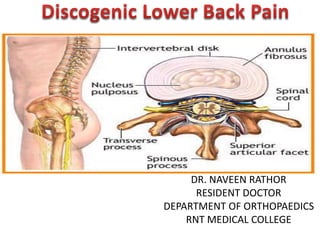
Dr. Naveen Rathor's Guide to Spine Anatomy and Low Back Pain
- 1. DR. NAVEEN RATHOR RESIDENT DOCTOR DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPAEDICS RNT MEDICAL COLLEGE
- 2. Cervical : C1-C7 =7 Sacrum: 5(fused) Coccyx: 4(fused) So there are total 33 vertebrae, but due to fusion of sacral and coccyx there are 26 functional vertebrae. Thoracic: T1-T12 =12 Lumbar: L1- L5 =5 ANATOMY OF THE SPINE
- 3. Cervical Lordosis 20°- 40° Sacral Kyphosis Lumbar Lordosis 30°- 50° Thoracic Kyphosis 20°- 40° Sagittal Plane Curves Adult Spinal Curvature Are Attained After The 10 Yr Converting Spine From a “ C” Shaped To An Irregular “S”-shaped Structure.
- 4. Anatomy Vertebra – Body, anteriorly Functions to Support weight – Vertebral arch, posteriorly Formed by two pedicles and two laminae Functions to protect neural structures
- 5. Vertebral Arch Pedicles (Latin for Little Feet) –Attached anteriorly to body –Continuous posteriorly with laminae –Intervertebral foramen Superior vertebral notch Inferior vertebral notch Laminae (Latin for Thin Plates) –Meet posteriorly to form spinous process. –Both pedicle and laminae meet to forms vertebral foramen which protect spinal cord.
- 6. Facet Joint Formed by articulation of inferior and superior processes of subsequent vertebrae. Orientation in lumbar spine is toward sagittal plane, allowing flexion and extension but limiting rotation of the lumbar vertebrae. Helps to prevent anterior movement of superior vertebra on inferior vertebra. Articular surfaces are made up of non-innervated articular cartilage. Capsule and synovial membrane are innervated with pain receptors.
- 7. Spinal Nerve Topography 31 pairs of spinal nerves • 8 cervical • 12 thoracic • 5 lumbar • 6 sacrococcygeal • Each Spinal nerve root consist sensory(supply particular dermatome) and motor division(supply muscles). • All spinal nerves ,except cervical, exit below their corresponding vertebrae.
- 8. Disc and Nerve root relationship every spinal nerve exits the canal by passing through the vertebral foramen present on the side of adjacent vertebrae.so in case of L4-L5 prolapse, there is L5 nerve root compression.
- 9. 1)Protection of spinal cord & internal organs. 2)Support & weight transmission. 3)Axial disposition 4)Provides attachment to muscles. 5)Movement Functions of the Spine
- 10. Intervertebral disc • Total 23(C6 T12 L5)-Present at levels C2-C3 to L5-S1. • Hydrostatic, load bearing , shock absorbing structure between the vertebral bodies. • Fibrocartilagenous joint of the motion segment. • Make up ¼ the length of the spinal column. (The discs vary in size and shape with their position in the spine. Discs also decrease in volume, resulting in a 16% to 21% loss in disc height after 6 hours of standing or sitting.). • Allows compressive, tensile, and rotational motion • Largest avascular structures in the body -Each disc unit has – strong outer ring of fibers called the annulus fibrosus – a soft , jelly like center called the nucleus pulposus – 2 endplates
- 12. Intervertebral Disc • Annulus Fibrosus – Outer portion of the disc Lamellae Great tensile, torsional & radial strength – Made up of lamellae fibrocartilage Annulus Fibrosus – Layers of collagen fibers Type I Arranged obliquely 30° Some radial fibers Thicker anteriorly >posteriolry Attached to end plates
- 13. Intervertebral Disc • Nucleus Pulposus Nucleus Pulposus– Inner structure – Notochord remnant – Type II collagen – Resists axial forces
- 14. Cartilage End Plate • Approx 1 mm thick • Considered part of disc rather than body • Made up of hyaline cartilage mostly (young) and fibrocartilage (old) • The collagen fibers of the inner 2/3rds of the annulus form the fibro cartilaginous component of the VEP • Provides nutritional support via passive diffusion.
