TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENTS.ppt
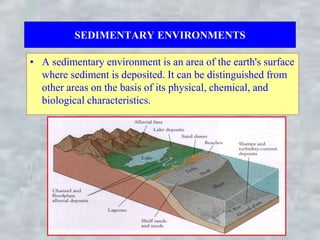
- 1. SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENTS • A sedimentary environment is an area of the earth's surface where sediment is deposited. It can be distinguished from other areas on the basis of its physical, chemical, and biological characteristics.
- 2. CONTINENTAL ENVIRONMENTS • Continental environments are those environments which are present on the continents and include: 1. Fluvial (Rivers) 2. Lacustrine (Lakes) 3. Paludal (Swamps) 4. Glacial 5. Desert
- 3. TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENTS • There are three main types of sedimentary environments: 1. Continental 2. Marine 3. Transitional
- 4. 1. Meandering streams • Have a single channel with a sinuous pattern and a broad floodplain. • The most common pattern on floodplains. • Meandering channels form where streams are flowing over a relatively flat landscape. • Associated facies are point bar, oxbow lakes, levees, crevasse splay and floodplain. Meandering river
- 5. Fluvial (Rivers) • The river channel includes two main types: • Meandering stream. • Braided stream. Meandering stream Braided stream
- 6. Point bar • It develops where stream flow is locally reduced because of friction and reduced water depth. • The eroded materials from the cut banks at the outside bend; will be deposited as point bars that lie at inside bend. • Point bar composed of cross-bedded sand.
- 7. Oxbow lake • As the channel migrates, parts of it may become abandoned and left behind as oxbow lakes which made up of fine-grained sand to silt (lake sediments). Point bar deposits Cut bank erosion Meander loop
- 8. Levees • They are ridges found along the sides of the stream channel and composed of silt and fine sand.
- 9. Crevasse splay • The crevasse splay will be formed when an overloaded stream breaks a natural or artificial levee and deposits sediments on a flood plain. It made up of sands, fining upwards to a mud. Crevasse splay Crevasse splay
- 10. Floodplain • It is a plain that subjected to periodic flooding and composed of fine-grained materials which are very fertile soil. Flood plain
- 11. Meandering river fining upward sequence
- 12. Sand dunes • They are the most common aeolian landforms; their geometry and resulting sedimentary structures depend primarily on sediment supply and prevailing wind direction. • Eolian sand sheets develop when sediment supply is limited and are characterized by planar stratification. • Vegetation can contribute to dune formation under such circumstances.
- 13. Sand dunes • Desert dune sands are characterized by a grain size of fine to coarse sand (0.1-1.00 mm), good sorting and a negative skewness. • Characterized by large-scale, high angle cross bedding. • The interdune areas are filled with lag deposits and sabkha.
- 14. Sand dunes • Geomorphologically, sand dunes include • Barchan dunes. • Transverse dunes. • Linear (longitudinal) dunes. • Star dunes.
- 15. Alluvial fans – It is a fan shaped deposits generally form at the margin of an uplift area, such as a mountain range front. – Streams in narrow valley (Canyon), carrying recently eroded material, and spread out their sediment load (alluvium) onto the plain at the base of the upland where the slope suddenly flattens. – They most commonly form under semi-arid and glacial climate conditions.
- 16. Alluvial fans – The deposits are generally texturally and compositionally immature. – The sediments become finer grained away from the apex of the fan. – Fans generally do not form as a single body, but are built up over time as a complex of coalescing and overlapping deposits. – Coalescence of alluvial fans forms Bajada. – They consist of stream-flow and debris-flow or mud- flow deposits.
- 17. MARINE ENVIRONMENTS –Marine environments are those environments in seas or oceans. – marine environments may be shallow or deep. –The shallow marine environments include reefs and continental shelf. – The deep marine environments are continental slope, continental rise and abyssal plain. Reefs
- 18. Reefs –They are mound-like, wave resistant structures made up of calcareous skeletons of organisms such as corals, bryozoa, etc. –Reefs are growing in the photic zone of warm, clear, shallow seas.
