Four-stage Sequential Planning
- 2. Four-step travel demand modelling • Four decisions are the basis of traditional travel demand modelling 1. The choice and reason to travel 2. The destination to travel to 3. The mode by which to travel 4. The route on which to travel
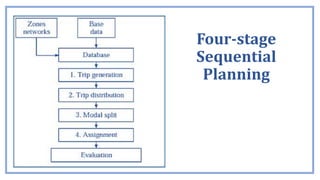
- 3. Four-stage Sequential Planning • Urban transportation planning process; • Trip generation- How many trips will be generated by a given location and how many of these will occur? • Trip distribution- What are the origins and destinations of these trips? • Modal split models- Which mode of transport will be used to make the trip? • Trip assignments- Which route on the transportation network will be used to make this trip ?
- 4. Four-stage Sequential Planning • Urban transportation planning process; • Trip generation, correlation analysis and regression analysis; • Trip distribution, Growth factor methods and Synthetic methods; • Modal split models, first generation, second generation, behavioural models; minimum travel path computations; • Trip assignments, route assignment, multiple assignment and network assignment.
- 6. • These techniques include assumptions about the four basic elements of estimation, which are: ➢Trip generation ➢Trip distribution ➢Modal split ➢Traffic assignment
- 7. • Trip generation is the number of trips starting or ending at an area (or zone) in a given time period, for example day or hour. • Trip distribution describes the number or proportion of trips from an origin zone spread among all destination zones. • Modal split is the split (or share) of these trips among different modes of travel (e.g. car, public transport, walk, cycle). • Assignment is the process whereby trips are routed from.
- 8. What factors influence travel demand??? • Location and intensity of land use • Extent , cost and quality of available transportation services • Socioeconomic characteristics of study area
- 9. TRIP GENERATION • Trip generation is the first stage of the classical first generation aggregate demand models. • The trip generation aims at predicting the total number of trips generated and attracted to each zone of the study area. • In other words this stage answers the questions to “how many trips” originate at each zone, from the data on household and socioeconomic attributes.
- 10. TRIP GENERATION- Intensity of travel has to be related to intensity of land use
- 12. TYPES OF TRIPS • Trip is classified as Production or Origin and Attraction or Destination. It should be note that the terminologies used are not identical. To understand with an example consider a single worker on a typical working day making a trip from his house which is in zone P to his office in Zone Q. • Thus his trip origin will be zone P and trip destination will be zone Q. For the return trip from office to house his trip origin will be zone Q and trip Destination will be Zone P. Thus from the above Example it can be understood that the term Origin and Destination are defined in terms of direction of the trip while Production and Attraction in terms of land use associated with each trip end. • Trip Production is the home end of home based trip and is the origin of trip of non home based trip. Trip Attraction is the non home end of home based trip and is the destination of a non home based trip.
- 13. TYPES OF TRIPS 1. Home Based Trip: One of the trip end is home. • Example: A trip from home to office. • Following are the list of home based trips that is trip purpose which are classified into five categories: • a. Work Trips • b. School Trips • c. Shopping Trips • d. Social- recreational Trips • e. Other Trips • The first two trips are mandatory trips while other trips are discretional trips. The other trip class encompasses all the trips made for less routine purpose such as health bureaucracy etc.
- 14. TYPES OF TRIPS 2. Non Home based trips: None of the trip end is home. • Example: A trip from office to Shopping Mall. • Trips can be classified by 1. trip purpose 2. 2. trip time of the day 3. 3. by person type.
- 16. • Trips can be classified by trip purpose, trip time of the day, and by person type. • Trip generation models are found to be accurate if separate models are used based on trip purpose. • The trips can be classified based on the purpose of the journey as trips for work, trips for education, trips for shopping, trips for recreation and other trips. • Among these the work and education trips are often referred as mandatory trips and the rest as discretionary trips. All the above trips are normally home based trips and constitute about 80 to 85 percent of trips.
- 17. • The rest of the trips namely non home based trips, being a small proportion are not normally treated separately. • The second way of classification is based on the time of the day when the trips are made. The broad classification is into peak trips and off peak trips. • The third way of classification is based on the type of the individual who makes the trips. This is important since the travel behaviour is highly influenced by the socio economic attribute of the traveller and are normally categorized based on the income level, vehicle ownership and house hold size.
- 18. Factors affecting trip generation • The main factors affecting personal trip production include income, vehicle ownership, house hold structure and family size. • In addition factors like value of land, residential density and accessibility are also considered for modelling at zonal levels. • In trip generation modelling in addition to personal trips, freight trips are also of interest.
- 19. MODELLING • Three major techniques used for Trip Generation Analysis ➢Multiple regression analysis ➢Cross classification ➢Experience based analysis (Expansion factor)
- 21. Simple Linear regression analysis
- 22. Simple Linear regression analysis
- 23. Simple Linear regression analysis
- 24. Example
- 28. • Let the trip rate of a zone is explained by the household size done from the field survey. • It was found that the household size are 1, 2, 3 and 4. • The trip rates of the corresponding household is as shown in the table below. • Fit a linear equation relating trip rate and household size.
- 32. GROWTH FACTOR METHOD • TRIP RATE • Growth factor modes tries to predict the number of trips produced or attracted by a house hold or zone as a linear function of explanatory variables. • The models have the following basic equation:
- 33. Example • Given that a zone has 275 household with car and 275 household without car and the average trip generation rates for each groups is respectively 5.0 and 2.5 trips per day. • Assuming that in the future, all household will have a car, find the growth factor and future trips from that zone, assuming that the population and income remains constant.