Proximity sensors
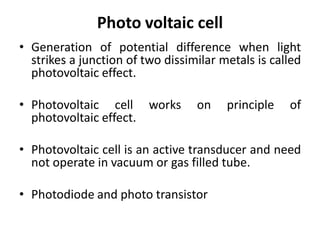
- 1. Photo voltaic cell • Generation of potential difference when light strikes a junction of two dissimilar metals is called photovoltaic effect. • Photovoltaic cell works on principle of photovoltaic effect. • Photovoltaic cell is an active transducer and need not operate in vacuum or gas filled tube. • Photodiode and photo transistor
- 2. Photo diode • The reverse bias is applied against the p-n junction that results in a very high resistance. • The light ray is made to fall on n-layer. • This results in decrease in resistance of the diode, developing the reverse current due to sweep up of the electron-hole pair. • The reverse current is the measure of intensity of the incident radiation. • The response of the photo diode is quick and they can be used as variable resistance devices.
- 3. Photo Transistor • A base collector is arranged in parallel to the photo diode, a bipolar transistor is formed. • In this p-n junction the collector base is photo sensitive. • The incidence radiation on the base results in reverse current of photo diode, which is the base current of the transistor. • The base current is proportional to the intensity of light. • If the base current is amplified by internal signal processing, then the higher sensitivity of the photo transistor can be achieved.
- 4. PROXIMITY SENSORS -Vinayak Kulkarni
- 5. PROXIMITY SENSORS • A proximity sensor detects an objects when the object approaches within the detection range and boundary of the sensor. • Proximity sensors include all sensor that perform non contact detection in comparison to sensors such as limit switch, that detects the object by physically contacting them. • Proximity sensors are used in various facets of manufacturing for detecting the approach of metal and non metal objects.
- 7. Inductive proximity sensors working principle • Inductive proximity sensors detect the presence of metallic objects. • Their operating principle is based on a coil and high frequency oscillator that creates a field in the close surroundings of the sensing surface. The presence of metal in the operating area causes a change in the oscillation amplitude. This change is identified by a threshold circuit, which changes the output of the sensor. The operating distance of the sensor depends on the coil’s size as well as the target’s shape, size and material.
- 8. Inductive proximity sensors • An inductive sensor is an electronic proximity sensor, which detects metallic objects without touching them. • Electric current generates a magnetic field, which collapses generating a current that falls asymptotically toward zero from its initial level when the input electricity ceases.
- 9. Construction • The proximity inductive sensor basically consists of a wound coil located in front of a permanent magnet. • The permanent magnet is encased in a rugged housing. • The change in current in the coil is output through the leads embedded in the resin. • The leads connected to the display through a connector gives signal for the presence of an object in the vicinity.
- 10. Applications • Common applications of inductive sensors include metal detectors, car washes, and a host of automated industrial processes. Because the sensor does not require physical contact it is particularly useful for applications where access presents challenges or where dirt is prevalent. The sensing range is rarely greater than 6 cm, however, and it has no directionality.
- 12. Capacitive proximity sensors working principle • Capacitive sensors are used for non-contact detection of metallic objects & nonmetallic objects (liquid, plastic, wooden materials and so on). Capacitive proximity sensors use the variation of capacitance between the sensor and the object being detected. When the object is at a preset distance from the sensitive side of the sensor, an electronic circuit inside the sensor begins to oscillate. The rise or fall of such oscillation is identified by a threshold circuit that drives an amplifier for the operation of an external load.
- 13. Applications • Capacitive touch sensors are used in many devices such as laptop track pads, digital audio players, computer displays, mobile phones, mobile devices and others. • More and more design engineers are selecting capacitive sensors for their versatility, reliability and robustness and cost reduction over mechanical switches.
- 14. Ultrasonic sensors • Ultrasonic sensors are some times used in place of optical sensors. Instead of using an light beam, a high frequency sound wave is used. • This sound wave is above normal hearing frequencies and are called ultrasonic. Frequencies around 40 KHz are common.
- 15. What does an ultrasonic sensor do? • It emits a short Ultrasonic Pulse ... Sensor
- 16. What does an ultrasonic sensor do? • ...and waits for the echo. Sensor
- 17. What does an ultrasonic sensor do? • It calculates the distance to the object – waiting time – speed of sound Sensor distance = waiting time x speed of sound / 2
- 19. Optical sensor
- 20. Optical sensor • The proximity of the object is detected by the action of the travelling light move. • The light emitted by the transmitter focuses on the object which reflects to be received by the receiver photo diode. • The light from the emitting diode is focused by the transmitter lens, on to the object surface. • The reflected waves travel back and received by the solid state photo diode, through the receiver lens. • The object within the range of the sensor can detect the presence. • The focal length of the sensor lenses decide the range within which the proximity of the object is detected.
- 21. DESIRABLE FEATURES FOR SENSORS AND TRANSDUCER FEATURES FUNCTIONS PRECISION Should be as high as possible Deviation in measurement reading should be minimum. ACCURACY Should be very high Error between sensed and actual value should approach zero. SPEED OF RESPONSE Time taken to respond should be minimum Response should be instantaneous. OPERATING RANGE Wide operating range Good accuracy over the range . RELIABILITY Life to be high Frequent failure are not acceptable. CALIBRATION Drift should be minimum Should be easy to calibrate COST AND EASE The purchase cost should be low The installation and operation should be easy.