- 15. MOLECULAR COMPOSITION OF DISC
- 16. FUCTION OF DISC 1)Seperation of veretebral bodies 2)strong and flexible structure for movement between vertebrae 3)spinal colum height 4)shock absorber
- 17. • The FUNCTIONAL UNIT of the spine movement. • Comprises of: – 1.Two adjacent vertebrae – 2.Intervertebral disc – 3. Two facet joints and capsules – 4.Connecting ligaments: – including the ligamentum flavum, interspinous, supraspinous, intertransverse ligament . – IVD provides the most resistence to compression, whereas the facet allow for rotation, lateral bending ,and extension. Spine Motion Segment
- 18. Lower Back Pain • Lower back pain is a symptom,not a disease. • Low back pain is one of the most common reason for all physician visits. • Approximately 90% of adults experience back pain at some time in life. 90% do not require active intervention. Acute Low Backache-pain duration is less than 3 month. usually self limiting. -Chronic low backache-persistent or fluctuating last longer then 3 months.
- 19. CausesMechanical (affecting spine only) • Muscle strain • Osteoarthritis • Spinal stenosis • Discogenic • Spondylolisthe sis • Vertebral fracture • congenital Non mechanical (systemic diseases) • Ankylosing spondylitis • Neoplasms • Infections( TB, Herpes, osteomyelitis) • Atherosclerosis • Visceral pain Biomechanical causes • Poor posture • Sedentary lifestyle Pyschological causes • Depression • stress ENDLESS PRACTICALLY
- 20. Causes of Back Pain 25-40% Back Pain (Discogenic Back Pain)-m/c cause
- 22. RED FLAG SIGN -indication for evaluation-> 50 yr age – History of Cancer – Weight loss – Unrelenting night pain – Steroid use – Fever – Significant trauma – Failure to improve conservative therapy – osteoporosis Cauda Equina Syndrome – Saddle anesthesia – Bowel/bladder dysfunction – Loss of sphincter tone – Rapid progression – Unilat or bilat major motor weakness
- 23. Yellow Flags indication of poor outcome • Affect-anxiety , depression , irritability • Belief -that back pain is harmful or severely disabling that it needs to be eliminated. • behaviour-avoidance behavior and reduced activity level • Social -withdrawal and low mood • Work-Expectation that pain increases with activity.
- 24. CONCEPT OF PAIN GENERATOR • Pain generator is pathoanatomic site or a pathological structure from which the primary cause of patients low back pain thought to be originate. • It is primary / sole cause of patient illness. • So basic approach is identification of pain generator and treat it. • So now a days focus on identification of pain generator first.
- 25. Pain generator in low backache • Lumbar IVD –m/c • Vertebral body- fracture/osteoporosis/infection/neoplasm • Nerve roots-lumber canal stenosis/radiculopathy • Facet joint-degeneration/fracture • Spinal muscle-myofascial pain/sprain • Sacroilliac joint • Spinal ligaments-ALL/PLL/interspinous ligaments
- 26. Discogenic back pain • Pain syndrome that originates from a lumber disc.(pain generator) • Broadly degenerative disc disease (DDD)is a cause of discogenic back pain. • Most common cause of lower backache.
- 27. DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE • Degenerative disc disease (DDD) has been used to describe a wide variety of clinical,morphologic and radiographic changes in the DISC. • Surgeons and radiologist describes it the presence of osteophytes ,loss of disc height and reduced signal intensity on MRI. • Pathologist describes it by changes in proteoglycans /water content,crack and fissures .
- 28. Factors Contributing To Disc Degeneration 1)Aging-most consistent physiological reason. -Reduction of concentration of cells in the disk. -Reduction of rate of synthesis of proteoglycans -Type 2 collagen replaced by type1 2)MECHANICAL-degeneration is more common and more severe at lower lumber levels. 3)Low grade infections-tuberculosis,gram positive 4) Metabolic disease - DM, Alkaptonuria 5) Toxic factors - low ph, smoking , alcohal 6)Genetic association-aggrecan gene polymorhism 7)Neurogrnic inflammation
- 29. Decrease in end plate Permiability Failure of nutrient supply & Accumulation of waste Low p H Injury Pathophysiology-Disc Degeneration
- 30. Pathophysiology-Disc Degeneration Loss of Proteoglycan & collagen and degradation Fall in osmotic pressure of disc matrix No longer behaves hydrostatically under load Loose height and fluid more rapidly Stress concentration along End plates and Annulus www.ipscindia.com
- 31. Pathophysiology-Disc Degeneration • Normal Disc – Pressure evenly distributed along end plates and annulus • Degenerated disc – Uneven stress across End plates and annulus –Fissures and Tear-disc prolapse-disc herniation •Due to uneven stress on disc causes secondary facet joint arthropathy
- 32. Degenerative Disc Disease • Pathophysiology: 1. Disc gradually dries out, loses height and volume. 2. NP changes from a turgid gelatinous bulb to brownish dessicated structure. 3. AF develops fissures parrallel to the vertebral end plates. 4. Compressive loads transfer away from nucleus to margins 5. Sclerosis of endplate reduces disc nutrition. 6. Facet joints wear away cartilage, begin to override 7. Motion segment becomes hypermobile 8. Osteophytes develop to attempt to stabilize motion segment 9. Osteophytes may encroach on neural structures.
