History and properties of viruses
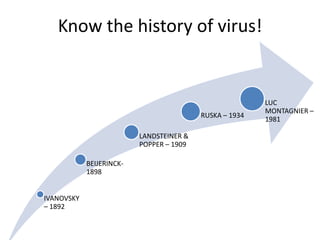
- 1. Know the history of virus! IVANOVSKY – 1892 BEIJERINCK- 1898 LANDSTEINER & POPPER – 1909 RUSKA – 1934 LUC MONTAGNIER – 1981
- 2. • They are obligate intracellular parasites. • Lack cell wall & membrane, metabolism. • Directs host cells to synthesize new virus particles. • Clinical symptoms appears late in course of diseases at a time where most viruses have replicated. (contrast to bacteria). • Responsible for 60% of human diseases. • Has genome (DNA/RNA), enzymes, capsid, envelope (lipid layer). ULTIMATE MICROBES - VIRUS
- 3. ABOUT PATHOGENESIS… 2.Release of viral genes & enzymes. 3.Replication of viral components. 4.Assembly into complete viral particles. 5.Release of viral particles. 1.Attachment to host cell.
- 4. VIEW OF VIRUS & DISEASES. COMMON VIRUSES ITS DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS A,E & B,C. HEPATITIS & CIRRHOSIS. 2. RHINO VIRUS COMMON COLD 3. VARICELLA ZOSTER CHICKEN POX 4. HUMAN IMMUNO DEFICIENCY AIDS 5. INFLUENZA (A) INFLUENZA (BIRD FLU) 6. RUBELLA & PARAMYXO MEASLES & MUMPS 7. HERPES SIMPLEX HERPES SIMPLEX 8. RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL RESPIRATORY INFECTION 9. LYSSA & POLIO RABIES & POLIO 10. ANDES & HANTAAN PULMONARY & RENAL SYNDROME 11. HUMAN HERPES 1 & 2 ORAL & GENITAL INFECTIONS 12. SUDAN & RESTON HEMORRHAGIC FEVER 13. RHADINO KAPOSI SARCOMA.
- 6. PROPERTIES OF ANTI VIRAL DRUGS:- Key characteristics of antiviral drugs: *Able to enter the cells infected with virus. *Interfere with viral nucleic acid synthesis and/or regulation. *Some agents interfere with ability of virus to bind to cells. *Some agent stimulate body’s immune system. Viruses killed by current antiviral therapy: • cytomegalovirus (CMV) • herpes simplex virus (HSV) • human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) • influenza A (the “flu”) • respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- 7. RECALL THE CLASSIFICATION!!. ANTI – HERPES VIRUS ANTI – INFLUENZA VIRUS NON SELECTIVE ANTI VIRALS *Idoxuridine *Acyclovir *Valacyclovir *Famciclovir *Ganciclovir *Foscarnet *Amantadine *Rimantadine *Oseltamivir *Zanamivir *Ribavirin *Lamivudine *Adefovir dipivoxil *Interferon.
- 8. Continued… ANTI-RETRO VIRALS • STAVUDINE • ABACAVIR • LAMIVUDINE • ZIDOVUDINE • DIDANOSINE Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. • NEVIRAPINE • EFAVIRENZ • DELAVIRDINE Non nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. • NELFINAVIR • INDINAVIR • RITONAVIR • SAQUINAVIR • LOPINAVIR Protease inhibitors.
- 9. ANTI-HERPES -ACYCLOVIR Deoxiguanosine analogue. Inhibits DNA synthesis and viral replication. Active only against herpes group of viruses. Acyclovir is taken up by virus infected cells. PK: Attains good CSF concentration. Penetrates cornea well. Plasma t ½:- 2-3 hours. Excreted unchanged in urine.
