Introduction to management by Prof. Saurabh S. Bhange
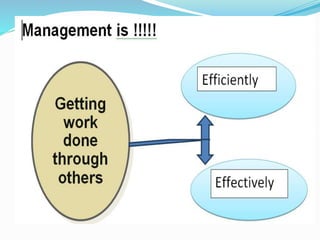
- 2. Efficiently and Effectively Efficiently (Focus on Process/means) Getting work done with a minimum of effort, expense, or waste Doings things right—most output for least input Ability to do the things in right way Ex. Ability to determine appropriate objectives Effectively (Focus on ends) Accomplishing tasks that help fulfill organizational objectives Ability to do the right things Ex. Ability to minimize the expenditure in achieving the objectives
- 3. ManageMenT Management is the process of designing & maintaining an environment in which individuals, working together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims PRODUCTTransformatio n Men Machin eMaterial Money M A N A G E M E N T
- 4. ManageMenT Things Time Method Place Process of doing right
- 6. The Father of Scientific Management 6 F. W. Taylor (1856-1915) • Important Contributions • Time and Motion Studies – Reduce motions in order to improve productivity – to establish appropriate standards for task performance • Wage - Incentive System – More wages when task is performed according to specifications within the allotted time – Ordinary wages if the time allotment is exceeded
- 7. Developed the specific principles of Scientific Management 7
- 8. Taylor’s 4 Principles of Scientific Management Scientifically study each part of a task and develop the best method for performing the task Carefully select workers and train them to perform the task by using the scientifically developed method Cooperate fully with workers to ensure that they use the proper method Divide work and responsibility so that management is responsible for planning work methods using scientific principles and workers are responsible for executing the work accordingly 8
- 9. Henri Fayol (1841-1925) FATHER OF MODERN MANAGEMENT
- 10. Fayol’s 14 Principles of Management 1. Division of Work 2. Authority 3. Discipline 4. Unity of Command 5. Unity of Direction 6. Subordination of Individual Interests to the General Interest 7. Remuneration 8. Centralization 9. Scalar Chain 10. Order 11. Equity 12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel 13. Initiative 14. Esprit de corps
- 11. 1. Division Of Work Work should be divided among individuals and groups to ensure that effort and attention are focused on special portions of the task. Fayol presented work specialization as the best way to use the human resources of the organization.
- 12. 2. AuthorityThe concepts of Authority and Responsibility are closely related. Authority was defined by Fayol as the right to give orders and the power to exact obedience. Responsibility involves being accountable, and is therefore naturally associated with authority. Whoever assumes Authority also assumes Responsibility.
- 13. 3. Discipline Employees must obey. A successful organization requires the common effort of workers. Penalties should be applied judiciously to encourage this common effort.
- 14. 4. Unity Of Command Each worker should have only one boss with no other conflicting lines of command.
- 15. 5. Unity of Direction The entire organization should be moving towards a common objective in a common direction.
- 16. 6. Subordination of individual interest The interests of one person should not take priority over the interests of the organization as a whole.
- 17. 7. Remuneration Payment is an important motivator although by analyzing a number of possibilities, Fayol points out that there is no such thing as a perfect system.
- 18. 8. Centralization (Or Decentralization) Centralization is lowering the importance of the subordinate’s role. Decentralization is increasing the importance. The degree to which centralization or decentralization should be adopted depends on the specific organization in which the manager is working.
- 19. 9. Scalar chain (Line of Authority) A hierarchy is necessary for unity of direction. But lateral communication is also fundamental, as long as superiors know that such communication is taking place. Scalar chain refers to the number of levels in the hierarchy from the ultimate authority to the lowest level in the organization. It should not be over-stretched and consist of too- many levels.
- 20. 10. Order Both material order and social order are necessary. The former minimizes lost time and useless handling of materials. The latter is achieved through organization and selection.
- 21. 11. Equity All employees should be treated as equally as possible.
- 22. 12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel Employees work better if job security and career progress are assured to them. An insecure tenure and a high rate of employee turnover will affect the organization adversely.
- 23. 13. Initiative Allowing all personnel to show their initiative in some way is a source of strength for the organization. Management should take steps to encourage worker initiative, which is defined as new or additional work activity undertaken through self direction.
- 24. 14. Esprit de CorpsManagement should encourage harmony and general good feelings among employees.
- 25. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Basic Needs Safety & Security Needs Social Needs Self Esteem Self Actualisation
- 26. The Management Process Plan what is to be done Organize how it is to be done Direct the work that is to be done Control or evaluate what has been done
- 27. Management The attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efficient manner through Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling organizational resources.