- 33. Aging of Disc Degeneration of Disc • Affects Nucleous • Increased proteoglycan fragmentation and water content is decreased • Nucleus is gradually replaced by collagen fibers. • Disc height is maintained. • Annulus & End plates • Concentric or radial tear in the annulus, Inwards buckling of annulus & radial bulging of outer annulus • Endplate defects & vertical bulging of endplates into the adjacent vertebral bodies. • Reduced disc height
- 34. DEGENERATIVE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC DISEASE (STAGES OF DISC DEGENERATION) A. ) - DISC BULGE B. ) - ANNULAR TEAR C. ) - HERNIATION PROTUSION EXTRUSION SEQUESTRATION MIGRATION
- 35. A ) DISC BULGE - Diffuse symmetrical outpouching of the annulus fibrosus caused by early disc degeneration & collapse. -Bulging can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. -The term bulge refers to a morphologic characteristic and is not correlated with etiology or symptomatology. -Bulging can be physiologic , can reflect advanced degenerative disc disease or can be associated with bone remodeling. (Fardon and Milette 2001).-
- 37. B ). ANNULAR TEAR Disruption of concentric collagenous fibers comprising the anulus fibrosus 1)Concentric tears are circumferential lesions which are found in the outer layers of the annular wall . They represent splitting between adjacent lamellae of the annulus, like onion rings. Concentric tears are believed to be of traumatic origin especially from torsion overload injuries. 2)Radial tears are characterized by an annular tear which permeates from the deep central part of the disc (nucleus pulposus) and extends outward toward the annulus, in either a transverse or cranial-caudal plane. *Responsible for disc degeneration. 3)Transverse tears, also known as “peripheral tears” or “rim lesions,” are horizontal ruptures of fibers, near the insertion in the bony ring apophyses.
- 38. CONCENTRIC TEARS TRANSVERSE TEARS / PERIPHERAL TEARS RIM LESIONS RADIAL TEARS
- 39. C). DISC HERNIATION Herniation is defined as a localized displacement of disc material (nucleus, cartilage, fragmented apophyseal bone, fragmented annular tissue) beyond the limits of the intervertebral disc space. (Fardon and Milette 2001). Intravertebral Herniations Protruded Disc Extruded Disc Sequestration Migration
- 40. -Herniated discs in the cranio-caudal (vertical) direction through a break in one or both of the vertebral body endplates are referred to as “intravertebral herniations” (also known as Schmorl’s nodes). -They are often surrounded by reactive bone marrow changes. - Nutrient vascular canals may leave scars in the endplates, which are weak spots representing a route for the early formation of intrabody nuclear herniations INTRAVERTEBRAL HERNIATIONS
- 41. The terminology “protruded disc” is used when the base of the disc is broader than any other diameter of the displaced material. Based on a two-dimensional assessment of the disc contour in the transverse plane, a protruded disc can be focal (involving <25% of the disc circumference) or broad-based (involving 25%–50% of the disc circumference). “ PROTRUDED DISC
- 42. The terminology “extruded disc” is used for a focal disc extension of which the base against the parent disc is narrower than the diameter of the extruded disc material, measured in the same plane. EXTRUDED DISC HERNIATIONS Extrusion: the base of the herniation is narrower than the apex (toothpaste sign)
- 43. Extrusion is also used when there is no continuity between the herniated disc material beyond the disc space and that within the disc space If the displaced disc material has no connection with the parent disc, it is called a “sequestrated fragment” (Fig. 6.19). This is synonymous with a “free fragment”.