- 10. USES OF ACYCLOVIR GENITAL HERPES SIMPLEX TYPE 2 PRIMARY DISEASE (TOPICAL & ORAL) - RECURRENT DISEASE(I.V.) - 6 TIMES/DAY X 10 DAYS 400mg/TDS X 10 DAYS 5mg/kg(1 hr.) rep. 8hrly x 10D MUCOCUTANEOUS HERPES SIMPLEX- TYPE 1 LOCALISED TO LIPS & GUMS. ORAL/I.V. ACYCLOVIR 15mg/kg/day x 7 DAYS HERPES SIMPLEX ENCEPHALITIS-TYPE 1 EARLY TREATMENT IS EFFECTIVE.(I.V.) 20mg/kg/8hr. X 10 days HERPES SIMPLEX KERATITIS – TYPE 1 EFFECTIVE IN SUPERFICIAL DENDRITIC CORNEAL ULCER – EYE OINTMENT 5 TIMES DAILY X 3 DAYS HERPES ZOSTER HIGHER DOSES REQUIRED. I.V./ORAL 10 mg/kg/8hr. X 7 DAYS 800 mg (5times daily) CHICKEN POX REDUCES FEVER,ERUPTION. HASTENS HEALING &PREVENT VISCERAL COMPLICATIONS. 15 mg/kg/day x 7 DAYS 400mg / q.i.d x 7 DAYS
- 11. ADVERSE EFFECTS: TOPICAL: Stinging & burning sensation after each application. ORAL: Headache, nausea, malaise, some CNS effects. Intravenous: Rashes, sweating, emesis, fall in B.P. Dose dependent decrease in G.F.R – important toxicity. Reversible neurological manifestations- tremors, hallucinations, lethargy, convulsion, coma.(higher doses).
- 12. IDOXURIDINE: • 5iodo 2deoxyuridine. • Thymidine analogue. • Effective against DNA viruses. • Treatment of H.Simplex keratitis, labial & genital herpes. • Not used now. VALACICLOVIR: • Ester prodrug of Aciclovir. • Converted to aciclovir by esterases • Effective in herpes zoster treatment. • Plasma t ½: 3 hrs. • Genital herpes simplex:1 gm bdx10d • Orolabial herpes: 2gm bd x 1 day.
- 13. FAMCICLOVIR:- Ester prodrug of guanine nucleoside analogue. Metabolised to active penciclovir. Active DNA polymerase inhibitor. Used as an alternative to acyclovir in genital herpes & herpes zoster. Side effects: nausea, headache loose motions, itching, rashes & mental confusions. GANCICLOVIR:- Analogue of aciclovir. Active against all herpes viruses. Given I.V., penetrates CSF. Excreted in urine T1/2: 2 to 4 hrs. Used in CMV retinitis. (10mg/kg/day). Side effects:rash, fever, vo mitting, bone marrow depression, neuro psychiatric disturbances. FOSCARNET:- Pyrophosphate derivative. Inhibits viral DNA polymerase & reverse transcriptase. Active against H.Simplex, CMV, HIV. Given I.V., t 1/2:- 4 to 8 hours. Used in CMV retinitis, other CMV infections in AIDS pt Side effects: anemia, phlebitis, trem or, convulsions,damage s kidney.
- 14. ANTI-INFLUENZA VIRUS DRUGS – AMANTADINE: Inhibits replication(viral uncoating) of influenza A virus. MOA: blocks viral membrane protein M2 which functions as channel for H2 ion. (this channel is required for fusion of viral membrane with cell membrane) PK: Well absorbed orally, penetrates CNS, eliminated in urine. Plasma t ½ : 16 hrs. RESISTANCE: Due to mutation in the M2 matrix protein. ADVERSE EFFECTS: Insomnia, dizziness, ataxia, nausea, anorexia, ankle edema. It is embryo toxic. Rimantadine t ½ is 30 hrs.(long acting).
- 15. USES OF AMANTADINE: Prophylaxis of influenza A2. Treatment of influenza A2.(5 days treatment). In parkinsonism: Acts on NMDA type of glutamate receptors, by promoting pre-synaptic synthesis & release of DA in brain. Dose:100mg B.D(lasts 12 hrs.) SIDE EFFECTS: Livedo reticularis(due to release of CA resulting in vasoconstriction) Ankle edema.