- 28. Management Functions CONTROLLING Monitor activities And make corrections LEADING Use influence to motivate followers ORGANIZING Assign responsibility for task accomplishment PLANNING Select goals and ways to attain them RESOURCES (Human, Financial, Raw Materials, Technological, Information) PERFORMANCE (Attain Goals, Products/Service, Efficiency, Effectiveness)
- 29. If you are planning for a year, sow the rice If you are planning for a decade, plant the trees If you are planning for a lifetime, educate the people Planning
- 30. Hierarchy of Plans Strategic Plans Plans reflecting decisions about resource allocations, company priorities, and steps needed to meet strategic goals Set Strategic Goals Analyze the Organization Analyze the Environment Match the Organization and its Environment Formulate Strategy & Strategy Formulation
- 31. The Nature of Planning Top management makes Strategic Plans. Middle Management makes Annual Plans (to implement the above). Supervisors planning period is usually a week, day, or shift ( to deal with daily work).
- 32. The Planning Process Define the purpose or problem and set objectives Collect & evaluate data relevant to forecasting the future (focus on the present) Develop alternative courses of action Decide on the best course of action Carry out the plan
- 33. Forecasting Forecasting: Predicting future needs on the basis of historical data, present conditions, and assured future. Forecasting controls staffing, purchasing, and production decisions. Forecasting is a very important function!
- 34. Qualities of a Good Plan Provides a workable solution and meets the stated objectives. Is comprehensive; it raises all relevant questions and answers them. Minimizes the degree of risks. Is specific as to time, place, supplies, tools, etc. Is flexible (can be adapted to a change in the situation).
- 35. Types of Plans and Planning Standing Plan: established routine, formula, or set of procedures designed to be used in a reoccurring situation. They standardize actions so the supervisors’ need to manage is reduced to seeing that workers meet standards and dealing with unexpected events known as management by exception. Potential drawback: Rigidity, must make them flexible enough to deal with daily realities. These plans must be updated regularly.
- 36. The Single Use Plan A one time plan developed for a single occasion or purpose. The amount of time you spend on it depends on its nature and importance. Often its purpose is a major change of some sort or budgets.
- 37. Day-by-Day Planning Top priority of the first line supervisor. Primary concern is what is to be done, who will be doing it, and adjusting various standing plans. Plan before the day begins. Establish routines simplify planning. Whenever possible reduce risks by increasing predictability.
- 38. Planning for Change Define problem and set objectives Gather past, present, and probable future data Evaluate pros and cons, generate alternatives Make the nessicary decisions Implement the plan
- 39. Management Functions CONTROLLING Monitor activities And make corrections LEADING Use influence to motivate followers ORGANIZING Assign responsibility for task accomplishment PLANNING Select goals and ways to attain them RESOURCES (Human, Financial, Raw Materials, Technological, Information) PERFORMANCE (Attain Goals, Products/Service, Efficiency, Effectiveness) The work a manager performs to arrange and relate work to be done so it can be performed effectively by people To provide the means of grouping people and assigned activities together so that the unit’s objectives are most effectively accomplished 1. Define each job within the organization 2. Assign activities 3. Establish clear communication channels 4. Assign responsibility and authority 5. Identify and limit the span of control
- 40. 40 Specifically, they include: 1. Division of labor 2. Delegation of authority 3. Departmentation 4. Span of control 5. Coordination Organizational Structure
- 41. Organizational Chart A schematic drawing that depicts hierarchical relationships (chain of command) among all positions in the organization. Nonmanager NonmanagersManagers Key Nonmanager Nonmanager Nonmanager Nonmanager Nonmanager Nonmanager Nonmanager Manager Director Director Director Director Director Director Manager Vice President Vice President Vice President President
- 42. The Universalism of Management Business Across Organizations of Different Size and Types Governmental Agencies Educational Institutions Social Services Health Care Delivery Across Functional Areas Production Marketing Finance Personnel Across Organizational Levels Middle Management Top Management Lower Management
- 43. Leading A function that includes Motivating employees, Directing others, selecting the most effective Communication channels, and Resolve conflicts.
- 44. Control Process 5 - 44 Establish Standards Measure Performance Does measured performance match standards? YES NO Continue Current Activities Adjust Performance or Standards
- 46. The Role of Managers : Interpersonal Role Informational Role Information + Power and Responsibility Decisional Role
- 47. The Manager
- 48. Basic Management Skills Technical Skills Skills needed to perform specialized tasks Human Relations Skills Skills in understanding and getting along with people Conceptual Skills Abilities to think in the abstract, diagnose and analyze different situations, and see beyond the present situation Decision-making Skills Skills in defining problems and selecting the best courses of action
- 49. Skills and the Manager Fundamental Management Skills Technical Skills Interpersonal Skills Conceptual Skills Diagnostic Skills Communication Skills Decision-Making Skills Time-Management Skills
- 50. Management Levels and Functional Areas
- 52. MANAGING HUMAN RELATIONS Skills needed at all levels Levels of Management Skills needed Top Middle Supervisory 35% 5% 60% 5% 20% 35% 20%
- 53. The Three Levels of Management Top managers CEO, president, or vice president Middle managers Sales manager, branch manager, or department head First-line managers Crew leader, supervisor, head nurse, or office manager
- 54. TYPES OF ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURES 1. LINE, MILITARY OR SCALER ORGANISATION
- 55. LINE, MILITARY OR SCALER ORGANISATION The oldest and the simples organisational structure. There is a hierarchical arrangement of authority. Each department is self contained and works independently of other departments. Lines of authority are vertical i.e. from top to bottom. Line structures are suitable for, 1. Small businesses where there are few subordinates, 2. Organisations where there is largely of routine nature and methods of operations are simple.