- 44. SEQUESTRATION & MIGRATION If the displaced disc material has no connection with the parent disc, it is called a “sequestrated fragment” (Fig. 6.19). This is synonymous with a “free fragment”. Sequestration -indicate that the displaced disc material has lost completely any continuity with the parent disc Migration -indicates displacement of disc material away from the site of extrusion.
- 46. STAGES OF DDD Disc bulge:- diffuse symmetrical outpouching of the annulus fibrosus caused by early disc degeneration& collapse Protrusion:- base wider than any diameter of the material displaced beyond disc space Extrusion:- displaced portion has a greater diameter than its connection with the parent disc at its base Sequestration:- when disc extrusion has lost all connection with the parent disc Migration:- an extruded disc, whether sequestrated or not, that has been displaced above or below the edge of the disc space
- 47. • Depending upon whether the displaced portion is completely enveloped by intact outer annulus or combination of annulus and PLL( s/t called capsule):- • Contained:- • Un contained:- – Subligamentous:- disc material contained beneath the PLL – Transligamentous – Submembranous:- disc material contained only by peridural menbrane CLASSIFICATION DD
- 48. • Depending upon the relationship of the herniated material to the posterior annulus and PLL: – Central( midline):- herniation along the posterior annulus – Posterolateral:- along the weaker lateral expansion of PLL m/c because it is weakest portion of annulus – Foraminal( lateral ) – Extraforaminal ( far lateral) • In relation to nerve root: – Shoulder herniation – Axillary herniation • According to the level of LDH:- – High LDH:- L1-L2, L2-L3, L3-L4 – Low LDH:- L4-L5, L5-S1 CLASSIFICATION
- 49. Shoulder v/s axillary disc Shoulder disc -Disc material compress the nerve root laterally displacing it medially. -Patient will bend to opposite side to relieve neural irritation. Axillary disc -disc material compress the nerve root medially displacing it laterally. -patient will bend to same side to relieve neural irritation.
- 51. APPROACH • HISTORY • PHYSICAL EXAMINATION • NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION • INVESTIGATION • MANAGMENT
- 52. HISTORY -PAIN- Commonest symptom -Onset of pain-Acute, chronic, or insidious -Consistency of the pain-Constant vs. Intermittent pain -Site of pain -Axial /Radicular involving limbs combination of both -Bowel and Bladder signs
- 53. Nature and intensity of pain Discogenic- focal,aching in nature,increased with activity causing axial loading(flexion),decreased with rest Facetal pain-pain on extension of spine (Can be of muscle strain) Degenerative-Pain and stiffness in morning Inflammatory-prolonged pain with stifness > 1hr Tumour/infection- Night Pain unrelieved by rest
- 54. Pain with… • Prone positionn – Facet, Lat HNP, systemic • Sitting – Paramedian HNP, annular tear • Standing – Lateral HNP, central stenosis, facet syndrome • Walking – central stenosis
- 55. Neurogenic Claudication Pain Vague cramping, aching, Location Back, buttocks, lower ' extremities Radiation Proximal to distal Exacerbation With standing, Particularly with trunk extended; less with walking; rare with bicycling unless trunk is extended Time to relief Prolonged(20 min) Walking uphill less pain Back pain Common Limitation of spinal movt Common Vascular Claudication Tightness, cramping (usually in calf) Calf Distal to proximal With walking and bicycling (activities involving lower extremities) Rapid(5 min) Pain Uncommon Uncommon
- 56. NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION SENSORY EXAMINATION L1-Anterior proximal thigh near inguinal ligament L2-Mid anteromedial thigh L3-Proximal and medial to patella L4-Medial lower leg and ankle( best tested just proximal to medial malleolus) L5-Lateral and anterolateral leg and dorsum of foot(Proximal to first web space)
- 57. S1-Posterior calf , planter foot ,lateral toes(posterolateral aspect of heel) S2-Posterior thigh and proximal calf(centre of popliteral fossa) S3,S4,S5-Perianal area
- 58. MOTOR EXAMINATION • Motor testing nerve Root Level • L1 ,L2 Iliopsoas(Hip flexion) • L3 Quadriceps(Knee extension) • L4 tibialis anterior(Dorsiflexion ankle)- heel walking • L5 EHL,EDL (Great toe extension) - • S1 Gastrosoleus(Plantarflexion & Eversion) Toe walking
- 64. REFLEXES • Two principal deep tendon reflexes are normally tested- • L4-Patellar tendon reflex • S1-Achilis tendon reflex • L5-Tibialis posterior reflex
