CH -11 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND OTHER STAKEHOLDERS
- 2. Stakeholder Concept • Recognition of Stakeholder Concept In Law • Stakeholder Engagement • Stakeholder Analysis •Types of Stakeholders • Caux RoundTable • Clarkson Principle of Stakeholder Management • Governance Paradigm and Stakeholders
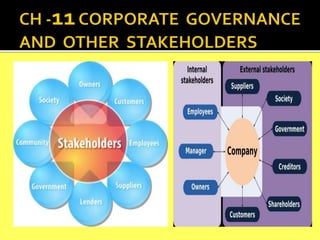
- 3. • Stakeholders provide resources that are more or less critical to a firm’s long-term success.These resources may be both tangible and intangible. Shareholders, for example, supply capital; suppliers offer material resources or intangible knowledge; employees and managers grant expertise, leadership, and commitment; customers generate revenue and provide infrastructure; and the society builds its positive corporate images. • A director of a company shall act in good faith in order to promote the objects of the company for the benefit of its members as a whole, and in the best interest of the company, its employees, the community and the environment. • Stakeholder engagement leads to increased transparency, responsiveness, compliance, organizational learning, quality management, accountability and sustainability. Stakeholder engagement is a central feature of sustainability performance. • Primary stakeholders are those whose continued association is absolutely necessary for a firm’s survival; these include employees, customers, investors, and shareholders, as well as the governments and communities that provide necessary infrastructure.
- 4. • Secondary stakeholders do not typically engage in transactions with a company and thus are not essential for its survival; these include the media, trade associations, and special interest groups. • Customers are considered as the king to drive the market and they can sometimes exercise influence by consolidating their bargaining power in order to get lower prices. •The lenders put a check and balance on the governance practices of an organization to ensure safety of their fund and as a societal responsibility. •The organization which builds a mutually strong relationship with its vendors improves its overall performance in the marketplace. •The society provides the desired climate for successful operation of a company business. If society turns against the company, then business lose its faith in the eyes of other stakeholders be it government or customer.
- 5. “stakeholders” mentioned in the media from time to time. In a business context, customers, investors and shareholders, employees, suppliers, government agencies, communities, and many others . Stakeholders provide resources that are more or less critical to a firm’s long-term success. The classic definition of a stakeholder is ‘any group or individual . 1. Principles of corporate legitimacy: The corporation should be managed for the benefit of its stakeholders: its customers, suppliers, owners, employees & local communities.The rights of these groups must participate, in some sense, in decisions that substantially affect their welfare. 2. The stakeholder fiduciary principle: Management bears a fiduciary relationship to stakeholders and to the corporation as an abstract entity. It must act in the interest of the stakeholders as their agent, and it must act in the interests of the corporation to ensure the survival of the firm, safeguarding the long-term stakes of each group. Another definition of Stakeholder given subsequently by Freeman: “Those groups who are vital to the survival & success of the corporation” and the two principles were altered and renamed: 1. The stakeholder enabling principle— Corporations shall be managed in the interest of stakeholders. 2. The principle of director responsibility: Directors of a corporation shall have a duty of care to use reasonable judgment to define and direct the affairs of the corporation in accordance with the stakeholder enabling principle.
- 6. Stakeholder engagement identifies stakeholders, assesses stakeholder needs, develops stakeholder relations plans and forms alliances with stakeholders. Corporations are often confronted with the difficulty of balancing competing or opposing stakeholder needs or demands. The success of stakeholder engagement is initially dependent upon the quality of stakeholder analysis Stakeholder engagement is undertaken for numerous reasons which include: • Improved corporate responsibility and financial performance across the globe. •To avoid conflict through negotiation, mediation and collaborative learning. • Development of a shared vision to direct future business decisions and operations. •To innovate through collaboration. Stakeholder engagement involves following steps: 1. Identify stakeholder 2. Establish the goals and objectives of the company for engagement 3. Identify stakeholder needs and interests. 4. Determine the stakeholder engagement strategy. 5. Evaluate outcome and internalize learnings.
