Gsm (Part 1)
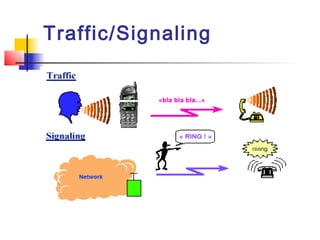
- 2. Traffic/Signaling The network can carry two types of information: Traffic: it concerns all the «user to user» information. It can be voice as well as data. Signaling: the network also requires to carry information for its own working. Their purposes are numerous: traffic data routing, maintenance, security... These data are usually not visible from user’s point of view.
- 3. Before GSM: Mobile Telephony Milestones
- 4. Before GSM: Mobile Telephony Milestones 1876: The telephone was introduced to the public at the Centennial Exposition of the United States in Philadelphia. Alexander Graham Bell was able to transmit speech electrically, in one direction only, over a copper wire circuit of several hundred feet in length. This “speaking telegraph” was quickly perfected for adequate two-way communication and was offered for business and residential service the following years. Within a short time there were thousands, then tens of thousand, and soon hundreds of thousand of paying customers. End of the 19th century: While the struggle to search for the ways to utilize the copper wire transmission facility more and more efficiently, a young German scientist named Heinrich Rudolf Hertz discovered a strange and wonderful phenomenon: from an electric spark there seemed to emanate invisible waves of force which could be captured at a distant location by a suitably constructed receiving device. Hertz’s own experiments extended only a few yards. 1897: Guglielmo Marconi shows the first wireless transmission over 15 km in Bristol. A few years later(1901), G. Marconi transmitted these waves overseas, and began to call it Radio.
- 5. Before GSM: Mobile Telephony Milestones 1946: The first public mobile telephone service was introduced in twenty five American cities. Each system used a single, high-powered transmitter and large tower in order to cover distances of over 50 km in a particular market. Nevertheless these early FM push-to-talk telephone systems of the late 1940s used 120 kHz of RF bandwidth in a half duplex mode (only one person on the telephone call could talk at a time), even though the actual telephone-grade speech because of the kHz of baseband spectrum. The large RF bandwidth was needed because of the difficulty in mass producing tight RF filters and low- noise, front-end receiver amplifiers. 1970: A.Pinet introduced in France the first digital switch. 1982: The first commercial cellular system was turned on in Chicago. 1992: GSM, the first fully digital cellular system, was introduced on in Germany and in France.
- 6. Analog Cellular Systems Around the World
- 7. Analog Cellular Systems Around the World There are several different types of analog cellular systems: NMT450 and NMT900: Scandinavia, Benelux, Spain, Austria, France, Switzerland AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System ) in more 34 countries: U.S.A., Canada, Argentine, Chile, Indonesia, Brazil Australia, Republic of Congo TACS (Total Access Communication System) in UK Ireland and Italy R2000: France C450: Germany NTT (1979) cellular and JTACS (1988) in Japan RTMS: Italy.
- 8. AMPS AMPS is a first-generation cellular technology This cellular service operates in the 800 MHz Cellular FM band. For each market area Its is the analog mobile phone system standard developed by Bell Labs, and officially introduced in the Americas in 1983 and Australia in 1987 As of February 18, 2008, Carriers in the United States were no longer required to support AMPS and companies such as AT&T and Verizon have discontinued this service permanently. AMPS was discontinued in Australia in September 2000
- 9. AMPS AMPS pioneers fathered the term "cellular" because of its use of small hexagonal "cells" within a system. This allowed a larger number of phones to be supported over a geographical area It suffered from some weaknesses when compared to today's digital technologies Very susceptible to static and noise No protection from eavesdropping Later, many AMPS networks were partially converted to D-AMPS D-AMPS is a digital, 2G standard
- 10. Development of the GSM Standard 1991: First system-trial are running at Telecom 91 exhibition. The GSM Recommendations comprise: 1992: Official commercial launch of GSM service in Europe.
- 11. Development of the GSM Standard 1993: Aside the GSM has 62 members (signatories) in 39 countries worldwide; and in addition 32 potential members (observers, applicants) in 19 other countries. GSM networks are operational in Denmark, Finland, France, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland, United kingdom. The end of 1993 shows one millions subscribers to GSM networks, however more than 80% of them are to be found in Germany alone.
- 12. GSM (short statistics, 2004) No. of Countries/Areas with GSM System: 199 Worldwide GSM Subscribers as at end of 2007 = 2,685,060,046 Ratified Operator and Regulator Members = 585 SMS messages sent per month: 24 Billion GSM accounts for 73 % of the World's digital market and 72% of the World's wireless market
- 13. GSM (statistics, end of 2007)
- 14. GSM Benefits
- 15. GSM Benefits The features and benefits expected in the GSM Superior speech quality (equal to or better than the existing analog cellular technology), Low terminal and services costs, A high level of security (confidentiality and fraud prevention), International roaming (under one subscriber directory number), Support of low power hand-portable terminals, Variety of new services and network facilities.
