Davila_Joshua-SURE2015
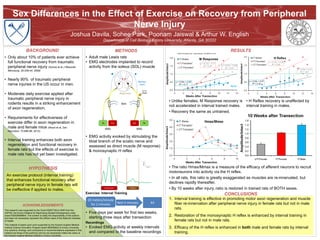
- 1. • The ratio Hmax/Mmax is a measure of the efficacy of afferent neurons to recruit motoneurons into activity via the H reflex. • In all rats, this ratio is greatly exaggerated as muscles are re-innervated, but declines rapidly thereafter. • By 10 weeks after injury, ratio is restored in trained rats of BOTH sexes. CONCLUSIONS 1. Interval training is effective in promoting motor axon regeneration and muscle fiber re-innervation after peripheral nerve injury in female rats but not in male rats. 2. Restoration of the monosynaptic H reflex is enhanced by interval training in female rats but not in male rats. 3. Efficacy of the H reflex is enhanced in both male and female rats by interval training. Sex Differences in the Effect of Exercise on Recovery from Peripheral Nerve Injury Joshua Davila, Sohee Park, Poonam Jaiswal & Arthur W. English Department of Cell Biology Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322 BACKGROUND • Only about 10% of patients ever achieve full functional recovery from traumatic peripheral nerve injury (Scholz et al J Reconstr Microsurg. 25:339-44, 2009) • Nearly 90% of traumatic peripheral nerve injuries in the US occur in men. • Moderate daily exercise applied after traumatic peripheral nerve injury in rodents results in a striking enhancement of axon regeneration. • Requirements for effectiveness of exercise differ in axon regeneration in male and female mice (Wood et al, Dev Neurobiol. 72:688-98, 2012) • Interval training enhances both axon regeneration and functional recovery in female rats but the effects of exercise in male rats has not yet been investigated. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This research was supported by the Grant NS057190 to AWE from the USPHS, the Emory Initiative for Maximizing Student Development under award R25GM099644. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. This material is based upon work supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute Science Education Program award #52006923 to Emory University. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute or Emory University. HYPOTHESIS An exercise protocol (interval training) that enhances functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury in female rats will be ineffective if applied to males. METHODS • Adult male Lewis rats • EMG electrodes implanted to record activity from the soleus (SOL) muscle 20 meters/minute for 2 minutes Rest 5 minutes X4 Recordings • Evoked EMG activity at weekly intervals and compared to the baseline recordings Exercise: Interval Training • Five days per week for first two weeks, starting three days after transection Sensory Axon Motor Axon SOLSOL Cut & Repair 2 ms 200µV M Response H Reflex • EMG activity evoked by stimulating the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve and assessed as direct muscle (M response) & monosynaptic H reflex *Data from Boeltz et al, J.Neurophysiol. 109;2645-57, 2013 RESULTS • Unlike females, M Response recovery is not accelerated in interval trained males. • Recovery the same as untrained. • H Reflex recovery is unaffected by interval training in males. N=4