- 65. Discogenic Pain-Special test *Primary focus on the L5 and S1 never roots, since 98% of clinically important disc herniations occur at L4-L5 and L5-S1. A)SCIATIC NERVE STRETCH TEST:-(L4 L5 S1 S2 S3) -straight leg raising test -laseague test -Well straight leg raise -Kernig’s/Brudzinski test -bowstring test B)femoral nerve stretch test:-(L2 L3 L4)
- 66. SLR TESTING • During SLR maneuver , the L5 and S1 nerve root either moves or passively deforms approx. 2 to 6 mm at the level of foramen. • Maximum tension is realized in the sciatic nerve at 30 to 70 degree of elevation from the supine. • Crossed SLR is more specific of a disc herniation( pathognomonic of micromotion in affected side nerve roots while raising normal side leg) • <40* suggest impingement of protruding disc on a nerve root • >40* indicates tension on nerve root
- 68. BOWSTRING TEST • reliable sign of nerve root compression - do SLR test At the point where the patient experiences pain, relax the tension by flexing the knee slightly; the pain should disappear. •Then apply firm pressure behind the lateral hamstrings to tighten the common peroneal nerve - the pain recurs in +ve test
- 69. SUDDEN SCIATIC STRETCH TEST SUDDEN SCIATIC STRETCH TEST • Hold the great toe of the suspected side and suddenly lift the bent knee to straight position. • Patient will feel bursting pain at the low back. • Can ne used to differentiate between a malingerer and a genuine patient of sciatic radicuitis.
- 71. • FEMORAL NERVE STRETCH TEST: • positive if the L2 L3 L4 roots
- 73. RADIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS • Radiographs – Early if ominous signs • Fever • night pain • age extremes • h/o Ca • wt loss • Trauma osteoporosis – Symptoms present > 1 month
- 74. RADIOLOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS No specific help in diagnosis , but they provide a global overview of the lumber spine alignment. AP VIEW • Alignment of vertebral column • Lesion of pedicles/ TP • Side to side collapse • Paravertebral soft tissue shadows • scoliosis LATERAL VIEW • Shape n size of vertebral body • Anterior n posterior walls integrity • Superior n inferior surfaces of body • Wedging • Disc space • Spinal canal-between post end of body n lamina-space occupied by cord
- 75. COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY • extremely useful diagnostic tool • painless, outpatient procedure can supply more information about spinal disease • Unfortunately, CT does not demonstrate intraspinal tumors or arachnoiditis and is unable to differentiate scar from recurrent disc herniation.
- 76. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING • newest technological advance in spinal imaging • Diagnostic imaging modelity of choice for lumber disc diseade. • The advantages :- – ability to demonstrate intraspinal tumors, examine the entire spine, and identify degenerative discs based on decreased H2O content – costly and requires specially constructed facilities,increased time to scan, problem with claustrophobic patients.
- 77. MRI • Test of Choice • Architecture of Disc • Disruption of endplates • Secondary changes • Herniation -T2 Weighted images are most commonly used to identify and assess primary LDH. -Contrast enhancement is required to the T1 weighted images to differentiate between scar tissue and herniated disc material in patients who had prior lumber spine surgery. -MRI is72% sensitive, 68% specific, and 70% accurate in detecting containment status of lumbar herniated discs.
- 78. Modic changes secondary to Disc degeneration MRI Type III Low signal in T1 and low signal in T2--sclerotic changes. Type- I Low signal in T1-weighed sequences and high signal in T2)--- edema. Type II High signal in T1-weighed sequences and either high or intermediate signal in T2) ---fatty replacement
- 79. MYELOGRAPHY • Indicated if MRI is not available or for patient in whom MRI is contraindicated( cardiac pacemaker or brain aneurysm clip) • valuable in a previously operated spine and in patients with marked bony degenerative change that may be underestimated on MRI • improved by the use of postmyelography CT scanning. • Poorly tolerated and have no place currently in diagnosis of LDH
- 80. Provocative Discography -Gold standered in confirming the diagnosis of discogenic pain • Should be follow up with ct discogram • Two component to make a definitive diagnosis- 1)provoke the concordent pain by presseurizing the disc with a contrast material. 2)painless discogram in adjacent disc.
