12-Marginal-Costing-WS-2022.pdf
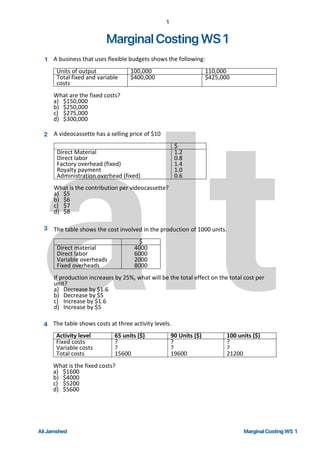
- 1. 1 Marginal Costing WS 1 1 2 3 4 Ali Jamshed MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A business that uses flexible budgets shows the following: Units of output 100,000 110,000 Total fixed and variable costs $400,000 $425,000 What are the fixed costs? a) $150,000 b) $250,000 c) $275,000 d) $300,000 2. A videocassette has a selling price of $10 $ Direct Material Direct labor Factory overhead (fixed) Royalty payment Administration overhead (fixed) 1.2 0.8 1.4 1.0 0.6 What is the contribution per videocassette? a) $5 b) $6 c) $7 d) $8 3. The table shows the cost involved in the production of 1000 units. $ Direct material Direct labor Variable overheads Fixed overheads 4000 6000 2000 8000 If production increases by 25%, what will be the total effect on the total cost per unit? a) Decrease by $1.6 b) Decrease by $5 c) Increase by $1.6 d) Increase by $5 4. The table shows costs at three activity levels. Activity level 65 units ($) 90 Units ($) 100 units ($) Fixed costs Variable costs Total costs ? ? 15600 ? ? 19600 ? ? 21200 What is the fixed costs? a) $1600 b) $4000 c) $5200 d) $5600 Ali Jamshed 45 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A business that uses flexible budgets shows the following: Units of output 100,000 110,000 Total fixed and variable costs $400,000 $425,000 What are the fixed costs? a) $150,000 b) $250,000 c) $275,000 d) $300,000 2. A videocassette has a selling price of $10 $ Direct Material Direct labor Factory overhead (fixed) Royalty payment Administration overhead (fixed) 1.2 0.8 1.4 1.0 0.6 What is the contribution per videocassette? a) $5 b) $6 c) $7 d) $8 3. The table shows the cost involved in the production of 1000 units. $ Direct material Direct labor Variable overheads Fixed overheads 4000 6000 2000 8000 If production increases by 25%, what will be the total effect on the total cost per unit? a) Decrease by $1.6 b) Decrease by $5 c) Increase by $1.6 d) Increase by $5 4. The table shows costs at three activity levels. Activity level 65 units ($) 90 Units ($) 100 units ($) Fixed costs Variable costs Total costs ? ? 15600 ? ? 19600 ? ? 21200 What is the fixed costs? a) $1600 b) $4000 c) $5200 d) $5600 Ali Jamshed 45 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A business that uses flexible budgets shows the following: Units of output 100,000 110,000 Total fixed and variable costs $400,000 $425,000 What are the fixed costs? a) $150,000 b) $250,000 c) $275,000 d) $300,000 2. A videocassette has a selling price of $10 $ Direct Material Direct labor Factory overhead (fixed) Royalty payment Administration overhead (fixed) 1.2 0.8 1.4 1.0 0.6 What is the contribution per videocassette? a) $5 b) $6 c) $7 d) $8 3. The table shows the cost involved in the production of 1000 units. $ Direct material Direct labor Variable overheads Fixed overheads 4000 6000 2000 8000 If production increases by 25%, what will be the total effect on the total cost per unit? a) Decrease by $1.6 b) Decrease by $5 c) Increase by $1.6 d) Increase by $5 4. The table shows costs at three activity levels. Activity level 65 units ($) 90 Units ($) 100 units ($) Fixed costs Variable costs Total costs ? ? 15600 ? ? 19600 ? ? 21200 What is the fixed costs? a) $1600 b) $4000 c) $5200 d) $5600 Ali Jamshed MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A business that uses flexible budgets shows the following: Units of output 100,000 110,000 Total fixed and variable costs $400,000 $425,000 What are the fixed costs? a) $150,000 b) $250,000 c) $275,000 d) $300,000 2. A videocassette has a selling price of $10 $ Direct Material Direct labor Factory overhead (fixed) Royalty payment Administration overhead (fixed) 1.2 0.8 1.4 1.0 0.6 What is the contribution per videocassette? a) $5 b) $6 c) $7 d) $8 3. The table shows the cost involved in the production of 1000 units. $ Direct material Direct labor Variable overheads Fixed overheads 4000 6000 2000 8000 If production increases by 25%, what will be the total effect on the total cost per unit? a) Decrease by $1.6 b) Decrease by $5 c) Increase by $1.6 d) Increase by $5 4. The table shows costs at three activity levels. Activity level 65 units ($) 90 Units ($) 100 units ($) Fixed costs Variable costs Total costs ? ? 15600 ? ? 19600 ? ? 21200 What is the fixed costs? a) $1600 b) $4000 c) $5200 d) $5600 Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 1 alt
- 2. 2 5 6 7 8 46 5. A company sells two products, X and Y. X Y Sales (units) Selling price/unit Contribution/unit 1000 $ 22 12 2000 $ 12 4 a) A 30% increase in sales of X b) A 50% increase in sales of both product c) An increase in selling price of X by $1 and Y by $6 d) A reduction in variable costs of both products by $5 6. A company is about to quote a price for making a special order, which requires 1000 kg of material X and 1500 kg of material Y. The following information is available about these resources Type of material Original cost per kg($) Current purchase price per kg ($) Net realizable value per kg ($) X Y 3 5 4 7 2 6 The inventory of material X cannot be used by the company for any other product. Material Y is used frequently for other products. Which cost of material should be included in the quotation for the manufacture of this special order? a) $10500 b) $11000 c) $12500 d) $14500 7. The table shows budgets for the next production period. Costs Output 2000 units ($) Output 4000 units ($) Direct material Direct labor Production overhead 30000 48000 76000 154000 60000 96000 92000 248000 What would be the budgeted production cost of 3000 units? a) $141000 b) $147000 c) $171000 d) $201000 Ali Jamshed 8. A business makes wedding dresses. Each machinist is paid $30 a day and each supervisor $40 a day. Each supervisor can work with up to 10 machinist and each machinist can product one wedding dress a day. If 95 wedding dresses a day are produced, what is the daily labour cost? a) $2850 b) $3210 c) $3230 d) $3250 9. A product has a contribution per unit of $20. Which action would increase the total contribution by the greatest amount? a) A 10% increase in selling price b) A 10% increase in volume of sales c) A 10% reduction in variable costs d) A 20% reduction in fixed costs 46 5. A company sells two products, X and Y. X Y Sales (units) Selling price/unit Contribution/unit 1000 $ 22 12 2000 $ 12 4 a) A 30% increase in sales of X b) A 50% increase in sales of both product c) An increase in selling price of X by $1 and Y by $6 d) A reduction in variable costs of both products by $5 6. A company is about to quote a price for making a special order, which requires 1000 kg of material X and 