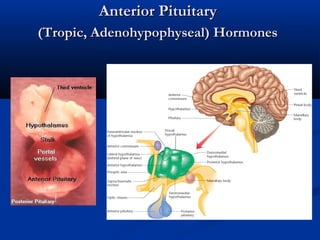
Anterior pituitary hormones
- 1. Anterior PituitaryAnterior Pituitary (Tropic, Adenohypophyseal) Hormones(Tropic, Adenohypophyseal) Hormones
- 2. They are Classified into:They are Classified into: Somatotropic Hormones:Somatotropic Hormones: 1- Growth Hormone (GH).1- Growth Hormone (GH). 2- Prolactin (Prl).2- Prolactin (Prl). 3- Placental Lactogen (PL).3- Placental Lactogen (PL). Glycoprotein Hormones:Glycoprotein Hormones: 1- Luteinizing Hormone (LH).1- Luteinizing Hormone (LH). 2- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH).2- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH). 3- Chrionic Gonadotropin (CG).3- Chrionic Gonadotropin (CG). 4- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH).4- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH). PPro-ro-OOpiopiommelanoelanoccortin (POMC) derived Hormones:ortin (POMC) derived Hormones: 1- Corticotropin: ACTH.1- Corticotropin: ACTH. 2- Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormones:2- Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormones: αα-MSH,-MSH, ββ-MSH.-MSH. 3- Lipotropins:3- Lipotropins: ββ-LPH,-LPH, γγ-LPH-LPH
- 3. Growth Hormone (GH)Growth Hormone (GH) Structure:Structure: It is a single polypeptide chain composed of 191It is a single polypeptide chain composed of 191 amino acid residues. It has two disulfide bonds.amino acid residues. It has two disulfide bonds.
- 4. Secretion:Secretion: Somatotropes of the Anterior Pituitary.Somatotropes of the Anterior Pituitary. Level:Level: High in children.High in children. Maximal during adolescence.Maximal during adolescence. Lowest during adulthood.Lowest during adulthood. Measurments:Measurments: During 24 hours.During 24 hours. After stimulation.After stimulation. Regulation:Regulation: Stimulation: By Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH).Stimulation: By Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH). Inhibition: By Somatostatin.Inhibition: By Somatostatin.
- 5. Physiological Effects:Physiological Effects: Direct Effects:Direct Effects: 1- Stimulation of Lipolyses (Hydrolyses of Triglycerides).1- Stimulation of Lipolyses (Hydrolyses of Triglycerides). 2- Stimulation of Hepatic glucose output.2- Stimulation of Hepatic glucose output. 3- Production of Insulin-like growth factors (IGF’s, Somatomedins)3- Production of Insulin-like growth factors (IGF’s, Somatomedins) Indirect Effects:Indirect Effects: Mediated by IGF-1:Mediated by IGF-1: 1- Increase cell numbers.1- Increase cell numbers. 2- Positive Nitrogen balance.2- Positive Nitrogen balance. 3- Increase Protein synthesis.3- Increase Protein synthesis.
- 6. Disease Conditions Related to GH:Disease Conditions Related to GH: Deficiency:Deficiency: * Dwarfism.* Dwarfism. Excessive Secretion:Excessive Secretion: ** Giantism:Giantism: Due to tumor in somatotrpes in young childrenDue to tumor in somatotrpes in young children or adolescents.or adolescents. ** Acromegaly:Acromegaly: Rare disease (3/Million).Rare disease (3/Million). Causes:Causes: 1- Benign tumor of Pituitary gland (90%).1- Benign tumor of Pituitary gland (90%). 2- Tumors of pancreas, lung or adrenal gland.2- Tumors of pancreas, lung or adrenal gland. Symptoms:Symptoms: Enlargements of extremities.Enlargements of extremities.
- 7. Treatment of Acromegaly:Treatment of Acromegaly: Transsphenoidal surgery to remove tumor.Transsphenoidal surgery to remove tumor. Radiation therapy usually follow the surgery.Radiation therapy usually follow the surgery. Drug Therapy:Drug Therapy: 1- Dopaminergic Agonists:1- Dopaminergic Agonists: Bromocriptine (Parlodel®).Bromocriptine (Parlodel®). 2- Synthetic Somatostatin analogs:2- Synthetic Somatostatin analogs: Octeroide (Sandostatin).Octeroide (Sandostatin).