- 81. Post Discography CT Scan- Modified Dallas Grades • Grade 0 – Normal disc, cotton ball appearance • Grade 1 – Radial tear upto inner 1/3 of AF • Grade 2 – Radial tear upto middle 1/3 of AF • Grade 3 – Radial tear upto outer 1/3 of AF, but extends < 30 degrees of disc circumference • Grade 4 – Radial tear upto outer 1/3 of AF & extends > 30 degrees of disc circumference • Grade 5 – Radial tear with extra-annular leakage into epidural space. Site and Extent of Tear Disc stimulation + Discography = Provocative Discography Step 1 and 2 Step 3
- 83. Management • Goal:- - pain relief -Rehabilitation -Improve quality of life *large gap between physician role and patient expectations. *appropriate patient selection , accurate diagnosis & Proper management plan is basis of success of therapy.
- 84. Conservative treatment 1)medication-analgesics and anti- inflammatory -membrane stabilizer(anticonvulsants) -narcotics -antidepressants -muscle relexants -topical medications 2)Lifestyle modifications- weight management -limit smoking & alcohal intake -psychosocial support 3)physiotherapy 4)interventional pain management
- 85. TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRIC NERVE STIMULATION (TENS) • TENS uses pulse electric current through the skin to stimulate underlying muscles. • Conventionally 10-30 ma of current is used at 50-100 Hz • Provide pain control by- 1)gate control theory 2)Release of endorphins
- 86. Interventional Pain management Interventional Pain management -Interventions pain management are Minimally Invasive, Non Surgical and Target Specific procedures to Diagnose and to treat Various painful conditions. -It fills the gap between pharmacologic management of pain & more invasive operative procedure.
- 87. Common interventional pain management in discogenic pain:- • epidural steroid injection • annuloplasty • provocative discography • chemonucleolysis • ozone nucleolysis • percutaneous disc decompresion • percutaneous discectomy • percutaneous vertebroplasty • Percutaneous kyphoplasty • epidural adhesiolysis • grey ramus block
- 88. EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION – offer relatively prolonged pain relief. – Methylprednisolone is the usual steroid injected. – The dosage may vary from 80 to 120 mg. – The anesthetics used may include lidocaine, bupivacaine, or procaine. – current protocol is to inject the patient three times. These injections are made at 7- to 10-day intervals. – Several proposed mechanism of action which include anti-inflammatory ,neuromembrane stabilization , modulation of peripheral nociceptor.
- 89. TECHNIQUES FOR EPIDURAL STEROID 1)loss of resistance method-loss of resistance feel when needle enter in epidural space - blind method - high failure rate 2)fluoroscopic guided- Proper localizationzation of epidural space and assures placement of steroide. -now considered standered for epidural steroid injections.
- 90. INDICATIONS:- • Lumbosacral radiculopathy • Lower back pain syndrome(spinal stenosis/postlaminectomy syndrome) • Phantom limb pain • Vertebral comopressions • Diabetic polyneuropathy Contraindiacations:- • Pregnancy • cauda equina syndrome • coagulopathy • Anaphylactic reactions
- 91. APPROACHES FOR EPIDURAL STEROID Three approaches:- 1)Lumbar Interlaminal- -Can be performed in sitting , lateral or prone position. - A syringe filled with air / saline is used to locate epidural space by loss of resistance or flouoroscopically(resistance is offered by ligamentum flavum) 2)caudal epidural- - performed with the patient in the prone position and flouroscopy in lateral view. - palpate the sacral cornua , a 22G needle is introduced in sacral hitus.a distinct pop is felt when sacrococcygeal membrane piereced.needle position checked by flouroscopy 3)Transforaminal epidural- -Thereputically more effective than lumbar interlaminal or caudal block as drug is deposited more anteriorly right closed to target. - Amount of drug is also much less(10-20 mg) -Choice of Approach in failed back surgery syndrome. -Technically difficult,more chances of nerve / spinal cord trauma, intraneural injection
- 92. INDICATIONS • Radicular symptoms in a specific dermatomal distribution that correlates with MRI findings. • Positive straight leg raising test or positive bowstring sign, or both. • No improvement after 6 weeks of conservative therapy. • Imaging studies (CT, MRI, discography) indicating a subligamentous contained disc herniation. • Well maintained disc height of 60%. percutaneous disc decompression
- 93. Minimally invasive procedure using small needle and probe to remove disc material of prolapsed disc ,releasing pressure on nerves and relieving pain in most of the patients of prolapsed/ bulging / slipped disc Management : Disc Herniation Percutaneous disc decompression
- 94. Percutaneous Disc decompression • Rotating probe is inserted through needle into the disc under X-Ray/ Fluoroscopic guidance. • Guiding needle is inserted through “triangular safe zone-kambin triangle”(just anterior to supetrior articular process and superior to transverse process) • Rotating tip removes small portion of disc material. • Because only enough of the disc is removed to reduce pressure inside the disc, the spine remains stable.