1500 kg of material Y. The following information is available about these resources Type of material Original cost per kg($) Current purchase price per kg ($) Net realizable value per kg ($) X Y 3 5 4 7 2 6 The inventory of material X cannot be used by the company for any other product. Material Y is used frequently for other products. Which cost of material should be included in the quotation for the manufacture of this special order? a) $10500 b) $11000 c) $12500 d) $14500 7. The table shows budgets for the next production period. Costs Output 2000 units ($) Output 4000 units ($) Direct material Direct labor Production overhead 30000 48000 76000 154000 60000 96000 92000 248000 What would be the budgeted production cost of 3000 units? a) $141000 b) $147000 c) $171000 d) $201000 46 5. A company sells two products, X and Y. X Y Sales (units) Selling price/unit Contribution/unit 1000 $ 22 12 2000 $ 12 4 a) A 30% increase in sales of X b) A 50% increase in sales of both product c) An increase in selling price of X by $1 and Y by $6 d) A reduction in variable costs of both products by $5 6. A company is about to quote a price for making a special order, which requires 1000 kg of material X and 1500 kg of material Y. The following information is available about these resources Type of material Original cost per kg($) Current purchase price per kg ($) Net realizable value per kg ($) X Y 3 5 4 7 2 6 The inventory of material X cannot be used by the company for any other product. Material Y is used frequently for other products. Which cost of material should be included in the quotation for the manufacture of this special order? a) $10500 b) $11000 c) $12500 d) $14500 7. The table shows budgets for the next production period. Costs Output 2000 units ($) Output 4000 units ($) Direct material Direct labor Production overhead 30000 48000 76000 154000 60000 96000 92000 248000 What would be the budgeted production cost of 3000 units? a) $141000 b) $147000 c) $171000 d) $201000 Marginal Costing WS 1 Ali Jamshed alt
- 3. 3 9 10 11 47 a) $2850 b) $3210 c) $3230 d) $3250 9. A product has a contribution per unit of $20. Which action would increase the total contribution by the greatest amount? a) A 10% increase in selling price b) A 10% increase in volume of sales c) A 10% reduction in variable costs d) A 20% reduction in fixed costs 10. A business has the following costs. Raw material $3 per unit Direct labor $2 per unit Stepped costs of $5000 for every 10000 units What is the cost of producing 15000 units? a) $75000 b) $82500 c) $85000 d) $105000 11. The details of a planned college course are shown below. $ Course fee per student Variable course cost per student Total fixed costs of the course 100 20 480 The budgeted number of students is 10. However, if a lower fee is charged 20 students would take the course. What is the maximum reduction in the course fee of $100, to earn the same total profit from either 10 or 20 students? a) $16 b) $24 c) $40 d) $50 1. A 7. D 2. C 8. D 3. A 9. A 4. C 10. C 5. B 11. C 6. C 47 machinist can product one wedding dress a day. If 95 wedding dresses a day are produced, what is the daily labour cost? a) $2850 b) $3210 c) $3230 d) $3250 9. A product has a contribution per unit of $20. Which action would increase the total contribution by the greatest amount? a) A 10% increase in selling price b) A 10% increase in volume of sales c) A 10% reduction in variable costs d) A 20% reduction in fixed costs 10. A business has the following costs. Raw material $3 per unit Direct labor $2 per unit Stepped costs of $5000 for every 10000 units What is the cost of producing 15000 units? a) $75000 b) $82500 c) $85000 d) $105000 11. The details of a planned college course are shown below. $ Course fee per student Variable course cost per student Total fixed costs of the course 100 20 480 The budgeted number of students is 10. However, if a lower fee is charged 20 students would take the course. What is the maximum reduction in the course fee of $100, to earn the same total profit from either 10 or 20 students? a) $16 b) $24 c) $40 d) $50 1. A 7. D 2. C 8. D 3. A 9. A 4. C 10. C 5. B 11. C 6. C 47 If 95 wedding dresses a day are produced, what is the daily labour cost? a) $2850 b) $3210 c) $3230 d) $3250 9. A product has a contribution per unit of $20. Which action would increase the total contribution by the greatest amount? a) A 10% increase in selling price b) A 10% increase in volume of sales c) A 10% reduction in variable costs d) A 20% reduction in fixed costs 10. A business has the following costs. Raw material $3 per unit Direct labor $2 per unit Stepped costs of $5000 for every 10000 units What is the cost of producing 15000 units? a) $75000 b) $82500 c) $85000 d) $105000 11. The details of a planned college course are shown below. $ Course fee per student Variable course cost per student Total fixed costs of the course 100 20 480 The budgeted number of students is 10. However, if a lower fee is charged 20 students would take the course. What is the maximum reduction in the course fee of $100, to earn the same total profit from either 10 or 20 students? a) $16 b) $24 c) $40 d) $50 1. A 7. D 2. C 8. D 3. A 9. A 4. C 10. C 5. B 11. C 6. C Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 1 alt
- 4. 4 Decision Making 12 13 14 64 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A company manufactures and sells widgets. The directors want to increase profitability and are considering buying-in the widgets instead of manufacturing them. The company should buy the widgets from an outside supplier if the price is: a) Less than the marginal cost of production b) More than the marginal cost of production but less than the marginal cost of sales c) More than the marginal cost of sales but less than the total cost d) More than the total cost but less the selling price 2. Department X Y Z Sales Less: variable costs Headquarter fixed costs- apportioned Net profit(loss) $ 200000 130000 80000 (210000) (10000) $ 240000 150000 90000 (240000) - $ 320000 100000 130000 (230000) 90000 Headquarters fixed costs will not be reduced if any department is closed. What should the company do, on the basis of these results? a) Close department X b) Close department Y c) Close department X & Y d) Keep all departments open 3. A company manufactures one product. It has variable costs of $600,000 and fixed costs of $300,000. If it bought all its production from another supplier, it could use its existing machinery to make a total contribution of $400,000. Fixed costs would not change. What is the maximum price it should pay to obtain all its production from another supplier? a) $600000 b) $700000 c) $900000 