- 16. GSM Benefits It was a logical consequence of the prevailing reality that a measure of Inter-working compatibility with the services offered by other existing telecommunication networks was sought. In particular, the basis for the services in GSM standard can be found in the ISDN concept.
- 19. Mobile Station
- 20. Mobile Station The Mobile Station (MS) is composed of three parts: The handset includes the radio equipment (receiver-transmitter) and the Man-Machine Interface (MMI), The SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module-card): this smart card allows the identification of any subscriber (not only of his equipment) by the network. In particular, he can borrow any mobile without changing anything from the network point of view since he keeps the same SIM-card, The battery.
- 21. Mobile Station (MS) Mobile Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Removable plastic card Stores Network Specific Data such as list of carrier frequencies and current LAI (Location Area Identifier). Stores International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) + ISDN Stores Personal Identification Number (PIN) & Authentication Keys. Also stores short messages, telephone book etc.
- 22. SIM-Card and GSM Mobile Equipment
- 23. SIM-Card and GSM Mobile Equipment The subscriber is identified within the system when he inserts the SIM-Card in the mobile equipment and switches it on. This provide a considerable amount of flexibility to the subscribers since they can use any GSM- specified mobile equipment. With the SIM-Card the idea of "personal communication" is already realized: the user only needs to take his smart card on a trip. You can rent a mobile equipment unit at the destination, even in other country, and insert your own SIM-Card. Any call you make will be charged to your home GSM account. Also the GSM system is able to reach you at the mobile unit you are currently using.
- 25. The SIM-Card Functions The SIM-Card is a removable smart card, the size of a credit card, and contains an integrated circuit chip with a microprocessor, random access memory, and read-only memory. When a mobile users want to make a call, they insert their SIM-Card and provide their Personal Identity Number (PIN), which is compared with a PIN stored within the SIM-CARD. The PIN can also be permanently bypassed by the subscribers if authorized by the service provider. Disabling the PIN code simplifies the call setup but reduces the protection of the user's account in the event of a stolen SIM-CARD.
- 26. Subscriber Identification The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is the primary identification of the subscriber within the GSM network and is permanently assigned to him. The Mobile Subscriber ISDN Number (MSISDN) is the number that the calling party dials in order to reach the GSM subscriber. It is used by the land networks to route calls toward an appropriate GSM network. MSISDN is stored in HLR.
- 27. GSM Mobile Equipment The Mobile Station (MS ) includes radio equipment and the man machine interface (MMI) that a subscriber needs in order to access the services provided by the GSM network. Mobile Stations can be installed in vehicles or can be portable or hand-held stations. The mobile station includes provisions for data communication as well as voice. Mobile Stations transmit and receive messages to and from the GSM over the air interface to establish and continue connection through the system. Each mobile station has an International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) that is permanently stored in the mobile unit. Upon request, the MS sends this number over the signaling channel to the network. The IMEI is used to identify mobile units that are reported stolen or operating incorrectly.
- 28. Mobile Identification Stored inside the Mobile Equipment. Some time can work without SIM card (example: Emergency calls without SIM-Card) or when required by the network (for maintenance). Can be used for EIR (Equipment Identification Register) database updating (when existing): TAC = 6 digits describing the type of equipment, FAC = 2 digits for identification of the factory, SNR = 6 digits for the serial number of the device. The type of MS must be given to the NSS at the beginning of each new connection, because this type can change between calls. The subscriber may insert this SIM-Card into another Mobile Equipment (ME).
- 29. Trends in Mobile Station Trends for MS are: Hands-free (2 W + booster 5 W). Increasing independence: idle mode: 40 hours to 140 hours, communication mode: 4 hours to 15 hours, Supplementary features (e.g. display of calling number). Additional features (e.g. voice recognition). Connection with terminals for data transmission: Modem on PCMCIA board for Laptop PC. Modem integrated. Dual-band terminal (GSM 900/1800 MHz). Radio organizer (Nokia 9000). Versatile terminal (under JAVA software's): fax, internet, pager, organizer.
