Y8 (s5) programme overview
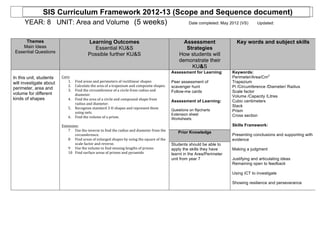
- 1. SIS Curriculum Framework 2012-13 (Scope and Sequence document) YEAR: 8 UNIT: Area and Volume (5 weeks) Date completed: May 2012 (VS) Updated: Themes Learning Outcomes Assessment Key words and subject skills Main Ideas Essential KU&S Strategies Essential Questions Possible further KU&S How students will demonstrate their KU&S Assessment for Learning: Keywords: In this unit, students Core: Perimeter/Area/Cm2 will investigate about 1. Find areas and perimeters of rectilinear shapes Peer assessment of Trapezium 2. Calculate the area of a trapezium and composite shapes. scavenger hunt Pi /Circumference /Diameter/ Radius perimeter, area and 3. Find the circumference of a circle from radius and Follow-me cards Scale factor volume for different diameter. Volume /Capacity /Litres kinds of shapes 4. Find the area of a circle and compound shape from Assessment of Learning: Cubic centimeters radius and diameter. Stack 5. Recognise standard 3-‐D shapes and represent them Questions on flipcharts Prism using nets. Extension sheet Cross section 6. Find the volume of a prism. Worksheets Extension: Skills Framework: 7 Use the inverse to find the radius and diameter from the Prior Knowledge circumference. Presenting conclusions and supporting with 8 Find areas of enlarged shapes by using the square of the evidence scale factor and reverse. Students should be able to 9 Use the volume to find missing lengths of prisms apply the skills they have Making a judgment 10 Find surface areas of prisms and pyramids learnt in the Area/Perimeter unit from year 7 Justifying and articulating ideas Remaining open to feedback Using ICT to investigate Showing resilience and perseverance
- 2. Learning Themes Development Resources Objectives Main Ideas Essential Questions 1. 1. Find areas and Students re-cap area and Follow-me cards WS11 -‐ (30 mins) perimeters of rectilinear perimeter of rectangles, These can be used as either a whole class activity Area_and_Perimeter_Fo shapes squares and triangles. or making a physical loop in pairs. llow_Me_Cards 2. 1. Find areas and To solve problems involving Starter problems Flipchart: (20 mins perimeters of rectilinear area and perimeter See flipchart. Pick and choose as appropriate FC1 - 3 Tasks shapes each) Task 1: Find rectangles with the same area as perimeter
- 3. Task 2: Find shapes with the same perimeter Task 3: Find the area of a compound shape using subtraction 3a. 2. Calculate the area of a Students can estimate areas of Area of a trapezium, Irregular shapes Worksheet: (1 hour) trapezium and irregular shapes WS1 -‐ Estimate Area of composite shapes. Students are given a worksheet and some bold a TRAPEZIUM squared paper. They can overlay the worksheet and count squares/half-squares to give a rough Flipchart: answer FC1 - Estimating Explain task to students. irregular areas Extension – if they appear to already know a formula, have them work out the areas and compare/discuss with those who are estimating. Can they explain the formula? Or derive it? Pathway A – no, add build on task Pathway B – keep task Link to others 10 ticks worksheet Add CFW’s task
- 4. 3b. 2. Calculate the area of a Students are able to see how All about trapeziums Flipchart: (1 hour) trapezium and the formula is derived, and FC2 - All about composite shapes. hence calculate the area of a Students should work in groups of three for the Trapeziums trapezium. main part of the lesson. All students are responsible for the work, but the following tasks FC3 - Proofs In groups, student think about could be assigned: FC4 – creating shapes how they can use what they with fixed area already know to help them find • Recorder: Records all important information on the the area. They are then record sheet. prompted, if required, to • Measurer: Double checks all measurements and calculations. consider methods to formalize • Reporter: Shares all pertinent information with the the derivation. class (Flipchart page 1) These roles are important because they hold each student in the group accountable. Teacher displays page 2 of flipchart, a standard trapezium. Students are then asked to find a “method’ for finding the area. Work your way through the images and ideas on the chart – using it as little as possible so that the students are not being too guided. Let them come up with their own ideas. Prompt Q: “What other shaped could help you?” Extension: the more algebraically able students would benefit from considering more than one deconstruction method – some images are shown on pageof the flip chart. Can they make up their own? To conclude: students can now work out the areas on the original sheet, and compare their estimates. Alternative (Pathway A) Getting students to prove the formula for the area of parallelogram, kite and trapezium