- 56. LINE, MILITARY OR SCALER ORGANISATION Advantages Simple to establish and operate Promotes prompt decision making. Easy to control as the managers have direct control over their subordinates. Communication is fast and easy as there is only vertical flow of communication. Disadvantages Lack of specialisation Managers might get overloaded with too many things to do. Failure of one manager to take proper decisions might affect the whole organisation.
- 57. TYPES OF ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURES 2. FUNCTIONAL ORGANISATION
- 58. Functional Organisation The organisation is divided into a number of functional areas. This organisation has grouping of activities in accordance with the functions of an organisation such as production, marketing, finance, human resource and so on.
- 59. Functional Organisation Advantages Is logical and reflection of functions Follows principle of occupation specialisation Simplifies training Better control as the manger in charge of each functional department is usually an specialist. Disadvantages Overspecialisation and narrow viewpoints of key personnel can limit the organisation growth. Reduced coordination between functions. Conflicts between different functions could be detrimental for the organisation as a whole. Difficult for general managers to coordinate different departments.
- 60. Line and Staff Organisation It is a combination of line and functional structures. In this organisation structure, the authority flows in a vertical line and get the help of staff specialist who are in advisory. When the line executives need advice, information about any specific area, these staff specialists are consulted.
- 62. A leader is best when people barely know he exists Not so good when people obey and acclaim him Worse when they despise him But of a good leader who talks little when this work is done his aim fulfilled they will say: “WE DID IT OURSELVES” - Lao-tse (c. 565 B.C.) (Philosopher in Ancient China) Functions of Management
- 63. Leadership “I suppose leadership at one time meant muscles; but today it means getting along with people.” -Mohandas K. Gandhi Functions of Management
- 64. Leading “A group of donkeys lead by a lion can defeat a group of lion lead by a donkey.” Socrates said 64
- 65. Leading Leading is a process of Inspiring, motivating or directing people so that they will contribute to organizational objective. Leading involves motivation, leadership theories and communication. An important role of a manager is to motivate the people working on a project. 65 Functions of Management
- 66. Leading Leadership involves using power, personality, and influence,, and communication skills Outcome of leadership is highly motivated and committed workforce 66
- 67. LEADING Trait Approach – focusses on personal qualities such as height, intelligence, genetic etc Transformational Approach – leads the organisation in new direction through leaders talent and drive Charismatic Approach – leads through personal magnetism, charm and other qualities – Eg Steve Jobs of Apple Computers, JW Marriott of Marriott Hotels Narcisstic Approach – leads through personal skills, magnetic attraction and also are distrustful of others and consider themselves invincible – Eg Napolean, Bill Gates, 67
- 68. 10 Commandments of Leadership 1. Treat everyone with respect and dignity 2. Set the example for others to follow 3. Be active 4. Maintain the highest standards of honesty and dignity 5. Insist on excellence and hold your people accountable 6. Build group cohesiveness and pride 7. Show confidence in your people 8. Maintain a strong sense of urgency 9. Be available and visible to your staff 10. Develop yourself to your highest potential video
- 69. Qualities of leadership Key Leadership Qualities Positive Self Image Clear Vision Innovative Ideas to Problems Quickly Sense and Respond to Changes
- 70. Types of leadership style Autocratic leadership style Democratic leadership style: persuasive or consultative Laissez-faire leadership style © PhotoDisc
- 71. Leadership styles A leadership style where the leader makes all decisions independently or without consulting with others Advantages: good in certain circumstances, such as urgent tasks or military actions Disadvantages: poor decisions, poor level of employee motivation Autocratic
- 72. Leadership styles A leadership style where a leader encourages employee participation in decision-making persuasive or consultative Advantages: better decisions, employee motivation Disadvantages: delayed decision, long consultation Autocratic Democratic
- 73. Leadership styles A leadership style where employees are encouraged to make their own decisions within limits. Advantages: more freedom for employees Disadvantages: few guidelines, little incentive, poor motivation video Autocratic Democratic Laissez-faire © PhotoDisc
- 74. Decision Making Functions of Management
- 75. Decision Making What is Decision Making? The word decision is defined as: “A choice between two or more alternatives”. Thus decision-making can be defined as: “The selection of a course of action from among alternatives ”.