- 16. OSELTAMIVIR-TAMIFLU Sialic acid analogues, inhibits viral neuraminidase enzyme. Has broad spectrum activity against influenza A & B. In liver hydrolysed to active form oseltemavir carboxylate. Active orally . t ½ 6-10 hrs. , eliminated in urine. Side effects –nausea, headache, diarrhoea, cough, g.i. irritation, insomnia. Resistance occurs by mutation of neuraminidase. ZANAMIVIR-RELENZA Sialic acid analogue, inhibits viral neuraminidase enzyme. Against influenza A & B, avian influenza. Administered intra- nasally(inhaled). T ½ 2-5 hrs. , eliminated in urine. Side effects – induce bronchospasm, headache, di zziness, nausea, rashes. Avoided in asthma & COPD patients.
- 17. NON-SELECTIVE ANTI-VIRALS: RIBAVIRIN: Synthetic guanosine analogue has broad spectrum anti-viral activity, including DNA & RNA virus. Used in treating infant & childrens with RSV infection. Also effective in influenza(A & B), measles, herpes infection & acute hepatitis.{combined with interferon used in chronic hepatitis C infection}. PK: Oral bioavailability is approximately 50%. Absorption is increased when drug is taken with fatty meal. Nebulized ribavirin is used in RSV broncholitis in children. Adverse effects: Dose dependent anemia, elevated bilirubin, hemolysis. Aerosol causes irritation of mucosa & bronchospasm. Contraindicated in pregnancy.(teratogenic effects)
- 18. DOSE: 200mg qid (children 10mg/kg/day) RIBAVIRIN RIBAVIRIN TRI- PHOSPJATE INHIBIT GUANOSINE TRI-PHOSPHATE FORMATION PREVENTS VIRAL mRNA capping BLOCKS RNA DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE
- 19. ADEFOVIR DIPIVOXIL: Nucleotide analogue, active against hepatitis B virus & other DNA viruses. Oral availability is approximately 60%. Plasma t ½ is 7 hrs. , excreted in urine. Dose 10mg/day. ADVERSE EFFECTS: Sore throat, headache , weakness, abdominal pain, flu syndrome, nephrotoxicity(in high doses) . ADEFOVIR MONO- PHOSPHATE ADEFOVIR DI- PHOSPHATE INCORPORATE INTO VIRAL DNA TERMINATION OF FURTHER DNA SYNTHESIS PREVENTS VIRAL REPLICATION MECHANISM
- 20. INTERFERON: Low molecular weight glycoprotein. Only naturally occuring anti-viral. Inhibit many RNA & DNA viruses. Not active orally. Administered s.c. /i.v./i.m Plasma t ½ : 24 hrs.
- 21. CHRONIC HEPATITIS B & C (HBV-DNA DISAPPEARS FROM PLASMA) AIDS RELATED KAPOSI’S SARCOMA. RHINO VIRAL COLD HERPES SIMPLEX, HERPES ZOSTER, CMV INFECTIONS IN IMMUNOCOMPRO MI-SED PATIENTS CONDYLOMA ACUMINATA CAUSED BY PAPILLOMA VIRUS MULTIPLE MYELOMA & CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKAEMIA ADVERSE EFFECTS: FLU-LIKE SYMPTOMS- fatigue, malaise, fever, dizziness, anorexia, aches. Neurotoxicity- tremor, numbness, sleepiness, neuropathy, rarely convulsions. Myelosuppression- neutropenia, thrombocytopenia. Thyroid dysfunction(hypo & hyper). Hypotension, alopecia, transient arrythmia, liver dysfunction.
- 23. :- First anti retro viral is ZIDOVUDINE. DRUGS USED IN POSTPONING COMPLICATION OF AIDS or AIDS RELATED COMPLEX. 1. NRTI’ s 2. NNRTI ‘s 3. PI’ s 4. Entry Inhibitors. 5. Integrase Inhibitors.