- 5. 4 1. Find areas and Building spreadsheet using ICT Tasks Student (1 hour – perimeters of rectilinear simple formulae Task 1 1 – Paper size shapes each task) 5. Recognise standard 3-‐D Paper sizes template shapes and represent Working out the ratio of different paper sizes and to 2 – Surface area them using nets. realize that the sum of all paper sizes equal to the template 6. Find the volume of a orginal size A0 3 – Volume template prism. Task 2 Teachers 9 Use the volume to find missing lengths of Surface Area investigation FC1 – ICT tasks prisms To calculate the maximum surface area 1 – Paper size solution 10 Find surface areas of 2 – Surface area prisms and pyramids Task 3 solution Using surface area to calculate the maximum 3 – Volume solution volume 5a. 3. Find the circumference Measure the circumference Apple Pi (1) Resources: (1 hour) of a circle from radius and diameter of various (Students should be asked to bring in flat Lengths of string (long) and diameter. circular objects circular, or cylindrical objects prior to the Circular objects to be lesson) measured Calculate the ratio of Warm-up: Ask students to measure width and Calculators circumference to diameter length of their desks. Then ask them to work out Rulers the distance around it. Discover the formula for the Q: What unit did you use? Why? Worksheet: circumference of a circle Why did some measurements differ? What do we WS1 - Apple Pi call this measurement? (for gentle sets) Recording Discovery by measuring & Main Part: Divide into groups of 4, each with a Flipchart: pattern spotting in order to main role: FC1 - Apple Pi determine relationships. • Task Leader: Ensures all students are participating; Link: lets the teacher know if the group needs help or has NCTM site a question. (includes some • Recorder: Keeps group copy of measurements and calculations from activity. thoughts on discussion • Measurer: Measures items (although all students Qs) should check measurements to ensure accuracy). • Presenter: Presents the group’s findings and ideas to the class. (On Flipchart) Students should measure the "distance around" and the "distance across" of the objects that they brought to school. Students should be allowed to
- 6. select which unit of measurement to use. However, instruct students to use the same unit for the distance around and the distance across. The recorder put the information on the Apple Pi worksheet and the team works out the last column. Discuss with class (on the flip chart). Compare averages. Discussion Questions: - Why did we use the ratio of circumference to diameter for several objects? Wouldn’t we have gotten the same result using just one object? - Were any of the ratios in the last column not close to 3.14? If not, explain what might have happened. - Describe some situations in which knowing the circumference (and how to calculate it) would be useful Extension: Have students plot the diameter of those objects along the horizontal axis of a graph and plot the circumference along the vertical axis. Consider line of best fit and the gradient….. Conclusion: Questions on flipchart to assist assessment. Pathway B – keep, good 5b. 3. Find the circumference Measure the radius and Apple Pi (2) Resources: (1 hour) of a circle from radius diameter of various circular Circular objects and diameter. objects using appropriate units Starter: Estimate the area of the circular objects Calculators 4. Find the area of a circle of measurement that they have brought to class. Using the Scissors and compound shape worksheet, students should individually complete Compasses from radius and Discover the formula for the the first two columns. (Differentiated methods Rulers diameter. shown on Flip if req’d) Centimeter grid paper
- 7. area of a circle Blank A4 Main Part: Students cut a circle template into Estimate the area of circles sectors (or construct on blank A4 if more able) and Worksheets: using alternative methods use to gradually form an approx. parallelogram – WS2 - Areas of follow flip chart. (read through before to plan Circular things how much you’ll use it – the more able may not WS3 – Circle template need guiding quite so much) WS6 – 10cm circle Discovery by measuring & Arrive at formula for Area of Circ pattern spotting in order to Link: determine relationships. Discussion Questions (on flip): NCTM site (Includes some - In your opinion, why did we use the properties of a thoughts on discussion parallelogram to discover the area formula for circles? Qs) -When would it be necessary to know the exact area of a circle? When would an estimate be sufficient? Explain your thinking. - Why did we approximate our answers for area? Can the area of a circle ever be exact? - Conclusion: Questions on flipchar 5c. 3. Find the circumference Students will discover a Square circles Worksheet: (1 hour) of a circle from radius relationship between the (alternative to Apple pi 1) WS4 - Square Circles and diameter. diameter of a circle and it’s WS5 – pi investigation 4. Find the area of a circle circumference To begin: using rulers, students complete the info Flipchart: and compound shape for squares on the worksheet. FC2 - Square circles from radius and Identify various units of measure diameter. based on their appropriateness for Then ask them to do the same for the circles, this Materials: each shape and size. will prompt a discussion on how to measure Counters Draw conclusions about the circumference…. Coins relationship of side/perimeter in Paperclips squares and diameter/circumference Practical: M&Ms if you wish in circles based on collected data. Hand out alternative units of measure to be used (M&Ms, String paper clips, coins, identical beads, etc.). Be sure there are Through physical representations, enough. You may wish to discuss how each unit of measure develop the idea of a constant that can be used, or you may prefer that the students discover relates a circle’s diameter and this on their own. FLIPCHART shows how this could be circumference, namely pi. done. The teacher can also discuss with students how they may have to estimate portions of a unit if the measure is not exactly an integer. Allow students to find a second measure of the squares and both measures of the circles using at least one non-traditional unit of measure.