- 30. Base Transceiver Station (BTS) One per cell Consists of high speed transmitter and receiver Function of BTS Controls several transmitters Provides two channels Signalling and Data Channel Performs error protection coding for the radio channel
- 31. Base Station Controller (BSC) Controls multiple BTS Functions of BSC Performs radio resource management Assigns and releases frequencies and time slots for all the MSs in its area Reallocation of frequencies among cells Hand over protocol is executed here Time and frequency synchronization signals to BTSs Knows which mobile stations are within the cell and informs the MSC/VLR about this Power Management of BTS and MS know the exact location of a MS before a call is made
- 32. Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) Switching node of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) Allocation of radio resource (RR) Handover Mobility of subscribers Location registration of subscriber There can be several MSCs in a PLMN
- 33. Gateway MSC (GMSC) Connects mobile network to a fixed network Entry point to a PLMN Usually one per PLMN Request routing information from the HLR and routes the connection to the local MSC
- 34. HLR/VLR HLR - Home Location Register For all users registered with the network, HLR keeps user profile MSCs exchange information with HLR When MS registers with a new GMSC, the HLR sends the user profile to the new MSC VLR - Visitor Location Register VLR is responsible for a group of location areas, typically associated with an MSC Contains the location of the active Mobile Stations
- 35. AuC/EIR/OSS AuC: Authentication Center is accessed by HLR to authenticate a user for service Contains authentication and encryption keys for subscribers EIR: Equipment Identity Register International Mobile Station Equipment Identity (IMEI) codes allows stolen or fraudulent mobile stations to be identified Operation subsystem (OSS): Operations and maintenance center (OMC), network management center (NMC), and administration center (ADC) work together to monitor, control, maintain, and manage the network
- 36. GSM identifiers International mobile subscriber identity (IMSI): unique 15 digits assigned by service provider = home country code + home GSM network code + mobile subscriber ID + national mobile subscriber ID International mobile station equipment identity (IMEI): unique 14 digits assigned by equipment manufacturer = type approval code + final assembly code + serial number + spare digit Temporary mobile subscriber identity (TMSI): 32-bit number assigned by VLR to uniquely identify a mobile station within a VLR’s area
- 37. Explosive Growth in Wireless Data
- 38. Motivations Growing demand of data services due to Internet PSTN/ISDN tends to become local islands connected with the IP backbone Solution: To associate the traditional GSM (Circuit switched ) network with Packet switched, all IP network No hardware/software change is requires in BTSs and BSCs. Same radio interface GPRS uses the same Radio Access Network (RAN) as GSM A Packet Control Unit is added to the BSS
- 39. Basic characteristics Using from 1 to 8 time slots on the same carrier max bit rate 171.2 kb/s, 8*21.4 kb/s User charging based on the amount of data transmission … Thus allowing, Always-On-Connections Interact with IP Supports various level of QoS
- 41. Important elements Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) Tracks the location of the MS Provides routing and mobility management Authenticates the MS Manages the session Collects billing data IP packets from the MS are treated as IP packets first time here Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) Connects the GPRS network to other networks, e.g. the Internet GSM VLR and HLR are used
- 42. GPRS Handovers There are no GPRS handovers as such Since there is no circuit to hand over The MS requests a cell reselection and the packets are routed to the new cell Requires dynamic routing
- 43. General Packet Radio Service GPRS is the first major revolution in GSM data, providing speeds over 100 kbit/s on a pseudo-packet switched radio interface and a real packet switched NSS. This will encourage users to connect to high-speed applications across the wireless network and optimizes the network resources for data transmission. There are however some limitations and the first implementations will have mobility constraints. However, it is likely to attract users to internet type services and provides operators with a natural migration path towards 3G systems.
- 44. Universal Mobile Telecommunication System UMTS, or more precisely IMT2000, will at first provide a capacity advantage for wireless data networks that become overcrowded. But it has to provide more than that. The higher data rates will allow applications such as video and multimedia (support 2mb/s). Open architecture will provide a service environment allowing a wide range of services to be developed by operators and service specialists. Total global roaming is one of the objectives of the specifications.
- 45. UMTS Handover Seamless handover between cells of one operator Efficient handover between UMTS and 2nd generation Compatibility with fixed network services ATM an ISDN services GSM services IP based services Facilities for quality of service provision Private and residential operators High spectrum efficiency Asymmetric band usage Reasonable network cost and complexity
- 46. Enhanced Data rate for GSM Evolution GSM Enhanced Data rate for GSM Evolution or EDGE is often referred to in GPRS context as the combination of the two technologies is seen by some groups in the mobile industry as an alternative for UMTS. This makes EDGE an alternative for operators without an UMTS license who wish to offer medium- speed mobile data services. EDGE is being defined for both GPRS and GSM data services. EDGE is a redefinition of the GSM modulation and coding scheme from GMSK to 8-PSK. It gives up to three times higher throughput compared to GSM, using the same bandwidth. This will enable end-user data rates of maximum 48 kbps per Time Slot for GPRS and 28.8 kbps per TS for GSM services. By combining multiple TSs as with GPRS, data rates of 384 kbps can be achieved.