- 24. NUCLEOSIDE/ NULEOTIDE REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITORS- zidovudine.. • Thymidine analogue. (azidothymidine) • Zidovudine inhibits viral reverse transcriptase enzyme. • Also gets incorporated into growing viral DNA & terminates chain elongation. Effective only against retroviruses. • PK:- oral bioavailability is 65%. Metabolism by hepatic glucoronidation, plasma t 1/2: 1 hour.
- 25. USES:- In HIV infected persons only in combination with other 2 anti retro virals. o Reduces neurological manifestations and kaposi’s sarcoma. o good choice of post exposure prophylaxis & in pregnancy transmissions. ADVERSE EFFECTS: oAnaemia & neutropaenia are important side effects. oNausea anorexia, headache, insomnia, myalgia, abdominal pain. INTERACTIONS:- oParacetamol increases AZT toxicity oStavudine & zidovudine exhibit mutual antagonism.
- 26. DIDANOSINE STAVUDINE LAMIVUDINE 1. Purine nucleoside analogue. Thymidine analogue. Deoxycytidine anlogue 2.DDL----> DDATP----> Incorporation into viral DNA Inhibit HIV revers transcriptase ---->terminates proviral DNA. Acts same as that of AZT. Terminates synthesis of the pro- viral DNA chain. Inhibits reverse transcriptase & hep.B DNA polymerase. 3. Due to its acid lability, absorption is best at fasting state. Well absorbed orally & rapidly metabolised. Oral bio availability is high. 4. Plasma T ½ :- 1 to 1.5 hrs. Crosses blood brain barrier. Plasma T ½ :- 1.5 hrs. Penetrates blood brain barrier. Plasma T ½ :- 6 to 8 hrs. 5. Used only in combination regimens. 2nd drug to treat HIV-1 infection. Used in combination regimens. Not combined with AZT,due to mutual antagonism Used with other HIV drugs. Frequently used for chronic hepatitis B infection. 6.Diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea, peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis. Peripheral neuropathy, lipodystrophy, rarely pancreatitis. Headache, fatigue, nausea, anorexia, abdominal pain. 7. DOSE- 200 mg BD for > 60 kg b wt.taken 2 hr before meal DOSE- 40 mg Bd for > 60 kg b wt. For HIV- 150 mg BD For chronic hepB- 100mg OD
- 27. ADVERSE EFFECTS Ϫ Guanosine analogue. Ϫ Converted to carbovir triphosphate & then acts. Ϫ Oral bioavailability is 80 %. Eliminated by kidney. Ϫ Plasma t ½ is 1 to 1.5 hrs. Intracellular t ½ is > 12hrs. Ϫ Hypersensitivity reactions like rashes, fever, flu-like symptoms are side effects. Ϫ Exhibit little cross resistance with other NRTI Ϫ DOSE: 300mg BD.
- 28. NON NUCLEOSIDE REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITORS – NEVIRAPINE & EFAVIRENZ. • They are nucleoside unrelated compounds. They directly inhibit HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase. • Viral resistance occurs by point mutations. • They induce CYP 3A4, 2D6 enzymes & enhance their own metabolism • Are indicated in combination regimens for HIV. NEVIRAPINE EFAVIRENZ WELL ABSORBED ORALLY METABOLISED IN LIVER PENETRATES CNS. INCOMPLETE ORAL ABSORPTION METABOLISED IN LIVER PENETRATES CNS. PLASMA T ½ IS – 30 Hrs. DOSE – 200 mg /day. PLASMA T ½ IS – 48 Hrs. DOSE – 600 mg OD on empty stomach. Side effects- rashes, nausea, headache, fever raise in liver enzymes. Side effects – rashes, headache, dizziness, insomnia, neuropsychiatric symptoms.
- 29. PROTEASE INHIBITORS: The structural proteins & enzymes production of the virus involves an aspartic protease enzyme encoded by HIV. This protease enzyme acts at a late step(maturation of new virus particles).RNA genome acquires core protein & genome. The protease inhibitors bind to protease molecule, interfere with its cleaving function. Effective in both newly & chronically infected cells. Salivary protein “secretory leucocyte protease inhibitor” has some anti-HIV activity.(HIV doesn’t spread through saliva). ADVERSE EFFECTS: G.i. intolerance, headache, dizziness, facial & limb tingling, numbness, rashes. Lipodystrophy.(abdominal obesity, buffalo hump, wasting of limbs & face. Dyslipidaemia.(raised triglycerides & cholesterol) Indinavir crystalises in urine- risk of urinary calculi.