- 19. Reefs –Ancient reefs buried within stratigraphic sections are of considerable interest to geologists because they provide paleoenvironmental information about the location in Earth's history. –In addition, reef structures within a sequence of sedimentary rocks provide a discontinuity which may serve as a trap for oil or ore deposits.
- 20. Reefs –The three principal reef types are: • Fringing reef: a reef that is directly attached to a shore or borders it with an intervening shallow channel or lagoon. • Barrier reef: a reef separated from a mainland or island shore by a deep lagoon. • Atoll: is an annular reef enclosing a lagoon.
- 21. The Continental Shelf (Continental Platform) – The continental shelf is the flooded edge of the continent and lies between shoreline and continental slope. – This shelf is relatively flat (slope < 0.1o), shallow (less than 200 m), and may be up to hundreds of miles wide. – Continental shelves are exposed to waves, tides, and currents. – The shelf area is commonly subdivided (toward deep water) into three zones each with their specific geomorphology and marine biology. – The inner continental shelf (neiritic zone). – The mid continental shelf. – The outer continental shelf.
- 22. The Continental Shelf (Continental Platform) – The continental shelves are commonly covered by terrigenous sediments, in addition to non-clastic sediments such as carbonates, phosphates. – Terrigenous sediments usually become increasingly fine with distance from the shoreline whereas, sand is limited to shallow, wave-agitated waters, while silt and clays are deposited in quieter, deep water far offshore. – The carbonates of the continental shelf (carbonate factory) are rich in algae, larger foraminfera etc.. – These shelf sediments accumulate at an average rate of 30 cm/1000 years, this rate is much faster than that for deep-sea pelagic sediments.
- 23. The continental slope and continental rise – They are located seaward of the continental shelf and may reach a depth of 4000 m. – The continental slope is the steep (5- 25o) part at the edge of the continent. – The continental slope passes seaward into the continental rise, which has a more gradual slope. – The continental rise is the site of deposition of thick accumulations of sediment, much of which is in submarine fans, deposited by turbidity currents. – Submarine fans are essentially turbidites dumps most typically at the mouths of the submarine canyons that feed them.
- 24. The abyssal plain – It is flat or very gently sloping areas of the deep ocean basin floor. – It covered by very fine-grained sediment, consisting primarily of clays and the shells of microscopic organisms (such as small foraminifera, radiolarians, and diatoms).
- 25. The abyssal plain – The carbonate rocks of the deep marine water (above the CCD) are formed mainly by the accumulation of tests such as planktonic foraminifera. – The Carbonate Compensation Depth (CCD) is the depth below which no carbonate sediments can accumulate. – Below CCD, the deep marine environments are cold, with high PCo2, due to the decay of the few organisms that may be buried there. – Therefore, this environment is not suitable for the direct precipitation of carbonates from seawater. As a matter of fact, below the depth of about 5000 m, no carbonate sediments can accumulate.
- 26. TRANSITIONAL ENVIRONMENTS – Transitional environments are those environments at or near the transition between the land and sea. – These environments include delta, tidal flats, beach, barrier islands and lagoons Delta Tidal Flat Lagoon Barrier Island Beach
- 27. Delta – A delta forms where a river transporting significant quantities of sediment enters a receiving basin such as ocean or other body of water. – Name from the Greek letter ‘∆’, from the shape of the Nile Delta.
- 28. Delta – Delta is subdivided into the delta plain, delta front and prodelta: 1. The delta plain comprises a flat area dominated by alluvial deposition. The resulting vertical deposits include alluvial channel fills, overbank muds and the fine-grained sediment infill of lakes. 2. The delta front is located at the distal edge of the delta plain; sediments are deposited in mouth bars as the rivers emerge into the sea. 3. The prodelta is most distal part of the delta whereas the finest grained sediments are deposited.
- 29. Delta – Controls on delta environments and facies.