d) $1000000 64 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A company manufactures and sells widgets. The directors want to increase profitability and are considering buying-in the widgets instead of manufacturing them. The company should buy the widgets from an outside supplier if the price is: a) Less than the marginal cost of production b) More than the marginal cost of production but less than the marginal cost of sales c) More than the marginal cost of sales but less than the total cost d) More than the total cost but less the selling price 2. Department X Y Z Sales Less: variable costs Headquarter fixed costs- apportioned Net profit(loss) $ 200000 130000 80000 (210000) (10000) $ 240000 150000 90000 (240000) - $ 320000 100000 130000 (230000) 90000 Headquarters fixed costs will not be reduced if any department is closed. What should the company do, on the basis of these results? a) Close department X b) Close department Y c) Close department X & Y d) Keep all departments open 3. A company manufactures one product. It has variable costs of $600,000 and fixed costs of $300,000. If it bought all its production from another supplier, it could use its existing machinery to make a total contribution of $400,000. Fixed costs would not change. What is the maximum price it should pay to obtain all its production from another supplier? a) $600000 b) $700000 c) $900000 d) $1000000 64 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A company manufactures and sells widgets. The directors want to increase profitability and are considering buying-in the widgets instead of manufacturing them. The company should buy the widgets from an outside supplier if the price is: a) Less than the marginal cost of production b) More than the marginal cost of production but less than the marginal cost of sales c) More than the marginal cost of sales but less than the total cost d) More than the total cost but less the selling price 2. Department X Y Z Sales Less: variable costs Headquarter fixed costs- apportioned Net profit(loss) $ 200000 130000 80000 (210000) (10000) $ 240000 150000 90000 (240000) - $ 320000 100000 130000 (230000) 90000 Headquarters fixed costs will not be reduced if any department is closed. What should the company do, on the basis of these results? a) Close department X b) Close department Y c) Close department X & Y d) Keep all departments open 3. A company manufactures one product. It has variable costs of $600,000 and fixed costs of $300,000. If it bought all its production from another supplier, it could use its existing machinery to make a total contribution of $400,000. Fixed costs would not change. What is the maximum price it should pay to obtain all its production from another supplier? a) $600000 b) $700000 c) $900000 d) $1000000 Marginal Costing WS 1 Ali Jamshed alt
- 5. 5 15 16 Ali Jamshed 65 4. A company manufactures 3 products X,Y and Z. the table provides information concerning the three products. Product X Product Y Product Z Selling price per unit Direct material cost per unit Direct labor cost per unit Variable overhead cost per unit Fixed overhead cost per unit Profit per unit $ 100 40 20 15 18 7 $ 120 45 25 18 18 13.5 $ 130 48 29 20 27 6 All 3 products are made from the same material. If the material is in short supply, which manufacturing pattern will maximize profits? Order of priority 1 2 3 A B C D Y Y Z Z X Z Y X Z X X Y 5. The table contains information for the two products of a company. Product X Y Contribution per unit Machine hours required per unit Estimated sales demand Required machine hours $12 6 200 1200 $9 3 200 600 Machine capacity limited to 1200 Hours What is the maximum possible contribution? a) $2100 b) $3000 c) $3300 d) $4200 65 4. A company manufactures 3 products X,Y and Z. the table provides information concerning the three products. Product X Product Y Product Z Selling price per unit Direct material cost per unit Direct labor cost per unit Variable overhead cost per unit Fixed overhead cost per unit Profit per unit $ 100 40 20 15 18 7 $ 120 45 25 18 18 13.5 $ 130 48 29 20 27 6 All 3 products are made from the same material. If the material is in short supply, which manufacturing pattern will maximize profits? Order of priority 1 2 3 A B C D Y Y Z Z X Z Y X Z X X Y 5. The table contains information for the two products of a company. Product X Y Contribution per unit Machine hours required per unit Estimated sales demand Required machine hours $12 6 200 1200 $9 3 200 600 Machine capacity limited to 1200 Hours What is the maximum possible contribution? a) $2100 b) $3000 c) $3300 d) $4200 Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 1 alt
- 6. 6 17 18 66 6. A company manufactures four products using different quantities of the same material, which is short in supply. The following data is given: Product Y1 $ per unit Y2 $ per unit Y3 $ per unit Y4 $ per unit Selling price Materials, $6 per kg Production costs Profits Machine time per unit(in minutes) 64 18 37 9 45 68 24 30 14 30 84 27 36 21 40 100 30 33 37 30 The production costs include fixed costs which have been absorbed using a machine hour rate of $36. Which product gives the most profitable use of raw materials? a) Y1 b) Y2 c) Y3 d) Y4 7. A business manufactures 3 products which all use the same material. The following information is available. X $000 Y $000 Z $000 Selling price Direct material Direct labor Variable overhead Contribution 160 56 35 28 41 190 68 32 34 56 240 90 50 45 55 Direct material is in short supply. In which order should the products be manufactured to maximize profits? a) X -> Y -> Z b) Y -> X -> Z c) Y -> Z -> X d) Z -> Y -> X 66 6. A company manufactures four products using different quantities of the same material, which is short in supply. The following data is given: Product Y1 $ per unit Y2 $ per unit Y3 $ per unit Y4 $ per unit Selling price Materials, $6 per kg Production costs Profits Machine time per unit(in minutes) 64 18 37 9 45 68 24 30 14 30 84 27 36 21 40 100 30 33 37 30 The production costs include fixed costs which have been absorbed using a machine hour rate of $36. Which product gives the most profitable use of raw materials? a) Y1 b) Y2 c) Y3 d) Y4 7. A business manufactures 3 products which all use the same material. The following information is available. X $000 Y $000 Z $000 Selling price Direct material Direct labor Variable overhead Contribution 160 56 35 28 41 190 68 32 34 56 240 90 50 45 55 Direct material is in short supply. In which order should the products be manufactured to maximize profits? a) X -> Y -> Z b) Y -> X -> Z c) Y -> Z -> X d) Z -> Y -> X 66 6. A company manufactures four products using different quantities of the