- 95. LASER DISCECTOMY • Holmium-yttrium-aluminium garnet(HO:YAG) Laser is most commonlu used. • Can ne paired with the endoscope for disc ablation. • Smaller fragment can be removed through endoscope and larger fragment are laser ablated. • Difficult technique , required steep learning curve.
- 96. Ozone Discectomy/ ozonucleolysis • It’s action is due to the active oxygen atom . • It attaches with the proteo-glycan bridges in the nucleus pulposus. • They are broken down and they no longer capable of holding water. • As a result disc shrinks and mummified and there is decompression of nerve roots.
- 97. . Under fluoroscopic Guidance Correct level of the prolapsed disc is identified Needle is inserted into the centre of the Disc and ozone is Injected. Pain relief starts usually within one week and ozone takes 3-4 weeks for its complete effect Percutaneous Ozonucleolysis Indicated for both contained and noncontained disc herniation Ozone 30-40 % is used with oxygen mixture(oxygen-ozone ratio-70:30 ratio) 2-3ml injected intradiscally and 10-20 ml injected in paravertebral space of affected disc snbsequently. Repeated 8-10 times
- 98. Nucleotomy • The herniation suctioned toward the probe where an integrated knife then cuts it away from the disk. The material is then suctioned away
- 99. INTRADISCAL ELECTROTHERMAL ANNULOPLASTY(IDET) • Indication • Mild to moderate Degeneration • Absent radicular symptom • Positive discogram • Contraindication • Large disc herniation • Canal stenosis • Disc height loss > 50% • Mechanism of Action – strengthen the collagen fibers, – Seal fissures, – denature inflammatory exudates, or coagulate nociceptors
- 101. Nucleoplasty or RF Coblation Based on concept that if volume of disc is reduced, it will shrink And back pain reduced. -nucleoplasty utilizes coblation technology in which ablation and coagulation of nucleus pulposes reduces the size of contained disc herniation. Indication • Discogenic pain with contained disc herniation (No prospective randomized controlled studies for purely Discogenic pain) Contraindication • Extruded disc • Disc herniation >33 % of sagittal diameter of spinal canal
- 102. Methylene Blue • Weak Neurolytic effect • Inhibition of Guanylate Cyclase and NO synthesis Intradiscal Methylene blue Injections
- 103. Hydrodiscectomy • Cutting with water fluid Jet technology – uses the Venturi Effect created by high velocity saline jets to cut and aspirate targeted tissue
- 104. GRAY RAMUS BLOCK • GRB can be used as diagnostic tool as well as therepeutic intervention to provide temporary pain relief. • Under fluoroscopy ,2-3 ml of local anaesthetic with or without steroid is injected after contrast confirmation of safe needle placement at three levels. • One level which is affected and lower each upper and lower side.
- 105. VERTEBROPLASTY Indications:- -Pathological compression fractures -Osteolytic bony lesion -Meelomas,haemangiomas -osteoporosis *Contraindicated in coagulation disorders and infectious disease of spine. *Low viscosity bine cement is introduced in fractured bone. *Immewdiate pain relief possibly due to thermal effect on small nerve ending responsible for pain.
- 106. KYPHOPLASTY modification of vertebroplasty by introduction of the percutaneous ballon ,where space for cement is created by ballon insertion prior to cement injection.
