa.
- 30. How Data binding works? Exactly what happen when you do event on a browser…. browser is waiting for events / user interactions. click on a button or write into an input. fire browser event loop. browser will make the appropriate changes in the DOM
- 31. How Data binding works? How angulerjs reacts? When you create ui component using directive Add $watch to watch list call $digest After fire event loop $digest loop will be fired. It checks values are updated. Call $apply() As a result of execution of $apply method, the view updated……
- 32. Scope…. scope is an object that refers to the application model Scopes are arranged in hierarchical structure which mimic the DOM structure of the application Create connection between view & controller
- 33. $rootscope / $parent / $scope You give angular a functionYou give angular a function
- 34. Exercise.. Writing own directory… ◦ Replace label with dropdown when click the edit button. ◦ When user change the dropdown automatically update the model.
- 35. Thank you….
Notas do Editor
- Use multiple points, if necessary.
- Use brief bullets and discuss details verbally.