same material, which is short in supply. The following data is given: Product Y1 $ per unit Y2 $ per unit Y3 $ per unit Y4 $ per unit Selling price Materials, $6 per kg Production costs Profits Machine time per unit(in minutes) 64 18 37 9 45 68 24 30 14 30 84 27 36 21 40 100 30 33 37 30 The production costs include fixed costs which have been absorbed using a machine hour rate of $36. Which product gives the most profitable use of raw materials? a) Y1 b) Y2 c) Y3 d) Y4 7. A business manufactures 3 products which all use the same material. The following information is available. X $000 Y $000 Z $000 Selling price Direct material Direct labor Variable overhead Contribution 160 56 35 28 41 190 68 32 34 56 240 90 50 45 55 Direct material is in short supply. In which order should the products be manufactured to maximize profits? a) X -> Y -> Z b) Y -> X -> Z c) Y -> Z -> X d) Z -> Y -> X 66 6. A company manufactures four products using different quantities of the same material, which is short in supply. The following data is given: Product Y1 $ per unit Y2 $ per unit Y3 $ per unit Y4 $ per unit Selling price Materials, $6 per kg Production costs Profits Machine time per unit(in minutes) 64 18 37 9 45 68 24 30 14 30 84 27 36 21 40 100 30 33 37 30 The production costs include fixed costs which have been absorbed using a machine hour rate of $36. Which product gives the most profitable use of raw materials? a) Y1 b) Y2 c) Y3 d) Y4 7. A business manufactures 3 products which all use the same material. The following information is available. X $000 Y $000 Z $000 Selling price Direct material Direct labor Variable overhead Contribution 160 56 35 28 41 190 68 32 34 56 240 90 50 45 55 Direct material is in short supply. In which order should the products be manufactured to maximize profits? a) X -> Y -> Z b) Y -> X -> Z c) Y -> Z -> X d) Z -> Y -> X Marginal Costing WS 1 Ali Jamshed alt
- 7. 7 Marginal Costing WS 2 1 2 33 COSTING -2 MARGINAL COSTING 1. Following data is available for ABC Manufacturing Company for production & sale of 4000 units. $ Sale 80000 Direct Material (DM) 40000 Direct Labor (DL) 16000 Variable Overheads (VOH) 4000 Fixed Overheads 10000 REQUIRED: Calculate Profit if o 2000 units are produced and sold o 6000 units are produced and sold 2. Following Data is available for Target Ltd for production & sale of 1200 units $ Sale 96000 Direct Material (DM) 24000 Direct Labor (DL) 18000 Overheads (60% Fixed) 30000 REQUIRED: Calculate Profit if o 2000 units are produced and sold o 500 units are produced and sold 33 COSTING -2 MARGINAL COSTING 1. Following data is available for ABC Manufacturing Company for production & sale of 4000 units. $ Sale 80000 Direct Material (DM) 40000 Direct Labor (DL) 16000 Variable Overheads (VOH) 4000 Fixed Overheads 10000 REQUIRED: Calculate Profit if o 2000 units are produced and sold o 6000 units are produced and sold 2. Following Data is available for Target Ltd for production & sale of 1200 units $ Sale 96000 Direct Material (DM) 24000 Direct Labor (DL) 18000 Overheads (60% Fixed) 30000 REQUIRED: Calculate Profit if o 2000 units are produced and sold o 500 units are produced and sold Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 8. 8 3 4 Ali Jamshed 34 3. Following information is available for two levels of activity. 4000 Units $ 10000 Units $ Sales 64000 160000 DM 12000 30000 DL 18000 45000 Production Overheads 20000 38000 REQUIRED: Calculate: (i) Variable Cost / Units (ii) Fixed Cost (iii) Profit if 7000 units are produced and Profit if 15000 units are produced. 4. Following information is available for two level of activity 2000 Units $ 10000 Units $ Sales 30000 150000 DM 10000 50000 DL 8000 40000 Production Overheads 5000 21000 REQUIRED: Calculate: (i) Variable Cost / Units (ii) Fixed Cost (iii) Profit if 7000 units are produced and Profit if 15000 units are produced. Ali Jamshed 34 3. Following information is available for two levels of activity. 4000 Units $ 10000 Units $ Sales 64000 160000 DM 12000 30000 DL 18000 45000 Production Overheads 20000 38000 REQUIRED: Calculate: (i) Variable Cost / Units (ii) Fixed Cost (iii) Profit if 7000 units are produced and Profit if 15000 units are produced. 4. Following information is available for two level of activity 2000 Units $ 10000 Units $ Sales 30000 150000 DM 10000 50000 DL 8000 40000 Production Overheads 5000 21000 REQUIRED: Calculate: (i) Variable Cost / Units (ii) Fixed Cost (iii) Profit if 7000 units are produced and Profit if 15000 units are produced. Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 9. 9 5 Ali Jamshed 35 5. The following budget is based on the full production capacity of 12000 units $ Sales 240000 DM 96000 DL 36000 Production Overheads (20% fixed) 20000 Sales overheads (50%) 24000 Calculate: (i) Breakeven point in units (ii) Contribution to sales ratio (CS ratio) (iii) Breakeven point in value (iv) How many units should be produced in order to make a profit of $20000 (v) The Margin of safety in units (vi) The Margin of safety in value (vii) The Margin of safety as a percentage Ali Jamshed 35 5. The following budget is based on the full production capacity of 12000 units $ Sales 240000 DM 96000 DL 36000 Production Overheads (20% fixed) 20000 Sales overheads (50%) 24000 Calculate: (i) Breakeven point in units (ii) Contribution to sales ratio (CS ratio) (iii) Breakeven point in value (iv) How many units should be produced in order to make a profit of $20000 (v) The Margin of safety in units (vi) The Margin of safety in value (vii) The Margin of safety as a percentage Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 10. 10 6 Ali Jamshed 36 6. Alberta Limited produces one product, plates, for which the following information is available. Per unit $ Selling price 12.00 Direct Materials 5.00 Direct Labour 2.80 Variable Overheads 2.20 Total fixed costs (per annum) $240000 Sales per annum (units) 400000 REQUIRED: (a) Using the information above, calculate the following: (i) Break-even point in units and sales value. (ii) Profit for one year, clearly showing the contribution per unit. (iii) Margin of safety in units and as a percentage of sales. Alberta Limited is now considering extending the product range by adding two products, cups and saucers. The fixed costs would double to $480,000 if any new product was introduced. The following information is available for the additional products. Cups $ per unit Saucers $ per unit Selling price 18.00 26.00 Direct Materials 7.20 14.00 Direct Labour 4.80 4.20 Variable Overheads 3.00 1.80 Sales per annum (units) 100,000 60,000 The current workforce is operating al full capacity in the production of the plates. There is, however, machine