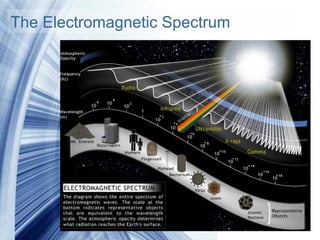
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- 1. The Electromagnetic Spectrum Powerpoint Templates
- 2. Electromagnetic Waves • Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves composed of two oscillating wave fields that vibrate perpendicular to each other – Direction of travel (propagation) on x axis – Electric Field (E) on y axis – Magnetic Field (B) on z axis - Electric Field - Magnetic Field Powerpoint Templates
- 3. Electromagnetic Radiation • Every wave in the electromagnetic spectrum is considered radiation or "radiant energy." – Radiation is energy emitted in the form of a wave as a result of the motion of electric charges. • A moving charge (i.e. electron) gives rise to a magnetic field. • A changing magnetic field creates electricity. • Electromagnetic waves transfer energy as they move through space or a medium Powerpoint Templates
- 4. Sources of Radiant Energy • Electromagnetic radiation is everywhere – in outer space • our sun (and other stars') nuclear fusion reactions – in Earth's atmosphere • radio towers, power lines, radon, radioactive materials – even moving through buildings and bodies • electric devices, microwave ovens, TV signals, medical imaging Powerpoint Templates
- 5. The Study of Light • Particle Theory (Sir Isaac Newton, 1704) – light comes in little packets or individual particles (photons) which are too small to see or distinguish • like a trickle of water is made of millions of individual molecules • Wave Theory (Christian Huygens, late 17th century) – light travels in waves • like an ocean wave or oscillating sound compressions Powerpoint Templates
- 6. Wave–Particle Duality • all light particles also have wave characteristics – Light is made of tiny waves of particles • (Max Planck, Albert Einstein, Louis de Broglie, Arthur Compton, Niels Bohr, and many others) Powerpoint Templates
- 7. Speed of Light • Adam Savage: TedEd video • Speed of light in a vacuum: 299,792,458 m/s – ALL electromagnetic waves travel at ~300,000 km/s when there is no matter present (vacuum) Medium Speed (km/s) Vacuum 300,000 Air 299,700 Liquid water 226,000 Glass 200,000 Diamond 124,000 Powerpoint Templates
- 9. Radio Waves • A radio wave is a low frequency electromagnetic wave used to transmit radio and television signals. – Produced by electrons vibrating in an antenna • Back and forth vibrations, picked up by a receiving antenna, produce an alternating current • Electronic circuitry converts the current into audio or video. Powerpoint Templates
- 10. Radio Frequencies Radio waves have different frequencies; by tuning a radio receiver to a specific frequency you can pick up a specific signal. • Short wave radio - bands from 5.9 megahertz to 26.1 megahertz • Citizens band (CB) radio - 26.96 to 27.41 megahertz • Television stations - 54 to 88 MHz for channels 2 through 6 • FM radio - 88 to 108 MHz • Television stations - 174 to 220 megahertz for channels 7 - 13 • Scanners can switch between a whole range of frequencies, stopping when it detects a signal Radio waves are used in many different types of devices to transmit audio and visual signals. • Garage door openers, alarm systems, etc.: ~ 40 MHz • Cordless phones: 40 - 50 or 900 megahertz • Baby monitors: 49 megahertz • Radio controlled (RC) cars: ~ 75 megahertz • Wildlife tracking collars: 215 to 220 MHz • Cell phones: 824 to 849 megahertz • Air traffic control radar: 960 to 1,215 MHz • GPS: 1,227 and 1,575 MHz • Microwave ovens: 2,450 megahertz (2.45Templates Powerpoint GHz)
- 11. RADAR vs. SONAR • SONAR uses sound waves – SOund Navigation And Ranging – frequencies of 20,000 Hz to 10,000,000 Hz – waves travel at about 343 meters per second in air • RADAR uses radio waves (electromagnetic waves) – RAdio Detecting And Ranging – frequencies of 3,000,000 Hz to 300 billion Hz – waves travel at almost 300 million meters per second in air Which one gives better results? Powerpoint Templates
- 12. Infrared Waves • Invisible to the human eye, IR waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies slightly lower than visible red light. – Near-infrared • closest in wavelength to visible light – used in TV remote-controls – Mid-infrared – Far-infrared • closer in wavelength to microwaves – cause the warmth you feel when basking in the sun – some snakes have thermal infrared vision capabilities – food-heating lamps use far-infrared waves Powerpoint Templates
- 13. Visible Light • Visible light represents only a small portion of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. – X-rays, gamma rays • high-frequency – UV & visible light, infrared radiation • mid-frequency – microwaves, radio waves • very low frequency Powerpoint Templates
- 14. Colors • Different wavelengths of electromagnetic waves produce different colors of visible light Light Wavelength Red 650 nm Orange 590 nm Yellow 570 nm • White light is a mixture of all Green 510 nm frequencies (colors) of light Blue 475 nm Indigo 445 nm Violet 400 nm 1 millimeter = 1,000,000 nanometers Powerpoint Templates
- 15. Ultraviolet Waves • UV waves have frequencies slightly higher than visible violet light. – UV light damages living cells • causes sunburn (penetrate top layer of skin) • used to disinfect surgical equipment – necessary for humans to produce vitamin D • Some substances fluoresce when exposed to UV waves (aka "black light"). – UV tattoos, some minerals, anti-freeze, $20 bill, body fluids, chlorophyll, jellyfish, banana spots Powerpoint Templates
- 16. High Frequency Waves • X Rays & Gamma Rays – Pass through many materials – Cause ionization: • Excite (speed up) the electrons in an atom or molecule to the point that an electron is lost, leaving a positive ion. • Ionization can damage DNA and cause tumors Powerpoint Templates
- 17. X Rays • Many uses: – airport baggage screening – bone density scans – astronomy – archaeology – inspection of manufactured goods • X rays pass through skin/muscle but are reflected by teeth and bones – Can cause cell mutations and/or cancer Powerpoint Templates
- 18. Gamma Rays • Produced by nuclear reactions – Sun's nuclear fusion reactions – Radioactive decay of certain elements – Atomic explosions (nuclear fission) • Only thick layers of lead or concrete can block gamma rays • Very damaging to living cells – Causes burns, mutations and damage to growing tissues – Used to sterilize food & medical equipment – "Radiation Therapy" used to strategically target & kill cancerous tumor cells Powerpoint Templates
Notas do Editor
- What comes to mind when you think of radiation? nuclear power plants...atomic bombs... X-rays?
