1. animal and plant cells v1.0
- 1. © Boardworks Ltd 20071 of 39
- 2. © Boardworks Ltd 20072 of 39
- 3. © Boardworks Ltd 20073 of 39 Where in the world? How does a cell resemble a city?
- 4. © Boardworks Ltd 20074 of 39 What is a cell? Multicellular organisms consists of many cells – humans are made from an estimated 50 trillion cells! Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria, consist of just a single cell. A cell is the basic unit of life, from which larger structures such as tissue and organs are made.
- 5. © Boardworks Ltd 20075 of 39 How big is a cell? Most plant and animal cells are between 0.025µm and 60µm in size – around half the diameter of a human hair – and too small to see without a microscope. The largest cell in the human body is the female egg cell, (ovum) at around 1,000µm in diameter. The smallest human cell is the sperm cell – the head is around 5 µm long.
- 6. © Boardworks Ltd 20076 of 39 Specialized cells Most plants and animals are multicellular. The human body is made up of around 200 different types of cell, all working together. Most cells are specialized, meaning that each type of cell has a specific structure and function. All cells with a nucleus contain the same genes, but different cells activate different genes so they only produce the proteins they need. However, all cells have certain common features and structures called organelles.
- 7. © Boardworks Ltd 20077 of 39 What do cells contain?
- 8. © Boardworks Ltd 20078 of 39 Animal or plant?
- 9. © Boardworks Ltd 20079 of 39
- 10. © Boardworks Ltd 200710 of 39 A closer look at animal cells
- 11. © Boardworks Ltd 200711 of 39 Exploring animal cells
- 12. © Boardworks Ltd 200712 of 39 How do animal cells specialize? red blood cell In animals, the first type of cells in the developing embryo are stem cells. These are unspecialized cells that go on to form all the different cell types in the adult. muscle cell stem cell sperm cell nerve cell
- 13. © Boardworks Ltd 200713 of 39 How are animal cells adapted?
- 14. © Boardworks Ltd 200714 of 39 Animal cells: fit for a purpose
- 15. © Boardworks Ltd 200715 of 39
- 16. © Boardworks Ltd 200716 of 39 A closer look at plant cells
- 17. © Boardworks Ltd 200717 of 39 Exploring plant cells
- 18. © Boardworks Ltd 200718 of 39 How do plant cells specialize? Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialize throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. sieve cell leaf cellroot cell meristem cell
- 19. © Boardworks Ltd 200719 of 39 How are plant cells adapted?
- 20. © Boardworks Ltd 200720 of 39 Plant cells: fit for a purpose
- 21. © Boardworks Ltd 200721 of 39 What is a cell wall? All plant cells have a cell wall – a rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is freely permeable to water and other molecules. maintain the shape and structure of the cell The plant cell wall is made from cellulose, a carbohydrate polymer. The purpose of the cell wall is to: protect the cell’s contents from pathogens prevent damage to the cell caused by excess water intake.
- 22. © Boardworks Ltd 200722 of 39 What is a vacuole? The vacuole is a fluid–filled sac found within plant cells and some bacteria. The vacuole has a range of functions, including: The site of vacuoles depend on how much water the plant has absorbed. storing waste products regulating the turgor pressure of the cell. maintaining the water and pH balance of the cell
- 23. © Boardworks Ltd 200723 of 39 What are chloroplasts? Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis in plant cells. thylakoids A green pigment in chloroplasts called chlorophyll absorbs the energy in sunlight. Chlorophyll is embedded in disk-like structures called thylakoids, which are arranged into stacks. This energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- 24. © Boardworks Ltd 200724 of 39 Which organelle?
- 25. © Boardworks Ltd 200725 of 39
- 26. © Boardworks Ltd 200726 of 39 How do cells get their energy? All organisms need energy to survive. Animals obtain their energy from the food they eat, but plants can make their own food by photosynthesis. In both cases, however, energy must first be converted into a form that can easily be used by cells. This process is called respiration.
- 27. © Boardworks Ltd 200727 of 39 Where does respiration take place? Mitochondria are cellular organelles in which respiration takes place. Mitochondria use enzymes to convert the energy from glucose into ATP – the basic energy source for all cells. Mitochondria have an inner membrane on which the enzymes are embedded. This membrane is highly folded to increase the surface area on which respiration can take place.