capacity available to undertake the production of both cups and saucers. Alberta Limited extended their product range by adding both products. (b) Calculate the maximum profit for one year that Alberta Limited could achieve if it was to produce plates, cups and saucers. Show the contribution per unit and total contribution for each product. Ali Jamshed 36 6. Alberta Limited produces one product, plates, for which the following information is available. Per unit $ Selling price 12.00 Direct Materials 5.00 Direct Labour 2.80 Variable Overheads 2.20 Total fixed costs (per annum) $240000 Sales per annum (units) 400000 REQUIRED: (a) Using the information above, calculate the following: (i) Break-even point in units and sales value. (ii) Profit for one year, clearly showing the contribution per unit. (iii) Margin of safety in units and as a percentage of sales. Alberta Limited is now considering extending the product range by adding two products, cups and saucers. The fixed costs would double to $480,000 if any new product was introduced. The following information is available for the additional products. Cups $ per unit Saucers $ per unit Selling price 18.00 26.00 Direct Materials 7.20 14.00 Direct Labour 4.80 4.20 Variable Overheads 3.00 1.80 Sales per annum (units) 100,000 60,000 The current workforce is operating al full capacity in the production of the plates. There is, however, machine capacity available to undertake the production of both cups and saucers. Alberta Limited extended their product range by adding both products. (b) Calculate the maximum profit for one year that Alberta Limited could achieve if it was to produce plates, cups and saucers. Show the contribution per unit and total contribution for each product. Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 11. 11 7 Ali Jamshed 37 7. Ranjeev Ali has decided to open his own business making leather jackets. He is not sure whether to produce high quality jackets or low quality jackets. If Ranjeev produces high quality jackets, he will use good quality material, each jacket will take longer to complete, and he will have to employ higher quality skilled labour. He will also have higher fixed costs Ranjeev will be able to sell each high quality jacket at a higher price, but he would sell more jackets if he produced low quality jackets. Ranjeev has prepared some estimated figures, shown below: High Quality Jacket Low Quality Jacket Material costs per square metre $11 $8 Material required per jacket (sq metres) 3 3 Labour costs per hour $15 $13 Labour time per jacket (hours) 4 3 Fixed Costs per month $2300 $2000 Selling Price per jacket $149 $99 Estimated number of sales per month (units) 160 210 REQUIRED: (a) Calculate the expected break even point in units for a month, for both the high quality jacket and the low quality jacket. (b) Calculate the margin of safety in units for one month, for both the high quality jacket and the low quality jacket. (c) Calculate the expected profit for a month, for both the high quality jacket and the low quality jacket. (d) Evaluate which type of jacket Ranjeev should produce. Ali Jamshed 37 7. Ranjeev Ali has decided to open his own business making leather jackets. He is not sure whether to produce high quality jackets or low quality jackets. If Ranjeev produces high quality jackets, he will use good quality material, each jacket will take longer to complete, and he will have to employ higher quality skilled labour. He will also have higher fixed costs Ranjeev will be able to sell each high quality jacket at a higher price, but he would sell more jackets if he produced low quality jackets. Ranjeev has prepared some estimated figures, shown below: High Quality Jacket Low Quality Jacket Material costs per square metre $11 $8 Material required per jacket (sq metres) 3 3 Labour costs per hour $15 $13 Labour time per jacket (hours) 4 3 Fixed Costs per month $2300 $2000 Selling Price per jacket $149 $99 Estimated number of sales per month (units) 160 210 REQUIRED: (a) Calculate the expected break even point in units for a month, for both the high quality jacket and the low quality jacket. (b) Calculate the margin of safety in units for one month, for both the high quality jacket and the low quality jacket. (c) Calculate the expected profit for a month, for both the high quality jacket and the low quality jacket. (d) Evaluate which type of jacket Ranjeev should produce. Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 12. 12 8 Ali Jamshed 38 8. Calthrop and Earle Ltd manufactures electronic ignition systems for the motor industry. The company has recently developed a new ignition system. The draft budget for the new ignition system for the financial year ending 30 June 2006 includes the following: Production and sales 100 000 units Direct materials 180 Direct labour 110 Variable overheads 60 Fixed costs: Production 7 000 000 Administration 2 500 000 Marketing and Advertising 3 700 000 Selling price p At a recent board meeting the following points were made: (i) The chief executive suggested that the business should aim for 70% margin of safety. (ii) The marketing director suggested that if the adv sales and production quantities would rise by 5%. The production director estimated that the business would then benefit from increased bulk purchases discounts and direct material costs would fall by 5%. All other costs would remain unchanged, and selling price REQUIRED (a) Using the original draft budget (i) Calculate the Break-even output in units. (ii) Calculate the margin of safety as a percentage. (iii) Calculate the profit for the year ending 30 June 2006 clearly showing contribution per unit. (b) calculate profit for the year ended 30 June 2006, clearly showing the contribution per unit. Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 13. 13 9 Ali Jamshed 39 9. Claret Limited manufactures a single product. Its sales and costs for the year ended 31 March 2001 were as follows: Unitssold 60,000 Selling price per unit £20 Variable costs per unit £8 Total fixed costs £300,000 To improve profits in its next financial year the following options are being considered. Option 1 Increase the selling price by £3 per unit, the loss in sales would be compensated by higher revenue. Costs would be unchanged. Option 2 Reduce the selling price by 10% per unit, this leading to an increase in demand. Costs would be unchanged. Option 3 Reduce part of the fixed salaries of the sales representatives and instead pay them a lower fixed salary plus a commission of £020 for each unit they sell. This would reduce fixed costs by £20,000. All other costs, selling price and quantity sold would be unchanged. REQUIRED (a) Calculate for the year ended 31 March 2001: (i) Break-even point in units; (ii) Profit, showing the contribution per unit In your calculations. (b) Calculate, for each of the Options 1 and 2, the sales in units required to maintain the profit of the year ended 31 March 2001. (c) Calculate the profit for Option 3. Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 14. 14 10 Ali Jamshed 40 10. A division of Hobbs Limited manufactures one product, the Wye. The directors had prepared the following forecast for the year ending 30 June 2016. $000 Sales revenue 4400 Direct materials 1400 Direct labour 1000 Variable administration costs 400 Fixed administration costs 300 Other fixed overheads 1200 Budgeted sales for the year ending 30 June 2016 are expected to be 40 000 units. REQUIRED (a) Calculate for product Wye: (i) the contribution per unit (ii) the budgeted break-even point in units (iii) the margin of safety in units Additional information The directors have been warned that trading conditions are likely to change in the coming year and they plan to make the following changes to their forecasts. Reduce the selling price of the product by 10%. Budget for a 20% increase in sales. Budget for a 3% increase in direct labour. Budget for a 10% decrease in fixed costs. (b)Calculate for product Wye: (i) the revised contribution per unit (ii) the revised break-even point in units (iii) the revised margin of safety in units Additional information Another division of Hobbs Limited also manufactures one product, the Exe. The following data is available for the year ending 30 June 2016. Unit selling price $20 Unit variable costs $15 Budgeted fixed costs per annum $30 000 Budgeted sales 8000 units Ali Jamshed (c) Calculate the monthly break-even point in revenue. (d) Prepare a break-even chart for product Exe for the year ending 30 June 2016. Clearly indicate the areas of profit and loss. (e) State three assumptions the accountant must make when preparing a break-even Additional information The company uses marginal costing in order to calculate its break- decisions. (f) State three further reasons why a business might use a marginal costing Ali Jamshed (c) Calculate the monthly break-even point in revenue. (d) Prepare a break-even chart for product Exe for the year ending 30 June 2016. Clearly indicate the areas of profit and loss. (e) State three assumptions the accountant must make when preparing a break-even Additional information The company uses marginal costing in order to calculate its break- decisions. (f) State three further reasons why a business might use a marginal costing Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 15. 15 11 Ali Jamshed 11. Ken produces components for mobile telephones. The following budgeted data is available for the year ending 31 December 2018: Per unit $ Selling price 5.25 Direct materials 0.50 Direct labour 0.75 Direct expenses 0.25 Break-even point 16 000 units REQUIRED (a) Calculate the budgeted fixed costs for the year ending 31 December 2018. Additional information The budgeted profit for the year ending 31 December 2018 is $75 000. (b) Calculate for the year ending 31 December 2018: (i) budgeted number of units to be sold. (ii) budgeted contribution to sales (C / S) ratio (to two decimal places) (c) State the meaning of C / S ratio. (d) (i) State the name given to the difference between the budgeted total sales units and the budgeted break-even sales units. (ii) Explain the significance of this difference to a business. (e) Prepare the break-even chart for Ken based on the relevant data. Clearly identify the area of profit, the area of loss and the break-even point. (f) State three limitations of a break-even analysis. Additional information Ken is considering increasing the selling price to $6.00 per unit from 1 January 2019. He expects that all costs will remain unchanged. (g) Calculate the number of units Ken must sell each month so the budgeted total contribution is the same as in 2018. (h) Advise Ken whether or not he should increase the selling price taking into account both financial and non-financial factors. 41 (c) Calculate the monthly break-even point in revenue. (d) Prepare a break-even chart for product Exe for the year ending 30 June 2016. Clearly indicate the areas of profit and loss. (e) State three assumptions the accountant must make when preparing a break-even Additional information The company uses marginal costing in order to calculate its break- decisions. (f) State three further reasons why a business might use a marginal costing Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 16. 16 12 Ali Jamshed 43 12. Bould Limited manufactures two products, Wye and Zed. The forecast data for the year ending 30 June 2016 is as follows. Wye Zed $ $ Revenue from Wye 70 000 units at $12 840000 Revenue from Zed 90 000 units at $8 720000 Materials (259 000) (180 000) Labour (233 000) (372 000) Overheads (190 000) (207 000) Profit / (Loss) 158 000 (39 000) Labour includes fixed costs 65 000 48 000 Overheads include fixed costs 36 000 45 000 REQUIRED (a) Calculate the contribution per unit of Wye (b) Calculate the contribution per unit of Zed. (c) Calculate the break-even point in units of Zed. (d) Calculate the break-even point in revenue of Zed. (e) Calculate the margin of safety in revenue for Zed. Additional information The directors are concerned about the forecast loss of manufacturing Zed and are considering two proposals. Proposal 1 Increase the selling price of Zed by $1.20 per unit. The sales volume is expected to fall by 5% as a result. Proposal 2 Stop manufacturing Zed. This will incur redundancy costs of $20 000. There would be an increased additional budget facility for advertising Wye, which would increase sales volume of Wye by 40%. (f) Calculate the revised forecast profit of Bould Limited for the year ended 30 June 2016 if proposal 1 is adopted. (g) Calculate the revised forecast profit if proposal 2 is adopted. (h) Advise, with reasons, which proposal the directors should adopt. Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 17. 