- 107. Interventional Pain Procedures • Limitations • Contraindications • Complications • Not Alternative to Surgery • Steep learning curve
- 108. Glucosamine and chondrointin sulphate- Enhance the Repair response of chondrocytes and retard the enzymatic degradation of cartilage. Cell based Therapies Stimulate the disc cell to produce matrix Direct injection of Growth factor/ Cytokine inhibitor- Unsuccessful Gene of interest is introduced into target cell Nucleous Pulposus augmentation Injectable Nucleous –Solution of Protein polymer and crosslinking agent Regenerative Therapies
- 109. Indication of surgery • Emergent/ absolute:- – Presence of cauda equina syndrome – Progressive neurologic deficit • Relative:- – Persistent radiculopathy despite an adequate trial of non surgical treatment( min of 6 wks). – Recurrent episodes of incapacitating sciatica – Significant motor deficit with persistent tension signs and pain – Pseudoclaudication( activity related leg pain) caused by canal stenosis resulting from a disc herniation • Goal of surgery:- – Alleviate the neural compression without further injury to the affected nerve root – Minimal disruption of surrounding normal tissues and maintenance of spinal stability
- 110. Waddell’s Non-organic sign indicate poor outcome of surgery if 3 out of 5 positive. Finding Description 1. Tenderness a. superficial - pain with light touch to skin b. deep - nonanatomic widespread deep pain 2. Stimulation a. pain with light axial compression on skull b. pain with light twisting of pelvis 3. Distraction No pain with distracted SLR 4. Regional a.nonanatomic or inconsistent motor findings during entire exam b. nonanatomic or inconsistent sensory findings during entire exam 5. Overreaction Overreaction noted at any time during examination
- 111. Surgical procedure -Surgery involve decompressing the canal by removing a piece of its wall(i.e. lamina)apart from removal of the herniated disc(discectomy). -the key of good results in disc surgery is appropriate patient selection. -before this step is taken , the surgeon must be sure of the diagnosis. -surgeon and Patient should be aware that the procedure is predominantly for symptomatic relief of leg pain. Patient with predominantly back pain may not experience relief.
- 112. Discectomy procedure -Standard open lumbar disectomy -Microlumbar disc excision - endoscopic / percutaneous discectomy - -Artificial total disc replacement Decompression procedure -fenestration -laminotomy -hemileminectomy -laminectomy -facetectomy
- 113. Decompression procedure • Fenestration-creating a hole in ligamentum flavum that connects the adjacent laminas , thereby opening the spinal canal. • Laminotomy-in addition to fenestration , a part of lamina is excised to widen the hole and create wider space for decompressing the canal. • Hemilaminectomy –removing of whole of lamina but only of one side. -usually is required when identifying the root is a problem. This may occur with a conjoined root. • Total laminectomy –the lamina of both side is removed along with the spinous process. -usually is reserved for patients with spinal stenoses that are central in nature, which occurs typically in cauda equina syndrome.
- 115. MICRODISCECTOMY • Micro lumber disc excision has replaced standered open laminectomy as procedure of choice. • Limited dissection required, less postoperative pain , shorter hospital stay . • The herniated disc is excised after creating a fenestration in ligamentum flavum to reach the disc.
- 117. TOTAL DISC REPLACEMENT• In this procedure degenerated disc material is removed and an artificial disc is implanted in the spine. • Prerequisite:- -demonstarble disc degeneration as the cause of pain. -intact facet joint posteriorly and no other pain generator is demonstrable. Indication:- -failure of aggressive conservative treatment with disabling LBP attributed to the lumber spine affecting no more than two disc. *material used for TDR are similar to arthroplasties (polyethylene ,titanium , chrome cobalt) and various replacement designs are also available.
- 118. THE FAILED BACK SYNDROME(FBSS) • Any condition where there is failure to improve satisfactorily following back surgery. – Classification of failure:- 1)Early-symptomes either present immedietly or within 2-3 weeks. wrong level surgery or wrong procedure is most common cause. 2)Intermediate- within weeks to monts mat be related to recuurent disc herniation, or haedware problems. 3)late-after several months. recureent pathology at the same or adjacent segment is the common cause.
- 119. ETIOLOGY -Wrong patient selection-m/c cause -Incomplete diagnosis -Wrong procedure -Revision surgery -Poor technique -Progressive disease -Systemic disorder
- 120. MANAGMENT • It is best to prevent FBSS. • Accurate diagnosis and presurgical patient assement increases the suucess of surgery. • In case of FBSS conservative treatment should be tried first:- -Intrathecal analgesia -Intradiscal electrotherapy -Medial branch radiofrequency lesioning -Spinal cord stimnulation -percutaneous adhesionolysis/percutaneous epidural neuroplasty(racz procedure) Remember success of revision surgery in spine reduce with revision procedure and hence FBSS would rise with more and more revision.
- 121. Debate is on…….
- 122. Surgery for back pain; MRI… • Clinical correlation is must • Discography is very helpful
- 124. Questions Please?