- 8. Collecting data: Once students have filled in the activity sheet, the teacher records sample on flipchart. (or on own copies of ‘What changes?’ worksheet). At this point, the teacher should lead the students into identifying a relationship between a square’s perimeter and its side. Many students will know that Perimeter = 4 × Side, or P = 4s, but try to get students to think of the 4 as a constant that is equal to P ÷ s. It is important for students to see that this relationship is the same regardless of the square’s size or unit of measure, which makes it a "constant." A discussion of constant versus variable may be necessary here. Same is done for circles leading to the discover of a constant(Pi) Assessment: Student to write a paragraph about what they discovered today – allow opportunity to share. In pairs, students find circles around school and challenge each other to find the circumference. Confirm by measuring with string? Problem at end of flipchart to consider. 6. (1 hour) 3. Find the circumference Students demonstrate that 3 in a row game Worksheet: of a circle from radius they can calculate area and WS1 – 3 in a row and diameter. circumference of circles, given Page 1 of worksheet is the Game Board (Game board and 4. Find the area of a circle a radius or diameter. Page 2 is to be cut up in to playing cards cards needed for each and compound shape Page 3 are answers pair) from radius and Game format. Students are diameter. given ‘answers’ and asked to Game: Playing card are shuffled face down. In fit them to the correct circle pairs, students take it in turns to pick a card from the pile and cover up the relevant circle on the board. If they can’t find a match, the card goes on the bottom of the pile. The aim is to get three in a row to win. Ext: Impose a time limit, controlled by the teacher. No calculator, practice estimation 7. (1 hour) Extension Students solve complex Extension Tasks - Circles Worksheet: 7. Use the inverse to find problems involving the area WS1 – answer sheet to the radius and diameter from the circumference. and perimeter of circles Task 1: Compound Shapes circle problems Let the students do these without instruction and WS2 – Compound see how they problem solving- asking questions of shapes them. Some could share solutions.
- 9. Flipchart: FC1 – Problems Task 2: Nrich Problems FC2 – Nrich problems Flip chart (links embedded) & worksheet. PP1 – Circle problems These are quite challenging!! 8a. Identify the names of three The Hunt for 3D Shapes Worksheets: (1 hour) 5. Recognise standard 3-‐D dimensional geometric shapes (gentle) shapes and represent (cube, rectangular solid, square Pathway C them using nets. Warm-up WS1 - Scavenger Hunt pyramid, prism,sphere, cone and Brainstorm the names of all the 3D shapes they WS2 - Scavenger Hunt cylinder). know- ensure all are written on IWB. Peer assessment Identify the number of faces, edges and vertices. Scavenger Hunt: In groups of 4-6, issue Assignment worksheets. Group members should Find 3D objects in real life and share our ‘shapes’ then follow instructions on the describe them. sheet. Students engage in a team Presentations: to the rest of the group. Peer hunt to identify common 3D assessment sheets available. objects and explain properties. 8b. 5. Recognise standard 3-‐D Students understand the Riddle me this Worksheet: (1 hour) shapes and represent properties of 3D shapes (gentle) WS3 - Riddle me this them using nets. Pathway C Go through examples on the worksheet. Note that Riddle describing a shape the first two lines describe the shape and the next two, how it moves. Give students a while to compose their riddle then collect them in. Share out randomly in order to challenge others in the class. 8c. 5. Recognise standard 3-‐D Students understand that 3D 3D shapes Resources: (1 hour) shapes and represent shapes can be constructed from Printed nets (selection them using nets. 2D nets Task: NETS on links below) Students come into the class where there are A4 Squared paper Exploration lesson where coloured printed sheets, scissors and tape on each Isometric paper Extension students are provided with a grouped table. No intro, the teacher just says, “Ok! Scissors variety of nets and just ‘left to Let’s see what you can make me!” tape 10. Find surface areas of prisms and pyramids it’ Be prepared with challenging platonic solids and Links: be ready to assist/pair up those who are struggling. Applet 2D to 3D Discuss, comment and classify. Encourage Printables
