3 bio265 microbial growth instructor dr di bonaventura
- 2. Microbial Growth Increase in number of cells rather than an increase in size Understanding the requirements for microbial growth Allow us determine how to control the growth of microbes Specifically, of those microbes that cause disease and food spoilage
- 3. The Requirements for Growth Physical requirements include Temperature pH Osmotic pressure Microorganisms have physical, chemical, and energy requirements for growth
- 4. Effect of temperature Minimum growth temperature - microbe is able to conduct metabolism Maximum growth temperature – microbe continues to metabolize Optimum growth temperature – highest growth rate Growth rate plotted against temperature Growth of Escherichia coli on nutrient agar at three different temperature
- 5. Categories of microbes based on temperature ranges for growth Human pathogens are mesophiles (Optimum growth temperature is ~ 37C) Effect of temperature
- 6. Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis) likes lower temperatures Lesions are first seen on exterior parts of the body including lips, tongue, and genitalia Variable temperature requirements are seen in certain diseases Chancroids Temperature and bacterial growth
- 7. Temperature and bacterial growth Variable temperature requirements are seen in certain diseases Mycobacterium leprae (the causative agent of leprosy) also likes lower temperatures Leprosy is initially seen on the extremities of the body, like face, ears, hands, feet, and fingers
- 8. Effect of pH Neutrophiles Grow best in a narrow range around neutral pH (pH 6.5-7.5) Acidophiles Grow best in acidic habitats Alkalinophiles Live in alkaline soils and water Most pathogens are neutrophiles Helicobacter pylori (causative agent of gastric ulcers) is not an acidophile but an acid-tolerant (secretes bicarbonate and urease) Vibrio cholerae, the cause of cholera, can thrive at a pH as high as 9.0.
- 9. Effect of Osmotic Pressure Isotonic Hypertonic (plasmolysis) Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted on bacterial cells by their environment Hypotonic: the bacterial cell gains water and swells to the limit of its cell wall Some opportunistic pathogens are facultative halophiles Staphylococcus aureus - colonizes the surface of the skin (salt)
- 10. Chemical Requirements Microorganisms use a variety of chemicals (nutrients) as a source of energy to build organic molecules and cell structures Several core chemicals are required for bacterial growth Chemoheterotrophs, which include pathogenic bacteria, use organic molecules as a source of carbon and energy
- 11. Trace elements or micronutrients are minerals essential for the function of certain enzymes Include copper zinc manganese molybdenum Trace elements and growth factors
- 12. Oxygen Requirements Capnophiles are microbes that require higher concentration of carbon dioxide (3-10%) in addition to low oxygen levels
- 13. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) converts superoxide radicals (O2 -) to molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which is also toxic Catalase converts hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to water and oxygen Catalase test Phagocytic cells use toxic forms of oxygen to kill ingested pathogens Hydrogen peroxide can be used as an antimicrobial agent
- 14. Many of the bacteria that form our normal flora and many pathogens are facultative anaerobes Some pathogens can be obligate anaerobes Gas gangrene is caused by Clostridium perfringens Exposure of this organism to air is a lethal event for the bacterium
- 15. How do we culture microbes? To cultivate (or culture) microorganisms A sample (inoculum) is placed into/on broths (liquid media) and solid media Microorganisms that grow from an inoculum are called a culture Cultures visible on solid media as discrete units are called colonies Petri plate Deeps Slants
- 16. What criteria must a culture medium meet? All nutrients required by bacteria in the specimen including growth factors Sufficient moisture, properly adjusted pH of the medium, oxygen requirements Proper temperature of incubation for growth Sterilization and aseptic techniques are designed to minimize contamination of the specimen
- 17. A chemically defined medium (synthetic medium)
- 18. A complex medium Nutrient broth is the liquid version of the medium - without agar (another example is TSB/TSA: Trypticase soy broth/agar)
- 19. Anaerobic microbial cultures, media, and systems Stab cultures Reducing media are used to culture anaerobes Contain chemicals such as thioglycollate that combines with oxygen and removes it from the medium Anaerobic culture system (anaerobic jar or GasPakTM jar)
- 21. Handling and culturing clinical specimens Clinical specimens are collected to identify a suspected pathogen Specimens often include microorganisms associated with the normal microbiota Suspected pathogen in the clinical specimen must be isolated from the normal microbiota in culture Several techniques can be used to isolate organisms in pure cultures (axenic cultures)
- 22. Handling and culturing clinical specimens Properly collected and labeled placed in sterile containers promptly transported to a clinical laboratory to avoid death of the pathogen minimize the growth of members of the normal microbiota transport media are often used to move specimens from one location to another If clinical specimens are not handled or cultured properly Pathogenic bacteria may be missed or may not survive leading to wrong diagnoses!!!!
