Transformer
- 1. Transformer Class -12th PRIYANKA JAKHAR PHYSICS LECTURER GGIC VIJAY NAGAR GHAZIABAD
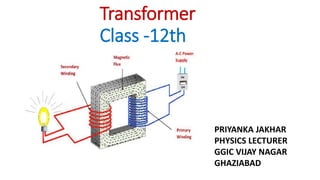
- 2. Transformer: Transformer is a device which converts lower alternating voltage at higher current into higher alternating voltage at lower current. S Load P •Transformer does not operate on direct current. It operates only on alternating voltages at input as well as at output. •Transformer does not amplify power as vacuum tube. •Transformer, a device based on mutual induction converts magnetic energy into electrical energy.
- 3. The transformer is a device used for converting a low alternating voltage to a high alternating voltage or vice-versa. A Transformer based on the Principle of mutual induction according to this principle, the amount of magnetic flux linked with a coil changing, an e.m.f is induced in the neighboring coil. A transformer is an electrical device which is used for changing the A.C. voltages. A transformer is most widely used device in both low and high current circuit. As such transformers are built in an amazing strength of sizes. In electronic, measurement and control circuits, transformer size may be so small that it weight only a few tens of grams where as in high voltage power circuits, it may weight hundred of tones. In a transformer, the electrical energy transfer from one circuit to another circuit takes place without the use of moving parts. Transformer is, therefore, an essential piece of apparatus both for high and low current circuits.
- 4. APPARATUS REQUIRED IRON ROD COPPER WIRE VOLTMETRE AMMETRE
- 5. WORKING PRINCIPLE The transformer works in the principle of mutual induction . “The principle of mutual induction states that when the two coils are inductively coupled and if the current in coil change uniformly then the e.m.f. induced in the other coils. This e.m.f can drive a current when a closed path is provide to it.” When the alternating current flows in the primary coils, a changing magnetic flux is generated around the primary coil. The changing magnetic flux is transferred to the secondary coil through the iron core . The changing magnetic flux is cut by the secondary coil, hence induces an e.m.f in the secondary coil. Now if load is connected to a secondary winding, this e.m.f drives a current through it . The magnitude of the output voltage can be controlled by the ratio of the no. of primary coil and secondary coil . The frequency of mutually induced e.m.f as same that of the alternating source which supplying to the primary winding .
- 6. STRUCTURE OF TRANSFORMER # The transformer two inductive coils ,these are electrical separated but linked through a common magnetic current circuit . # These two coils have a high mutual induction. # One of the two coils is connected of alternating voltage .this coil in which electrical energy is fed with the help of source called primary winding (P) . # The other winding is connected to a load the electrical energy is transformed to this winding drawn out to the load .this winding is called secondary winding(S) . # The primary and secondary coil wound on a ferromagnetic metal core . # The function of the core is to transfer the changing magnetic flux from the primary coil to the secondary coil . # The primary has N1 no of turns and the secondary has N2 no of turns the of turns plays major important role in the function of transformer.
- 7. EP = - NP dΦ / dt ES = - NS dΦ / dt ES / EP = NS / NP = K (where K is called Transformation Ratio or Turns Ratio) For an ideal transformer, Output Power = Input Power ESIS = EPIP ES / EP = IP / IS ES / EP = IP / IS = NS / NP Efficiency (η): η = ESIS /EPIP For an ideal transformer η is 100%
- 8. Type of transformer Step - up Transformer Step-down transformer Transformer It is a device which can change a low voltage of high current into a high voltage of low current and vice-versa. Its working is based on mutual induction. There is no electrical contact between them . The desire change in voltage or current without any change in frequency.
- 9. There are two types of transformers. (i) Step-up Transformers It converts a low voltage of high current into a high current. A transformer which increases the voltages is called a step- up transformer. Step - up Transformer: Load P S NS > NP i.e. K > 1 ES > EP & IS < IP
- 10. (ii) Step-down Transformer It converts a high voltage of low current into a low voltage of high current. Step - down Transformer: P S Load NS < NP i.e. K < 1 ES < EP & IS > IP
- 11. Energy Losses in a Transformer: 1. Copper Loss: Heat is produced due to the resistance of the copper windings of Primary and Secondary coils when current flows through them. This can be avoided by using thick wires for winding. 2. Flux Loss: In actual transformer coupling between Primary and Secondary coil is not perfect. So, a certain amount of magnetic flux is wasted. Linking can be maximised by winding the coils over one another. 3. Iron Losses: a)Eddy Currents Losses: When a changing magnetic flux is linked with the iron core, eddy currents are set up which in turn produce heat and energy is wasted. Eddy currents are reduced by using laminated core instead of a solid iron block because in laminated core the eddy currents are confined with in the lamination and they do not get added up to produce larger current. In other words their paths are broken instead of continuous ones.
- 12. Solid Core Laminated Core b) Hysteresis Loss: When alternating current is passed, the iron core is magnetised and demagnetised repeatedly over the cycles and some energy is being lost in the process. This can be minimised by using suitable material with thin hysteresis loop. 4. Losses due to vibration of core: Some electrical energy is lost in the form of mechanical energy due to vibration of the core and humming noise due to magnetostriction effect.
- 13. USES OF TRANSFORMERS 1. In voltage regulator for T.V., refrigerator, computer, air conditioner, etc. 2. A step down transformer is used for welding purposes. 3. A step down transformer is used for obtaining large current. 4. A step up transformer is used for the production of X- Rays and NEON advertisement. 5. Transformers are used in voltage regulators and stabilized power supplies. 6. Transformers are used in the transmissions of a.c. over long distances. 7. Small transformers are used in Radio sets, telephones, loud speakers and electric bells etc
- 14. IDEAL V/S PRACTICAL TRANSFORMER A transformer is said to be ideal if it satisfies the following properties, but no transformer is ideal in practice. It has no losses . Windings resistance are zero . There is no flux leakage . Small current is required to produce the magnetic field While the practical transformer has windings resistance , some leakage flux and has lit bit losses .