- 10. students to walk around and see what other have made, and to ask questions. Extension nets to print Extension: Students set each other problems from, “Make a cube with edge 3 cm” to “Make me a 4 cm square based pyramid with height on 5 cm” 9. (1 hour) 6. Find the volume of a Roughly estimate the Filling Boxes! Folding Boxes! Links: prism. volume/capacity of everyday Cubes applet objects Warm up- What is my VOLUME? Estimation task. Discuss and deal with any Flipchart: Understand how to calculate misunderstandings. FC1 - Estimating the volume of a cuboid Volume Project on IWB – cubes applet and familiarize Understand ho doubling length studetns with how if works (if necessary) Resources: will increase the volume by a cm2 cubes (or factor of 8. Activity1: Following the ‘Filling Boxes worksheet, multilinks) students use cm cube to assist them in answering 8.5 x 11” paper – 2 per Understand and apply the the questions. Be sure to place enough centimeter student. formula for the volume of a cubes that students can measure the length, width, cuboid and height of their prisms, but not so many that Worksheets: they can completely fill their prisms. WS1 - Filling Boxes Use origami to create a three- WS2 - Folding dimensional prism from a two- Activity 2: Have students make the origami cuboid instructions dimensional sheet of paper – according to written instructions. Ready –made find the volume. models may help. Assign groups carefully so that you have one spatially aware student in each. Discussion: How can the volume can be determined without completely filling the cuboid with cubes? Summarize: Key concepts at the end of class. Ask volunteers to explain how they approximated the volume of the box using centimeter cubes. The first two rows from the table in Question 2 will reinforce the concept that doubling all three dimensions will result in a box with a volume that is eight times as large.
- 11. Extensions: Show symbolically that when the dimensions of a prism are doubled, the volume of the new box will be eight times as large as the original box. Students research another mathematical origami model that is not a rectangular prism and share it with the class. Explore the surface area of rectangular prisms, take special notice of how surface area changes as the dimensions of a prism change 10. (1 hour) Extension Students will understand and Scaling up Materials: 8. Find areas of enlarged use the relationship between (student to bring in a common cuboid or Common rectangular shapes by using the square of the scale length, area and volume of cylindrical object- have a few spares) or cylindrical objects factor and reverse. similar figures. (cereal box, soda can, Activity: Brief discussion of scale factor and what pack of gum) Using a rectangle. Students it means. Expand if necessary. (englrmt done in Rulers or tape will individually investigate the prev unit) measures effect of increasing length by a scale factor on area and Page two asks the students to visualize an Flipchart: volume. enlarged version of their object and think about the FC1 - Scaling Up area and volume. Worksheet: WS1 - Scaling up Page three sets them the challenge of investigating what happens if it is enlarged by a factor of 3. Link: Class should discuss their predictions before being Alternative task-nrich encouraged to perform calculations to support their investigation. Other scale factors should then be investigated. A scaffolded investigation is provided on worksheet ‘scaling up’. As students discover this relationship, they will understand the effects of scale factors on volume and surface area. More importantly, they will begin to develop an understanding of why
- 12. square units are used for area and why cube units are used for volume. It is most important for students to discover this relationship on their own. If they cannot write their own conclusion at first, be patient. Exploring the results for other scale factors, hearing about the results of their classmates, and investigating other objects may help students to grasp this important mathematical concept. Assessment: On the last page of the flip chart is a statement. Have students write their response to this, giving example if possible to support their thinking. Extension: (on flipchart) Have students examine cubes with side lengths of 1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm. Compute the surface area of each, and create a graph showing the relationship between side length and surface area. As the side length increases, what happens to the surface area? Does it increase at a constant rate? Describe the shape of the graph. If the side length is n, what is the surface area? Students may also make a similar graph comparing the side length to the volume. If the side length is n, what is the volume? 11a. Extension: Problems solving task ZIN Obelisk Worksheets: 9. Use the volume to find Task: Zin Obelisk WS1 - Zin Obelisk missing lengths of prisms Flip chart has task (nrich link embedded) - you will 10. Find surface areas of need to print off information cards Flipchart: prisms and pyramids FC1 - Zin Obelisk http://nrich.maths.org/5 992
- 13. 11b. Extension: Problem solving tasks for more Nrich extension tasks Flipchart: 7. Use the inverse to find able students Task: Nrich Volume – 4 Qs FC1 - Nrich Volume the radius and diameter from the circumference. Flipchart has nrich links embedded. Worksheet FC2 – Units all in a available jumble 9. Use the volume to find Worksheet: missing lengths of WS1 - Nrich volume prisms WS2 – Nrich problems 10. Find surface areas of WS3 – Cubedcan prisms and pyramids extension WS4 – ATM handout 12 Additional resources WS1 – circumference and area WS2 – circumference and area answers WS2 – Curved surface area and volume of cylinders and answers WS3 – Area and Perimeter Compound Figures WS4 – Area and compound figures