Forms of market 11
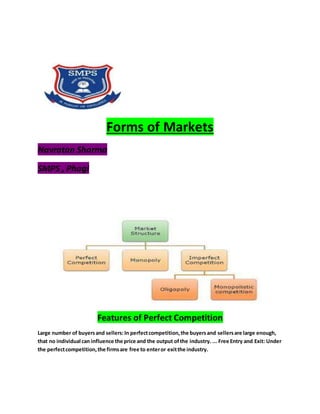
- 1. Forms of Markets Navratan Sharma SMPS , Phagi Features of Perfect Competition Large number of buyersand sellers:In perfectcompetition,the buyersand sellersare large enough, that no individual can influence the price and the output ofthe industry. ... Free Entry and Exit: Under the perfectcompetition,the firmsare free to enteror exitthe industry.
- 2. Agricultural markets are examplesofnearly perfectcompetitionas well.Imagine shoppingat your local farmers' market: there are numerous farmers, sellingthe same fruits, vegetablesandherbs.You can easilyfindout the pricesfor the goods,but theyare usually all about the same.
- 3. 1. Large number of buyers and sellers 2. Homogenous product is produced by every firm 3. Free entry and exit of firms 4. Zero advertising cost 5. Consumers have perfect knowledge about the market and are well aware of any changes in the market. Consumers indulge in rational decision making. 6. All the factors of production, viz. labour, capital, etc, have perfect mobility in the market and are not hindered by any market factors or market forces. 7. No government intervention 8. No transportation costs 9. Each firm earns normal profits and no firms can earn super-normal profits. 10. Every firm is a price taker. It takes the price as decided by the forces of demand and supply. No firm can influence the price of the product. Monopoly In a Monopoly Market Structure, there is only one firm prevailing in a particular industry. However, from a regulatory view, monopoly power exists when a single firm controls 25% or more of a particular
- 4. market. For example, Indian Railway, De Beers is known to have a monopoly in the diamond industry. A Natural Monopoly Market Structure is the result of natural advantages like a strategic location or an abundance of mineral resources. For example, many Gulf countries have a monopoly in crude oil exploration because of abundant naturally occurring oil resources. Characteristics of a Monopoly Market Structure 1. A Lack of Substitutes One firm producing a good without close substitutes. The product is often unique. Ex: When Apple started producing the iPad, it arguably had a monopoly over the tablet market. 2. Barriers to Entry There are significant barriers to entry set up by the monopolist. If new firms enter the industry, the monopolist will not have complete control of a firm on the supply. These barriers imply that under a monopoly there is no differ-ence between a firm and an industry. 3. Competition There are no close competitors in the market for that product. 4. Price Maker The monopolist decides the price of the product, since it has the market power. This makes the monopolist a price maker. 5. Profits While a monopolist can maintain supernormal profits in the long run, it doesn’t necessarily make profits. A monopolist can be a loss making
- 5. or revenue maximizing too. This is not possible under perfect competition. If abnormal profits are available in the long run, other firms will enter the competition with the result abnormal profits will be eliminated. Advantages of a Monopoly 1. Stability of prices In a monopoly market structure the prices are pretty stable. This is because there is only one firm involved in the market that sets the prices since there is no competing product. In other types of market structures prices are not stable and tend to be elastic as a result of the competition. 2. Economies of Scale Since there is a single seller in the market it leads to economics of scale because big scale production which lowers the cost per unit for the seller. The seller may pass this benefit down to the consumer in terms of a lower price. 3. Research and Development Since the monopolist is making abnormal or supernormal profits, the firm can invest that money into research and development. Customers may get better a quality product at reduced price leading to enhanced consumer surplus and satisfaction. Disadvantages of a Monopoly 1. Higher prices The monopolist could set a very high price for the product leading to exploitation of consumers as they have no option but to buy it from seller due to the lack of competition in the market.
- 6. 2. Price discrimination Monopolists can sometimes use price discrimination, where they charge different prices on the same product for different consumers. This depends on market conditions. 3. Inferior goods and services The lack of competition may cause the monopoly firm to produce inferior goods and services because they know the goods will sell. 1 Monopolistic
- 7. Monopolistic Competition refers to the market situation in which there is a keen competition, but neither perfect nor pure, among a group of a large number of small producers or suppliers having some degree of monopoly because of the differentiation of their products. Thus, we can say that monopolistic competition (or imperfect competition) is a mixture of competition and a certain degree of monopoly, on the basis of a correct appraisal of the market situation. The main features of monopolistic competition are as under: 1. Large Number of Buyers and Sellers: There are large number of firms but not as large as under perfect competition. That means each firm can control its price-output policy to some extent. It is assumed that any price-output policy of a firm will not get reaction from otherfirms that means each firm follows the independent price policy. 2. Free Entry and Exit of Firms: Like perfect competition, under monopolistic competition also, the firms can enter or exit freely. The firms will enter when the existing firms are making super-normal profits. With the entry of new firms, the supply would increase which would reduce the price and hence the existing firms will be left only with normal profits. Similarly, if the existing firms are sustaining losses, some of the marginal firms will exit. It will reduce the supply due to which price would rise and the existing firms will be left only with normal profit. 3. Product Differentiation:
- 8. Another feature of the monopolistic competition is the product differentiation. Product differentiation refers to a situation when the buyers of the product differentiate the product with other. Basically, the products of different firms are not altogether different; they are slightly different from others. Although each firm producing differentiated product has the monopoly of its own product, yet he has to face the competition. This product differentiation may be real or imaginary. Real differences are like design, material used, skill etc. whereas imaginary differences are through advertising, trade mark and so on. 4. Selling Cost: Another feature of the monopolisticcompetition is that every firm tries to promote its product by different types of expenditures. Advertisement is the most important constituent of the selling cost which affects demand as well as cost of the product. The main purpose of the monopolist is to earn maximum profits; therefore, he adjusts this type of expenditure accordingly. 5. Lack of Perfect Knowledge: The buyers and sellers do not have perfect knowledge of the market. There are innumerable products each being a close substitute of the other. The buyers do not know about all these products, their qualities and prices. Therefore, so many buyers purchase a product out of a few varieties which are offered for sale near the home. Sometimes a buyer knows about a particular commodity where it is available at low price. But he is unable to go there due to lack of time or he is too lethargic to go or he is unable to find proper conveyance. Likewise, the seller does not know the exact preference of buyers and is, therefore, unable to get advantage out of the situation. 6. Less Mobility: Under monopolistic competition both the factors of production as well as goods and services are not perfectly mobile. 7. More Elastic Demand: Under monopolistic competition, demand curve is more elastic. In order to sell more, the firms must reduce its price.