- 28. © Boardworks Ltd 200728 of 39 What is aerobic respiration? Aerobic respiration is the process of releasing energy through the oxidation of glucose molecules. Aerobic respiration is summarized by the equation: This reaction releases energy in the form of ATP – a compound that can readily be used in cellular processes. oxygen carbon dioxide glucose + + water ( energy)+ 6O2 6CO2C6H12O6 + + 6H20 ( ATP)+
- 29. © Boardworks Ltd 200729 of 39 What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic respiration takes place without oxygen, and releases less energy than aerobic respiration because glucose molecules are only partially broken down. During strenuous exercise, cells are deprived of oxygen but still need energy to work. The body responds by converting glucose into lactic acid and energy, leading to an oxygen ‘debt’. Lactic acid causes muscle cramps. When exercise stops, oxygen levels rise, paying off the oxygen debt and oxidising the lactic acid.
- 30. © Boardworks Ltd 200730 of 39 How is energy used? The chemical energy produced by respiration, ATP, is used by cells to undertake work. movement – enabling muscles to contract Where might ATP be used? thermoregulation in mammals and birds active transport – moving molecules against a concentration gradient. biosynthesis – building new molecules, cells and tissues
- 31. © Boardworks Ltd 200731 of 39 What is photosynthesis? Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction where light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This reaction can be summarized by the equation: The reaction uses light energy from the Sun and takes place in chloroplasts of plant cells. carbon dioxide + water oxygenglucose + 6CO2 + 6H20 6O2C6H12O6 + light energy chlorophyll
- 32. © Boardworks Ltd 200732 of 39 Using energy from photosynthesis The glucose produced by photosynthesis has many uses in plants, such as for: energy release in respiration making cellulose for cell walls combining with minerals to make proteins and other essential compounds an energy store in the form of insoluble starch.
- 33. © Boardworks Ltd 200733 of 39 Protein synthesis
- 34. © Boardworks Ltd 200734 of 39 Protein synthesis
- 35. © Boardworks Ltd 200735 of 39
- 36. © Boardworks Ltd 200736 of 39 Glossary (1/2) aerobic respiration – The process of releasing energy through the oxidation of glucose molecules. anaerobic respiration – The process of releasing energy from glucose molecules in the absence of oxygen. ATP – Adenosine triphosphate, the major form of energy used by cells. cell – The basic structural and functional unit of life. cell membrane – The partially-permeable barrier that regulates substances entering and leaving a cell. cell wall – The rigid external coat that protects and supports plant cells. chlorophyll – The green pigment found in chloroplasts.
- 37. © Boardworks Ltd 200737 of 39 Glossary (2/2) chloroplast – The site of photosynthesis in plant cells. cytoplasm – The jelly-like material in which all a cell’s organelles are found, and in which most cellular processes and reactions occur. mitochondria – The site of energy release by respiration. nucleus – The location of a cell’s DNA. photosynthesis – The chemical reaction in which light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. ribosome – The site of protein synthesis. vacuole – The fluid-filled cavity found in plant cells that stores water and nutrients.
- 38. © Boardworks Ltd 200738 of 39 Anagrams
- 39. © Boardworks Ltd 200739 of 39 Multiple-choice quiz
Notas do Editor
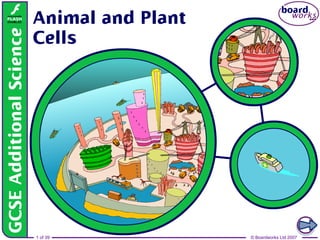
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This illustration contains several discussion points relating to cell structure, and could form the basis of a debate about the similarity between a cell and a city/country. For example, both cells and cities/countries: produce their own power: represented by pink/red buildings (mitochondria) have a central controlling organisation: represented by tall building in centre (nucleus) have border controls: represented by perimeter wall (membrane/wall) have storage facilities: represented by the harbour and lakes (vacuoles) import food and gas: represented by oil tankers some can produce their own food: represented by green building (chloroplast) export waste: represented by dumper trucks have good communication links with neighbours: represented by communications satellites (neurones and hormones) have good defence: represented by heavily-armoured ships and white boats (white blood cells)
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: © 2007 Jupiterimages Corporation Image shows the phytoplankton Pleurosigma angulatum. Phytoplankton are microscopic algae that live close to the surface of oceans and fresh water. Pleurosigma angulatum belong to a group of phytoplankton called diatoms, which are often unicellular. Teacher notes There is considerable uncertainty about the number of cells in a human body. Estimates vary from 10 trillion to 100 trillion cells.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: Eye of Science / Science Photo Library Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of sperm (blue) attempting to penetrate a human egg (red). Each sperm (spermatozoa) has a rounded head and a long tail with which it swims. Women usually release one egg (ovum) per month, whereas men release millions of sperm in each ejaculation. Only one of these sperm can penetrate the egg's thick outer layer (zona pellucida) and fertilise it. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm's genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) fuses with the egg's DNA. When this occurs the egg forms a barrier to other sperm. Magnification: x650 when printed 10 centimetres wide. Teacher notes One micrometer (µm), also known as a micron, is equal to one-millionth of a meter. 1 µm = 0.000001 m.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: © 2007 Jupiterimages Corporation Cross section of the leaf from a Dianthus (carnation) plant. Image shows epidermis, spongy and palisade cells. Teacher notes Red blood cells are an example of a type of cell which has no nucleus. Gametes (such as egg cells and sperm cells) only have half a full set of genes. See the ‘Cell Division’ presentation for more information about gametes.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This activity could be used to gauge students’ existing knowledge of the major organelles in animal and plant cells.