- What comes to mind when you think of radiation? nuclear power plants...atomic bombs... X-rays? Radon is an invisible, cancer-causing, radioactive gas created during the natural breakdown of uranium in rocks and soils. It's found in nearly all soils. It typically moves up through the ground and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation, although there are other radon sources . Your home traps radon inside, where it can accumulate. Any home can have a radon problem , not just those built on soil and rock types with high geologic potential for radon release.
- pronounced "heirgens"
- pronounced "heirgens"
- You've probably heard about "AM radio" and "FM radio," "VHF" and "UHF" television , "citizens band radio," "short wave radio" and so on. Have you ever wondered what all of those different names really mean? What's the difference between them? In the United States, the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) decides who is able to use which frequencies for which purposes, and it issues licenses to stations for specific frequencies. See How Radio Works for more details on radio waves. When you listen to a radio station and the announcer says, "You are listening to 91.5 FM WRKX The Rock!," what the announcer means is that you are listening to a radio station broadcasting an FM radio signal at a frequency of 91.5 megahertz, with FCC-assigned call letters of WRKX. Megahertz means "millions of cycles per second," so "91.5 megahertz" means that the transmitter at the radio station is oscillating at a frequency of 91,500,000 cycles per second. Your FM (frequency modulated) radio can tune in to that specific frequency and give you clear reception of that station. All FM radio stations transmit in a band of frequencies between 88 megahertz and 108 megahertz. This band of the radio spectrum is used for no other purpose but FM radio broadcasts. In the same way, AM radio is confined to a band from 535 kilohertz to 1,700 kilohertz (kilo meaning "thousands," so 535,000 to 1,700,000 cycles per second). So an AM (amplitude modulated) radio station that says, "This is AM 680 WPTF" means that the radio station is broadcasting an AM radio signal at 680 kilohertz and its FCC-assigned call letters are WPTF.
- FCC monitors and dictates which frequencies are used 1 megahertz = 1,000,000 hertz (million) 1 gigahertz = 1,000,000,000 hertz (billion) 256 hz = middle C AM radio station in the frequency band from 535 kilohertz to 1.7 megahertz
- 1 megahertz = 1,000,000 hertz (million) 1 gigahertz = 1,000,000,000 hertz (billion) 256 hz = middle C
- Fluorescent substances absorb the ultraviolet light and then re-emit it almost instantaneously. Some energy gets lost in the process, so the emitted light has a longer wavelength than the absorbed radiation, which makes this light visible and causes the material to appear to 'glow'. Fluorescent molecules tend to have rigid structures and delocalized electrons.
- They are also used by astronomers - many objects in the universe emit X-rays, which we can detect using suitable radio telescopes. X-Rays can cause cell damage and cancers . This is why Radiographers in hospitals stand behind a shield when they X-ray their patients. Although the dose is not enough to put the patient at risk, they take many images each day and could quickly build up a dangerous dose themselves. Around 200 witch bottles have been found in the past but this is thought to be the first time one with its contents intact has been discovered. Scientists have analysed the contents of the former wine jug after it was discovered by builders redeveloping a site in Greenwich, south east London. They found it contained a number of pins, finger nails and hair as well as a liquid – discovered to be urine. Burial of vessels holding personal items, typically from someone suffering an illness and believing themselves persecuted by a witch, was a common practice in the 17th century. The belief was that the act would reflect the spell back at the witch who would then be forced to relinquish it. The pins and nails were thought to act like pins in voodoo dolls. Analysis of the contents showed the patient was a smoker and probably quite wealthy judging by the length of the finger nails, the researchers told British Archaeology.