17 13 Ali Jamshed 44 13. Albert Ross Limited produces a single product. Its costs and sales for the year ended 31 December 2001 were as follows: Units sold 20,000 $ Sales revenue 900,000 Direct wages 200,000 Direct materials 300,000 Variable overheads 120,000 Fixed costs 205,000 The selling price and all costs were at a constant rate throughout the year. To improve profit for the year commencing 1 January 2002, the following changes are planned: i. Units to be sold to increase by 5%. ii. Selling price to be maintained at the 2001 price. iii. Wages to be increased by 3% per unit. iv. Materials costs to be reduced by 5% per unit, this being achieved b changing from a local supplier to an overseas supplier. v. Variable overheads to be reduced by $0.55 per unit. vi. Fixed costs to increase by $5000 per annum. REQUIRED: (a) Calculate for the year commencing 1 January 2002: (i) Break-even point in units and sales value (ii) Profit for the year showing the contribution per unit in your calculations (iii) The margin of safety in units and sales value (iv) The sales in units required to maintain the profit level for the year ended 31 December 2001 (b) Evaluate the effects of the decision to change from a local to an overseas supplier. Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 18. 18 Decision Making 14 Ali Jamshed 48 COSTING 3-MARGINAL COSTING AND DECISION MAKING 1. Sairum manufacturing makes three types of products. Following information is available for each product. Product A Product B Product C Selling price / Unit $35 $20 $60 DM / Unit $8 $6 $12 DL / Unit $10 $3 $30 VOH / Unit $4 $3 $5 Demand (Units) 3000 2400 1000 Annual Fixed Overheads for Sairum Manufacturing is $20000. 1kg of DM = $8/kg Labour in the factory is paid at the rate of $5 per hour. REQUIRED: a) (i) If only 5000 kg of material is available and there is no shortage of labour, draw a production schedule which will maximize profits. (ii) Calculate the maximum profit. b) Assuming material is not in short supply but labour hours available are restricted to 10000 hours. (i) Draw a production schedule which will maximize profit. (ii)Calculate the maximum profit. c) Now assuming labour is not in short supply and availability of material is 4500 kg. Mr Sairum has ordered that at least 500 units of each product must be produced. This order must be accepted if the workers want to stay ALIVE. (i) Draw a production schedule which will maximize profit. (ii) Calculate the maximum profit. Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 19. 19 15 Ali Jamshed 49 2. Reed Ltd manufactures three products A, B and C. Budgeted costs and selling prices for the three months ending 30 September 1999 were as follows: A B C Sales (units per month) 6000 8000 5000 $ $ $ Selling price per unit 45 44 37 Unit costs Direct labour 6 9 6 Direct materials 20 24 16 Variable overheads 4 3 2 The total fixed costs are $100000 per month, and are unavoidable. The company has been advised by its supplier that, due to a material shortage, its material requirement for the month of September will be reduced by 15%. Material costs are $4 per kilo for all products. REQUIRED: a) A statement to show the net profit for July 1999, clearly showing the contribution per unit for each product. b) A statement to show the maximum net profit for the three months ending 30th September 1998 taking into account the material shortage for the month of September 1998, clearly showing the total contribution for each product. Ali Jamshed 49 2. Reed Ltd manufactures three products A, B and C. Budgeted costs and selling prices for the three months ending 30 September 1999 were as follows: A B C Sales (units per month) 6000 8000 5000 $ $ $ Selling price per unit 45 44 37 Unit costs Direct labour 6 9 6 Direct materials 20 24 16 Variable overheads 4 3 2 The total fixed costs are $100000 per month, and are unavoidable. The company has been advised by its supplier that, due to a material shortage, its material requirement for the month of September will be reduced by 15%. Material costs are $4 per kilo for all products. REQUIRED: a) A statement to show the net profit for July 1999, clearly showing the contribution per unit for each product. b) A statement to show the maximum net profit for the three months ending 30th September 1998 taking into account the material shortage for the month of September 1998, clearly showing the total contribution for each product. Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 20. 20 16 Ali Jamshed 50 3. Passabuck Ltd makes three products: Meenibuck, Teenibuck and Deluxibuck for which the following details are given: Product Meenibuck Teenibuck Deluxibuck Direct material (kilos per unit) 5 7 10 Direct labour (hours per unit) 4 6 8 Direct expenses (per unit) $7 $4 $9 Selling price per unit $74 $85 $115 Further information: All three products are made from material X. Material X costs $3 per kilo. All three products require the same type of labour which is paid at $7 per hour. Total fixed costs amount to $70000. Budgeted production (based upon maximum demand) is: Menibuck 2000 units Teenibuck 2400 units Deluxibuck 1800 units It has now been discovered that the supply of material X is limited to 38000 kilos. REQUIRED: a) Calculate the contribution per kilo of material X used for each product. b) Prepare a production budget based on your calculation in (a) to give maximum profit from the material available Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 21. 21 17 52 5. Garden supplies Ltd make 3 styles of ornamental pot: African $ British $ Chinese $ Unit selling price 10.00 12.00 15.50 Direct labour 3.00 4.00 5.00 Direct materials 3.00 2.00 4.00 Variable overheads 3.00 4.00 4.00 Annual fixed costs total $60000 Machine hours needed to make 10 pots 3 4 6 Three machines are used in the manufacturing process. Each machine runs for a maximum of 6000 hours per annum. Each machine can make any type of pot. Annual demand in units is 24000 20000 18000 REQUIRED: a) What is the unit contribution of each type of pot? b) To maximize profits: (i) How many of each type should be made? (ii) How much profit would be made? c) What are the answers to (b) if at least 6000 of each pot must be made per annum? Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 22. 22 18 Ali Jamshed 55 7. Clarke Limited manufactures one product, the Apex. The following forecast information for the Apex is available for the year ending 31 December 2014: Per unit: Selling price $45.50 Direct material ($4 per metre) $14.00 Direct labour ($12 per hour) $18.00 Variable production overhead $ 3.00 Sales demand 4 000 units Fixed overheads are forecast to be $23 100 for the year. REQUIRED a) Calculate the breakeven point in units for the sales of the Apex. b) Calculate the margin of safety for the Apex in terms of revenue. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Clarke Limited has decided to introduce two new products in addition to the Apex; the Bond and the Cord. Both products use the same direct material and the same grade of direct labour as the Apex. The following forecast information is available for the year ending 31 December 2014: Per unit: Bond Cord Selling price $52.00 $67.50 Direct material ($4 per metre) $16.00 $20.00 Direct labour ($12 per hour) $24.00 $30.00 Variable production overhead $ 4.00 $ 5.00 Sales demand 6 000 units 2 000 units Fixed overheads are expected to double as a result of producing all three products. c) Calculate the contribution per unit of the Bond and the Cord. d) Calculate the total quantity of direct material required by Clarke Limited for the year ending 31 December 2014. e) Clarke Limited has been told that due to a shortage of direct material, only 40 000 metres will be available for the year. Calculate the maximum forecast profit for Clarke Limited for the year ending 31 December 2014 using 40 000 metres of direct material. Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 23. 23 19 56 8. Y Limited manufactures three products, Exe, Wye and Zed. The following budgeted information is available for the month of July 2017: Per unit Exe Wye Zed Selling price $96.00 $128.00 $140.00 Direct material at $4 per kilo 7 kilos 9 kilos 15 kilos Direct labour at $8 per hour 3 hours 4 hours 4 hours Machine hours 1.00 2.50 5.00 Variable overhead $2.40 $3.20 $3.20 Fixed overhead $10.00 $25.00 $50.00 Maximum monthly demand 100 units 120 units 60 units Fixed overheads are forecast to be $7000 per month. Y Limited has enough resources and capacity to meet the maximum monthly demand. REQUIRED a) Calculate the contribution per unit for each product. b) Prepare a statement to show the maximum contribution and maximum profit that Y Limited can earn for the month of July 2017. c) Calculate the total machine hours required to meet maximum demand for the month of July 2017. Additional information Due to a machine breakdown, only 500 machine hours will be available for July 2017 production. d) Calculate the maximum contribution and the maximum profit for the month of July 2017, taking into account the limited machine hours available. Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 24. 24 20 Ali Jamshed 60 10. Nasri at $1100 each. However his manager has already produced the following figures for 2009 $ $ Sales (8000 x $1100) 8800000 Direct materials 1024000 Direct wages 5000000 Production overheads 640000 Sales overheads 480000 7144000 Profit 1656000 All overheads are 50% fixed and 50% variable. 250000 labour hours are worked. There are 3 options under consideration which will allow sales to increase to 10000 tables. Option 1: Purchase 2000 tables from another manufacturer at $920 each. Option 2: Lease new and improved machinery at a cost of $260000 for the year. This would allow production of 10000 tables per annum with no change in unit variable costs. This was previously under consideration and $40000 has been spent on a feasibility study. Option 3: Using the existing machinery introduce an evening shift thus providing an additional 62500 labour hours. Wage rates for this shift would have to increase by 15% to take into account unsocial hours to be worked. Also the additional staff needed would have to be trained at a cost of $50000- this cost would be absorbed in 2009. REQUIRED: a) Calculate the original unit contribution b) Calculate profit under each option Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt
- 25. 25 21 62 12. Fernando manufactures 3 types of refrigerator for Household, Business and Factory use. The following data apply to the year ended 30 April 2007. Household Business Factory Total Sales (units) 2400 900 2250 5550 Total sales value ($) 240000 108000 360000 708000 Total costs $ $ $ $ Direct material 96000 45000 112500 253500 Direct labour 72000 28800 94500 195300 Variable overheads 24000 13500 45000 82500 Fixed overheads _57600 _27000 _67500 _152100 249600 114300 319500 683400 Profit (loss) (9600) (6300) 40500 24600 REQUIRED: a) For the year ended 30 April 2007 calculate for each type of refrigerator: (i) the contribution per unit; (ii) the contribution as a percentage of sales. Give answers to a maximum of two decimal places. Working must be shown. b) Calculate the break-even point for each type of refrigerator in both units and dollars. Give your answers to the nearest whole number. Working must be shown c) The table at the beginning of the question shows that both the Household and the Business models appear to be making a loss. Explain why Fernando should not cease production of these two types of refrigerator. 62 12. Fernando manufactures 3 types of refrigerator for Household, Business and Factory use. The following data apply to the year ended 30 April 2007. Household Business Factory Total Sales (units) 2400 900 2250 5550 Total sales value ($) 240000 108000 360000 708000 Total costs $ $ $ $ Direct material 96000 45000 112500 253500 Direct labour 72000 28800 94500 195300 Variable overheads 24000 13500 45000 82500 Fixed overheads _57600 _27000 _67500 _152100 249600 114300 319500 683400 Profit (loss) (9600) (6300) 40500 24600 REQUIRED: a) For the year ended 30 April 2007 calculate for each type of refrigerator: (i) the contribution per unit; (ii) the contribution as a percentage of sales. Give answers to a maximum of two decimal places. Working must be shown. b) Calculate the break-even point for each type of refrigerator in both units and dollars. Give your answers to the nearest whole number. Working must be shown c) The table at the beginning of the question shows that both the Household and the Business models appear to be making a loss. Explain why Fernando should not cease production of these two types of refrigerator. 62 12. Fernando manufactures 3 types of refrigerator for Household, Business and Factory use. The following data apply to the year ended 30 April 2007. Household Business Factory Total Sales (units) 2400 900 2250 5550 Total sales value ($) 240000 108000 360000 708000 Total costs $ $ $ $ Direct material 96000 45000 112500 253500 Direct labour 72000 28800 94500 195300 Variable overheads 24000 13500 45000 82500 Fixed overheads _57600 _27000 _67500 _152100 249600 114300 319500 683400 Profit (loss) (9600) (6300) 40500 24600 REQUIRED: a) For the year ended 30 April 2007 calculate for each type of refrigerator: (i) the contribution per unit; (ii) the contribution as a percentage of sales. Give answers to a maximum of two decimal places. Working must be shown. b) Calculate the break-even point for each type of refrigerator in both units and dollars. Give your answers to the nearest whole number. Working must be shown c) The table at the beginning of the question shows that both the Household and the Business models appear to be making a loss. Explain why Fernando should not cease production of these two types of refrigerator. Ali Jamshed Marginal Costing WS 2 alt
- 26. 26 Answers WS 1 1 A 2 C 3 A 4 C 5 B 6 C 7 D 8 D 9 A 10 C 11 C 12 A 13 D 14 D 15 B 16 B 17 A 18 B Marginal Costing WS 2 Ali Jamshed alt