- Teacher notes Appropriately coloured voting cards could be used with this classification activity to increase class participation.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: Dr. Gopal Murti / Science Photo Library Light micrograph of squamous epithelial cells from the human mouth. These flat, scale-like cells have oval nuclei (purple) and granular cytoplasm. The epithelia are tissues that cover all body surfaces, cavities and tubes apart from the blood and lymph vessels. Epithelial cells form a protective layer within the mouth. Normally, they rest on a basement membrane which separates the epithelium from underlying connective tissue. Blood vessels do not extend beyond the basement layer, and epithelial cells are dependent on oxygen and metabolites diffusing from underlying tissue. Magnification: x1000 at 35mm size. Teacher notes This five-stage animation shows how to make and examine a cheek cell. Suitable prompts could include: How are animal cells different to plant cells? Why are cheek cells a good example of a typical animal cell? Which organelles can you identify within the cheek cells?
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This click and reveal activity could be used to check students’ understanding of the organelles found in animal cells.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes See the ‘Growth and Development’ presentation for more information about stem cells and human growth.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This click and reveal activity could be used to check students’ understanding of animal cell structures and function.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This matching activity could be used as a plenary or revision exercise on animal cells. Students could be asked to complete the questions in their books and the activity could be concluded by the completion on the IWB.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: Andrew Syred / Science Photo Library Light micrograph of the epidermis of an onion, showing the bands of large, rectangular cells. The spot in the centre of each cell is its nucleus. Magnification: x200 at 35mm size. Teacher notes This five-stage animation shows how to make and examine an onion cell. Suitable prompts could include: How are plant cells different to animal cells? Why are onion cells a good example of a typical plant cell? Which organelles can you identify within the onion cells?
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This click and reveal activity could be used to check students’ understanding of the organelles found in plant cells.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes See the ‘Growth and Development’ presentation for more information about meristems and plant growth.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This click and reveal activity could be used to check students’ understanding of plant cell structures and function.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This matching activity could be used as a plenary or revision exercise on plant cells. Students could be asked to complete the questions in their books and the activity could be concluded by the completion on the IWB.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes Some animal cells have a small/temporary vacuole involved in digestion or secretion.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes Chloroplasts are between 2 µm and 10 µm in diameter.
- Teacher notes This activity could be used to check students’ understanding of cell structure and function. Students could work individually or in small groups, with mini-whiteboards used to convey the answers.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: © 2007 Jupiterimages Corporation
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes ATP = adenosine triphosphate Mitochondria = plural; mitochondrion = singular
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells
- Photo credit: © 2007 Jupiterimages Corporation
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes See the ‘Photosynthesis’ presentation for more information on photosynthesis.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Photo credit: © 2007 Jupiterimages Corporation Teacher notes See the ‘Transport in Plants’ presentation for more information on how nutrients are transported in plants.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This three-stage sequence introduces the link between genes and proteins before the mechanism of protein synthesis is explored on the next slide.
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This six-stage sequence shows how proteins are made. Suitable prompts could include: What is the name of the three-dimensional structure of DNA? What are the base-pairing rules? Why does the messenger RNA move out of the nucleus? How many bases are involved in the code for one amino acid? How will protein synthesis differ in different specialized cells?
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells
- <number> Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Biology Animal and Plant Cells Teacher notes This multiple-choice quiz could be used as a plenary activity to assess students’ understanding of animal and plant cells. The questions can be skipped through without answering by clicking “next”. Students could be asked to complete the questions in their books and the activity could be concluded by the completion on the IWB.