- 76. Decision Making Decision Making is at the heart of organizational effectiveness, climate, and health. Decision Making The process by which managers respond to opportunities and threats that confront them by analyzing options and making determinations about specific organizational goals and courses of action.
- 77. Decision Making • Decisions in response to opportunities occurs when managers respond to ways to improve organizational performance to benefit customers, employees, and other stakeholder groups • Decisions in response to threats events inside or outside the organization are adversely affecting organizational performance
- 78. Six Steps in Decision Making Figure 7.4
- 79. Decision Making Steps Step 1. Recognize Need for a Decision Sparked by an event such as environment changes. Managers must first realize that a decision must be made. Step 2. Generate Alternatives Managers must develop feasible alternative courses of action. If good alternatives are missed, the resulting decision is poor. It is hard to develop creative alternatives, so managers need to look for new ideas.
- 80. Decision Making Steps Step 3. Evaluate Alternatives What are the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative? Managers should specify criteria, then evaluate.
- 81. Decision Making Steps Criteria Legality Is the alternative legal and will not violate any domestic and international laws or government regulations? Ethicalness Is the alternative ethical and will not bring harm stakeholders unnecessarily? Economic Feasibility Can organization’s performance goals sustain this alternative? Practicality Does the management have the capabilities and resources required to implement the alternative? Step 3. Evaluate alternatives
- 82. Decision Making Steps Step 4. Choose Among Alternatives Rank the various alternatives and make a decision Managers must be sure all the information available is brought to bear on the problem or issue at hand
- 83. Decision Making Steps Step 5. Implement Chosen Alternative Managers must now carry out the alternative. Often a decision is made and not implemented. Step 6. Learn From Feedback Managers should consider what went right and wrong with the decision and learn for the future. Without feedback, managers do not learn from experience and will repeat the same mistake over.
- 84. Types of decisions 1. Major & Minor Decisions: Major decisions involve more risk & heavy expenditures and vice versa. e.g. Major decisions: Purchase of land, machine. Minor decisions: Purchase of stationary like pen, pencils, etc.
- 85. Types of decisions 2. Policy & operating decisions: Top management takes policy decisions whereas middle & lower management takes operating decisions. 3. Individual & Group Decisions: 4. Programmed & Non-programmed Decisions:
- 87. Communicating Communicating is a process by which instructions, ideas, thoughts or information are transmitted, received and understand, by the person working in organisation.
- 88. Creating idea information need by the sender Encoding (Designing) Transmission of Message over a channel Receiving the message by receiver Receiver analyses, interprets & decodes the message Action Feedback
- 89. Process of Effective Communication Step 1. Idea Creation: It is preliminary step where the sender creates an idea to communicate. Step 2. Encoding: Use of proper codes like printed, sounds, gestures, pictures and real objects. Step 3. Transmission: Selection of proper channel like written papers, letter, lecture, speech, illustration, pictures, phone calls, etc. (Contd….)
- 90. Process of Effective Communication Step 4. Receiving: Step 5. Decoding: Decoding means the act of translating the message by the receiver in his own words and experience. Step 6. Action: It is the response from the receiver. Step 7. Feed Back: video
- 91. Methods of Communication 1. Verbal or Written Communication 2. Formal or Informal Communication 3. Downward, Upward or Horizontal Communication
- 92. Verbal or Written Communication Examples of Verbal Communication: Face to face conversion, telephonic talk, lectures, conferences, interviews, etc. Examples of Written Communication: Letters, memos, emails, notice, circulars, newsletters, etc.
- 93. Formal or Informal Communication Formal Communication Mostly in written form. e.g. when manager instructs his subordinates by virtue of his superior position. Informal Communication
- 94. Downward, Upward or Horizontal Communication Downward Communication takes place from top executive to the lower grade executive whereas in Upward Communication messages are sent from subordinates to superiors. Horizontal Communication takes place between persons having the same level of authority in the organisation.
- 96. “Everything that increasing the role of subordinates is decentralisation and that decreases the role is centralisation.”
- 98. BASIS FOR COMPARISON CENTRALIZATION DECENTRALIZATION Meaning The retention of powers and authority with respect to planning and decisions, with the top management, is known as Centralization. The dissemination of authority, responsibility and accountability to the various management levels, is known as Decentralization. Communication Flow Vertical Open and Free Decision Making Slow Comparatively faster Advantage Proper coordination and Leadership Sharing of burden and responsibility
- 99. BASIS FOR COMPARISON CENTRALIZATION DECENTRALIZATION Power of decision making Lies with the top management. Multiple persons have the power of decision making. Reasons Inadequate control over the organization Considerable control over the organization Best suited for Small sized organization Large sized organization