- 7. Stakeholder analysis is the identification of a project's/activity’s key stakeholders, an assessment of their interests The underlining factor in the stakeholder concept is that every activity of an organization should be based taking into account the interests of all the stakeholders. A major reason for increasing adoption of a Stakeholder Concept in setting business objectives is the recognition that businesses are affected by the "environment Doing a stakeholder analysis can: — draw out the interests of stakeholders in relation to the problems which the project is seeking to address (at the identification stage) or the purpose of the project (once it has started). — identify conflicts of interests between stakeholders, — help to identify relations between stakeholders which can be built upon, and may enable establish synergies — help to assess the appropriate type of participation by different stakeholders
- 8. • Experts, such as academics, who have been invited to contribute knowledge and strategic advice to the company’s board; • Technical advisors with expertise on the social and environmental risks associated with particular Representatives of special interests, such as employees, local communities or the environment, commonly invited to participate in stakeholder panels to review company performance and/or reporting practices; • Co-implementers, such as NGOs, who have partnered with the company to implement a joint solution or program to address a shared challenge; TYPES OF STAKEHOLDERS Primary stakeholders are those whose continued association is absolutely necessary for a firm’s survival; these include employees, customers, investors, and shareholders, as well as the governments and communities that provide necessary infrastructure. Secondary stakeholders do not typically engage in transactions with a company and thus are not essential for its survival; these include the media, trade associations, and special interest groups
- 9. The Caux RoundTable (CRT) is based on the belief that the world business community should play an important role in improving economic and social conditions. The CRT Principles for Business were formally launched in 1994, and presented at the United NationsWorld Summit on Social Development in 1995. The Caux RoundTable was founded in 1986 by Frederick Phillips,
- 10. Section 1. Preamble The mobility of employment, capital, products and technology is making business increasingly global in its transactions and its effects. Law and market forces are necessary but insufficient guides for conduct. Responsibility for the policies and actions of business and respect for the dignity and interests of its stakeholders are fundamental. Shared values, including a commitment to shared prosperity, are as important for a global community as for communities of smaller scale. Section 2. General Principles Principle 1.The Responsibilities of Businesses: Beyond Shareholders toward Stakeholders The value of a business to society is the wealth and employment it creates and the marketable products and services it provides to consumers at a reasonable price commensurate with quality. Principle 2.The Economic and Social Impact of Business Principle 3. Business Behavior Principle 4. Respect for Rules In addition, they should recognize that some behavior, although legal, may still have adverse consequences. Principle 5. Support for MultilateralTrade Principle 6. Respect for the Environment A business should protect and, where possible, improve the environment, promote sustainable development, and prevent the wasteful use of natural resources. Principle 7. Avoidance of Illicit Operations A business should not participate in or condone bribery, money laundering, or other corrupt practices: indeed, it should seek cooperation with others to eliminate them
- 11. Max Clarkson (1922-1998) founded the Centre for Corporate Social Performance and Ethics in the Faculty of Management, now the Clarkson Centre for Business Ethics & Board Effectiveness, or CC(BE) 2. The Clarkson Principles emerged from a project undertaken by the Centre for Corporate Social Performance and Ethics : Principle 1: Managers should acknowledge and actively monitor the concerns of all legitimate stakeholders, and should take their interests appropriately into account in decision-making and operations. Principle 2: Managers should listen to and openly communicate with stakeholders about their respective concerns and contributions, and about the risks that they assume because of their involvement with the corporation. Principle 3: Managers should adopt processes and modes of behavior that are sensitive to the concerns and capabilities of each stakeholder constituency Principle 4: Managers should recognize the interdependence of efforts and rewards among stakeholders, and should attempt to achieve a fair distribution of the benefits and burdens of corporate activity among them, taking into account their respective risks and vulnerabilities. Principle 5: Managers should work cooperatively with other entities, both public and private, to insure that risks and harms arising from corporate activities are minimized and, where they cannot be avoided, appropriately compensated. Principle 6: Managers should avoid altogether activities that might jeopardize inalienable human rights (e.g., the right to life) or give rise to risks which, if clearly understood, would be patently unacceptable to relevant stakeholders. Principle 7: Managers should acknowledge the potential conflicts between (a) their own role as corporate stakeholders, and (b) their legal and moral responsibilities for the interests of all stakeholders, and should address such conflicts