- 23. Health care professionals collect specimens according to the CDC - Standard precautions Sterile swabs Needle aspiration Intubation Catheter Clean catch method Sputum (coughing/catheter) Biopsy
- 24. Streak-plate technique of isolation The method of serial dilutions Techniques to isolate microorganisms in pure cultures or axenic cultures Pour-plate/spread-plate techniques of isolation
- 25. Plating serial dilutions of the specimen Pour plate method Spread plate method
- 26. Characteristics of bacterial colonies can help in the process of identification * * * * * * * * Mixed culture Pure culture
- 27. Clinical implications of bacterial growth and culture media Bacteria can be “fastidious” in a laboratory setting, Nesseria gonorrhoeae or Haemophilus influenzae Some cannot be grown on culture media: Mycobacterium leprae (armadillos) or Treponema pallidum (rabbits) Some others are obligate intracellular parasites (chlamydias and richettsias) and require cultures of living cells Chocolate agar used to culture H. influenzae and N. gonorrhoeae Enriched medium
- 28. Enriched, selective, and differential media help establish the presence of pathogens A selective medium contains ingredients that inhibit the growth of some organisms while encouraging the growth of others Sabouraud dextrose agar selects for the growth of fungi while inhibits the growth of bacteria Nutrient agar - pH 7.3 Sabouraud agar - pH 5.6
- 29. Enriched, selective, and differential media help establish the presence of pathogens Blood agar plate (BAP) is an enriched and differential medium, which is usually used to detect hemolytic activity No hemolysis (gamma-hemolysis) Alpha-hemolysis Beta-hemolysis Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus pneumoniae Enterococcus faecalis
- 30. Beta-hemolysis
- 31. Enriched, selective, and differential media help establish the presence of pathogens Many selective media are also differential media
- 33. Enriched, selective, and differential media help establish the presence of pathogens Many selective media are also differential media MSA (Mannitol salt agar) High salt concentration (7.5%) to select for Staphylococcus species while inhibiting the growth of other species Mannitol sugar in MSA helps differentiate Staphylococcus species
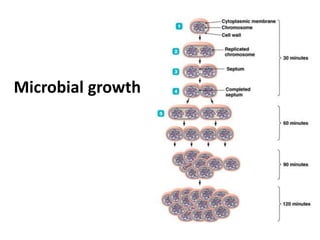
- 34. Bacterial growth by binary fission – asexual reproduction Generation time is the time required for a bacterial cell to grow and divide Under optimal conditions, E. coli or S. aureus have a generation time of ~ 20 min
- 35. Typical microbial growth curve Stationary phase Death (decline) phase Log (exponential) phase Lag phase Time Numberoflivecells(log) When bacteria are grown in a broth, the bacterial growth curve has four distinct phases
- 36. How do we measure microbial growth? Direct Methods • Plate counts* • Filtration* • MPN • Direct microscopic count Indirect Methods • Turbidity* • Metabolic activity • Dry weight Working with clinical specimens can involve quantitative analysis such as assessing a significant bacteriuria - urine samples Assessing effectiveness of disinfectants, antibiotics …… requires quantitative analysis!!!!
- 37. Direct Method: Viable Plate Counts After incubation, count colonies on plates 25 to 250 colonies - CFUs: colony-forming units Serial dilutions of the specimen
- 38. Direct Method Counting Bacteria by Membrane Filtration
- 39. Direct Method: Counting Bacteria by Membrane Filtration Bacteria are filtered out and retained on the surface of the filter The filter is transferred to a culture medium Colonies arise from the bacterial cells on the surface of the filter
- 40. Indirect Methods Turbidity This method uses an instrument called spectrophotometer The amount of light hitting the detector is inversely proportional to the number of bacteria The less light transmitted, the more bacteria in the sample
- 41. Preserving Bacterial Cultures Bacterial cultures are stored by slowing the cell’s metabolism Prevent exhaustion of all nutrients and excessive accumulation of waste products Storage for short period of time Refrigeration (weeks to months) Long-term storage Deep-freezing (years) Lyophilization (freeze-drying) (decades) Involves removing water from a frozen culture using an intense vacuum. Lyophilized cultures are restored by adding them to liquid media