- 30. BUFFALO HUMP
- 31. INDINAVIR 800mg TDS • To be taken on empty stomach(g.i. intolerance common). • Excess fluids intake – avoid nephrolithiasis. NELFINAVIR 750mg TDS • Taken with meals. • Side effects include diarrhoea, flatulence. RITONAVIR 600mg BD • Potent protease inhibitor. • Nausea, diarrhoea, fatigue, lipid abnormalities. • Lopinavir – available in combination with RTV.improve bioavailability SAQUINAVIR 1200mg TDS • Hard gel & soft gel capsules available. •Side effects include photosensitivity.
- 32. ANTI-RETRO VIRAL THERAPY: All cases of symptomatic HIV disease – treatment necessary. Asymptomatic HIV disease with CD4 count<200/µl – treatment necessary. Highly active antiretroviral therapy involves combination of 3 or more drugs as indicated.(HAART) ZIDOVUDINE+LAMIVUDINE+NEVIRAPINE ZIDOVUDINE+LAMIVUDINE+LOPINAVIR/RTV ZIDOVUDINE+LAMIVUDINE+NEVIRAPINE LAMIVUDINE+STAVUDINE+EFAVIRENZ LAMIVUDINE+STAVUDINE+NEVIRAPINE LAMIVUDINE+ABACAVIT+NEVIRAPINE LAMIVUDINE+ZIDOVUDINE+INDINAVIR LAMIVUDINE+STAVUDINE+RITONAVIR LAMIVUDINE+ABACAVIR+NELFINAVIR ZIDOVUDINE+LAMIVUDINE+ABACAVIR BASIC(2 DRUG) REGIMEN LOW RISK ZIDOVUDINE 300mg+ LAMIVUDINE 150mg BD X 4WKS EXPANDED(3 DRUG) REGIMEN HIGH RISK ZIDOVUDINE 300mg+LAMIVUDINE 150mg BD X 4 WKS +INDINAVIR 800mg TDS
- 33. Viral Infections IN OBSTETRICS….. AGENTS CAUSING VIRAL INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY:- Rubella, cyto megala virus, herpes simplex, varicella zoster, influenza, mumps, HIV, hepatitis and entero viruses. Incidence of malformations :- THE FETAL DEFECTS:- Cataracts, deafness, CNS defects & Heart defects. Most common fetal viral infection :- cytomegala virus(3rd – 9th week, highly teratogenic) PARVO VIRUS B- 19 :- erythema infectiosum ( 5th disease of childhood). Leads to non immune fetal hydrops. ( 2nd or 3rd trimester). ANTIVIRALS UNSAFE DURING PREGNANCY:- Acyclovir, ganciclovir, Foscarnet, Amantadine, Vidarabine, Interferon-a. ANTI RETRO VIRALS UNSAFE DURING PREGNANCY:- Didanosine, Abacavir, Indinavir, Ritonavir, Efavirenz. 1st TRIMESTER 2nd TRIMESTER 3rd TRIMESTER 50% 20% 7%
- 34. PHARMACO ECONOMICS ACYCLOVIR ACIHERPIN 200mg Rs.60 DIDANOSINE VIROGINE Cap. Rs.42 RITONAVIR RITOMAX Tab. Rs.28 FAMCICLOVIR FAMTREX 250mg Rs.40 GANCICLOVIR GANGUARD 250mg Rs.122 INDINAVIR VIREDIN 400mg Rs.25 INTERFERON SHANFERON 1 vial Rs.810 RIBAVIRIN VIRAZIDE Tab. Rs.56 NELFINAVIR NELVIR Tab. Rs.24 NEVIRAPINE NEVIMUNE 200mg Rs.14 DRUG NAME TRADE NAME DOSE COST