Bio
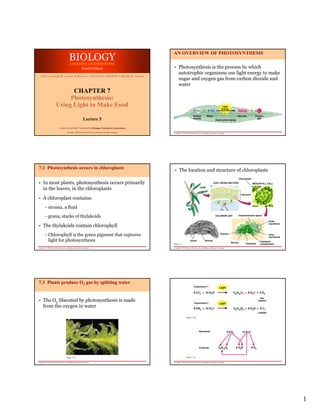
- 1. BIOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition • Photosynthesis is the process by which autotrophic organisms use light energy to make Neil A. Campbell • Jane B. Reece • Lawrence G. Mitchell • Martha R. Taylor sugar and oxygen gas from carbon dioxide and water CHAPTER 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Carbon Water Glucose Oxygen Lecture 5 dioxide PHOTOSYNTHESIS gas From PowerPoint® Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 7.2 Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts • The location and structure of chloroplasts Chloroplast • In most plants, photosynthesis occurs primarily LEAF CROSS SECTION MESOPHYLL CELL in the leaves, in the chloroplasts LEAF Mesophyll • A chloroplast contains: – stroma, a fluid – grana, stacks of thylakoids CHLOROPLAST Intermembrane space Outer • The thylakoids contain chlorophyll membrane – Chlorophyll is the green pigment that captures Granum Inner membrane light for photosynthesis Grana Stroma Stroma Thylakoid Figure 7.2 Thylakoid compartment Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 7.3 Plants produce O2 gas by splitting water Experiment 1 • The O2 liberated by photosynthesis is made Not labeled Experiment 2 from the oxygen in water Labeled Figure 7.3B Reactants: Products: Figure 7.3A Figure 7.3C Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1
- 2. 7.4 Photosynthesis is a redox process, as is cellular 7.5 Overview: Photosynthesis occurs in two stages respiration linked by ATP and NADPH • Water molecules are split apart and electrons • The complete process of photosynthesis and H+ ions are removed, leaving O2 gas consists of two linked sets of reactions: – These electrons and H+ ions are transferred to – the light reactions and the Calvin cycle CO2, producing sugar • The light reactions convert light energy to Reduction chemical energy and produce O2 Oxidation • The Calvin cycle assembles sugar molecules Figure 7.4A Oxidation from CO2 using the energy-carrying products of the light reactions Reduction Figure 7.4B Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings • An overview of photosynthesis THE LIGHT REACTIONS: CONVERTING SOLAR ENERGY TO CHEMICAL ENERGY H2 O CO2 7.6 Visible radiation drives the light reactions Chloroplast Light • Certain wavelengths of visible light drive the NADP+ light reactions of photosynthesis ADP + P LIGHT CALVIN REACTIONS CYCLE (in grana) (in stroma) Gamma Micro- Radio X-rays UV Infrared rays waves waves ATP Ele ctro NADPH ns Visible light O2 Sugar Wavelength (nm) Figure 7.5 Figure 7.6A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 7.7 Photosystems capture solar power Reflected Light light • Each of the many light-harvesting photosystems consists of: Chloroplast – an “antenna” of chlorophyll and other pigment molecules that absorb light – a primary electron acceptor that receives excited electrons from the reaction-center chlorophyll Absorbed light Transmitted light Figure 7.6B Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 2
- 3. • Excitation of Primary electron acceptor Primary chlorophyll in electron acceptor a chloroplast Other compounds PHOTOSYSTEM Photon Reaction center Photon Chlorophyll molecule Pigment molecules of antenna Figure 7.7C Figure 7.7B Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 7.8 In the light reactions, electron transport chains generate ATP, NADPH, and O2 • Where do the electrons come from that keep • Two connected photosystems collect photons of the light reactions running? light and transfer the energy to chlorophyll • In photosystem I, electrons from the bottom of electrons the cascade pass into its P700 chlorophyll • The excited electrons are passed from the primary electron acceptor to electron transport chains – Their energy ends up in ATP and NADPH Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings • Photosystem II regains electrons by splitting THE CALVIN CYCLE: CONVERTING CO2 TO SUGARS water, leaving O2 gas as a by-product 7.10 ATP and NADPH power sugar synthesis in the El Primary ec tro n tra Calvin cycle electron acceptor ns p or t • The Calvin cycle occurs Primary INPUT electron acceptor El ec tro n tra ns p in the chloroplast’s or tc ha in stroma Photons – This is where carbon CALVIN CYCLE fixation takes place and Energy for sugar is manufactured synthesis of PHOTOSYSTEM I PHOTOSYSTEM II OUTPUT: by chemiosmosis Figure 7.8 Figure 7.10A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 3
- 4. • Details of the • The Calvin cycle constructs G3P using Calvin cycle INPUT: 3 CO2 In a reaction catalyzed by rubisco, 3 molecules of CO2 are fixed. – carbon from atmospheric CO2 Step 1 Carbon 1 fixation. – electrons and H+ from NADPH 3 P P 6 P RuBP 3-PGA 6 ATP 3 ADP – energy from ATP Step 2 Energy consumption and redox. 6 ADP + P 3 ATP CALVIN 2 4 CYCLE 6 NADPH • Energy-rich sugar is then converted into 6 NADP+ glucose Step 3 Release of one molecule of G3P. 5 P 6 P G3P G3P 3 Step 4 Regeneration of RuBP. Glucose OUTPUT: 1 P and other compounds G3P Figure 7.10B Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings PHOTOSYNTHESIS REVIEWED AND EXTENDED • Many plants make more sugar than they need 7.11 Review: Photosynthesis uses light energy to make food molecules – The excess is stored in roots, tuber, and fruits • A summary – These are a major source of food for animals of the Chloroplast Light chemical processes Photosystem II Electron of photo- transport CALVIN chains CYCLE Stroma Photosystem I synthesis Ele ctr ons Cellular respiration Cellulose Starch Other LIGHT REACTIONS CALVIN CYCLE organic Figure 7.11 compounds Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 7.12 C4 and CAM plants have special adaptations that save water • Leaf cross section • Most plants are C3 plants, which take CO2 directly from the air and use it in the Calvin cycle – In these types of plants, stomata on the leaf surface close when the weather is hot – This causes a drop in CO2 and an increase in O2 in the leaf • Stomata, open and closed – Photorespiration may then occur Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 4
- 5. • Photorespiration in a C3 plant • Some plants have special adaptations that enable them to save water – Special cells in C4 plants—corn and sugarcane—incorporate 4-C compound CALVIN CO2 into a four-carbon CYCLE molecule – This molecule can then donate CO2 to the CALVIN 2-C compound Calvin cycle CYCLE Figure 7.12A Figure 7.12B 3-C sugar Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings • The CAM plants—pineapples, most cacti, and succulents—employ a different mechanism – They open their stomata at night and make a four-carbon 4-C compound compound Night – It is used as a CO2 Day source by the same cell during the day CALVIN CYCLE 3-C sugar Figure 7.12C Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings 5