- 12. Section 3. Customers All customers should be treated with dignity, irrespective of whether they purchase our products and services directly from us or otherwise acquire them in the market. Therefore there is a responsibility to: — provide customers with the highest quality products and services consistent with their requirements; — treat customers fairly in all aspects of our business transactions, including a — high level of service and remedies for their dissatisfaction; — make every effort to ensure that the health and safety of customers, as well as the quality of their environment, will be sustained or enhanced by the products and services; — assure respect for human dignity in products offered, marketing and advertising; — and respect the integrity of the culture of customers. Employees Dignity of every employee and in taking employee interests seriously. Therefore there is a responsibility to: — provide jobs and compensation that improve workers' living conditionskeholder Principles provide working conditions that respect each employee's health and dignity; — be honest in communications with employees and open in sharing information, — limited only by legal and competitive constraints; — listen to and, where possible, act on employee suggestions, ideas, requests and complaints; — engage in good faith negotiations when conflict arises; — avoid discriminatory practices and guarantee equal treatment and opportunity in areas such as gender, age, race, and religion; — promote in the business itself the employment of differently-abled people in places of work where they can be genuinely useful; — protect employees from avoidable injury and illness in the workplace; — encourage and assist employees in developing relevant and transferable skills and knowledge; and
- 13. Owners/Investors Honoring the trust of investors.Therefore there is a responsibility to: — apply professional and diligent management in order to secure a fair and competitive return on the owners' investment; — disclose relevant information to owners/investors subject to legal requirements and competitive constraints; — conserve, protect, and increase the owners/investors' assets; and — respect owners/investors' requests, suggestions, complaints, and formal resolutions. Suppliers The relationship with suppliers and subcontractors must be based on mutual respect.Therefore there is a responsibility to : — seek fairness and truthfulness in all activities, including pricing, licensing, and rights to sell; — ensure that business activities are free from coercion and unnecessary litigation; — foster long-term stability in the supplier relationship in return for value, quality, competitiveness and reliability; — share information with suppliers and integrate them into planning processes; — pay suppliers on time and in accordance with agreed terms of trade; and — seek, encourage and prefer suppliers and subcontractors whose employment practices respect human dignity. Competitors Fair economic competition is one of the basic requirements for increasing the wealth of nations and ultimately for making possible the just distribution of goods and services
- 14. — foster open markets for trade and investment; — promote competitive behavior that is socially and environmentally beneficial and demonstrates mutual respect among competitors; — refrain from either seeking or participating in questionable payments or favors to secure competitive advantages; — respect both tangible and intellectual property rights; and — refuse to acquire commercial information by dishonest or unethical means, such as industrial espionage. Communities As global corporate citizens companies can contribute to such forces of reform and human rights as are at work in the communities in which corporates operate.Therefore they have a responsibility in those communities to: — respect human rights and democratic institutions, and promote them wherever practicable; — recognize government's legitimate obligation to the society at large and support public policies and practices that promote human development through harmonious relations between business and other segments of society; — collaborate with those forces in the community dedicated to raising standards of health, education, workplace safety and economic well-being; — promote and stimulate sustainable development and play a leading role in preserving and enhancing the physical environment and conserving the earth's resources; — support peace, security, diversity and social integration; — respect the integrity of local cultures; and — be a good corporate citizen through charitable donations, educational and cultural contributions, and employee participation in community and civic affairs.
- 15. EMPLOYEES Employee participation in corporate governance systems can be found in many countries and corporations throughout the world • Right to consultation - where employees must be consulted on certain management decisions.This right increases transparency of management decisions and allows employee opinion to ameliorate the asymmetry of information between management and the market. • Right to nominate/vote for supervisory board members - In many cases employee participation on the board is mandated. • Compensation/privatization programs that make employees holders of shares, thereby empowering employees to elect the board members, which, in turn holds management responsible
- 16. CUSTOMERS Customer satisfaction is one of the most important aspects of firm performance. In today’s global environment, customers have innumerable choices.Therefore, corporates need to establish a differentiation.Customers are also driving corporates to consider environmental factors in designing the products and services. Over and above this, the customers consider the reputation which a corporate builds.The trust and loyalty that an organization earns is based on its successful delivery over a long period of time. Governance plays a big role in improving the relation between the organization and the
- 17. LENDERS Lenders are the one providing financial stability to the organisation by way of loans, overdraft facility etc. It includes banks/lending institutions Lenders like shareholders provide the capital for a company. Lenders may include covenants relating to environment and sustainability. VENDORS Vendors play a key role in the success of an organisation. The organisation which builds a mutually strong relationship with its vendors improves its overall performance in the marketplace. The time, money and energy used to nurture a positive vendor relationship cannot be measured directly against the company's bottom line. A proper systematic approach of vendor management will benefits all the employees, organisation, customer and vendors.
- 18. I M POSSIBLE 1 I M POSSIBLE Bibek Prajapati (FCMA, CS , MBA, M COM, ). My kind request for you Please like , subscribe ,comment and don’t forget to share Pray to God for the success in Life Thank You