- 8. Uses of Growth Hormone:Uses of Growth Hormone: * Replacement therapy for children with GH deficiency.* Replacement therapy for children with GH deficiency. * Administered by intramuscular or subcutaneous.* Administered by intramuscular or subcutaneous. Sources:Sources: * Recombinant DNA technology.* Recombinant DNA technology.
- 9. Growth Hormone Releasing HormoneGrowth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH)(GHRH) Structure:Structure: Single polypeptide chain composed of 108 amino acidSingle polypeptide chain composed of 108 amino acid residues.residues. Function:Function: Stimulate the secretion of GH.Stimulate the secretion of GH. Uses:Uses: Treatment of children with GH deficiency due toTreatment of children with GH deficiency due to hypothalamic defects.hypothalamic defects. Diagnoses of the cause of GH deficiency.Diagnoses of the cause of GH deficiency.
- 10. Prolactin (Prl)Prolactin (Prl) Structure:Structure: It is a single polypeptide chain composed of 199It is a single polypeptide chain composed of 199 amino acid residues. It has three disulfide bonds.amino acid residues. It has three disulfide bonds. Secretion:Secretion: Lactotropes of the Anterior Pituitary.Lactotropes of the Anterior Pituitary. Level:Level: Starts early in the fetal stages.Starts early in the fetal stages. Decline shortly after birth and remain low in males.Decline shortly after birth and remain low in males. In female increase with pregnancy reach maximum level atIn female increase with pregnancy reach maximum level at term and remains high during lactation.term and remains high during lactation. Regulation:Regulation: Inhibited by Dopamine.Inhibited by Dopamine. No hypothalamic stimulation.No hypothalamic stimulation. Stimulated by TRH but this is of pathological importance.Stimulated by TRH but this is of pathological importance.
- 11. Physiological Effects:Physiological Effects: Breast developments and initiation of lactation.Breast developments and initiation of lactation. Prolactin imbalance:Prolactin imbalance: Hyperprolactinemia:Hyperprolactinemia: Causes:Causes: Tumors in the lactotropes.Tumors in the lactotropes. Dopamine antagonists.Dopamine antagonists. Hypothyroidism associated with high level of TRH.Hypothyroidism associated with high level of TRH. Hypothalamus or Anterior Pituitary disorders.Hypothalamus or Anterior Pituitary disorders. Renal failure.Renal failure. Sympotoms:Sympotoms: In females: Galactorrhea, Amenorrhea, Infertility.In females: Galactorrhea, Amenorrhea, Infertility. In males: Galactorrhea, Impotence, Infertility.In males: Galactorrhea, Impotence, Infertility.
- 12. Treatment:Treatment: Dopamine agonists: Bromocriptine (Parlodel®)Dopamine agonists: Bromocriptine (Parlodel®)
- 13. Gonadotropic Hormones:Gonadotropic Hormones: They were given this name due to their effect onThey were given this name due to their effect on Gonads.Gonads. They includes:They includes: 1- Luteinizing Hormone (LH).1- Luteinizing Hormone (LH). 2- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH).2- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH). 3- Chrionic Gonadotropin (CG).3- Chrionic Gonadotropin (CG). Structures:Structures: They are glycoproteins. All glycoproteins are composed of two subunitsThey are glycoproteins. All glycoproteins are composed of two subunits αα andand ββ. The. The αα-subunit is similar in all hormones and contain two N--subunit is similar in all hormones and contain two N- linked oligosaccharide chains. Thelinked oligosaccharide chains. The ββ-subunit is specific for each-subunit is specific for each hormone. In LH, TSH it contains one N-linked oligosaccharide chain,hormone. In LH, TSH it contains one N-linked oligosaccharide chain, while in CG and FSH it contain two N-linked oligosaccharide chains.while in CG and FSH it contain two N-linked oligosaccharide chains.
- 14. Secretion:Secretion: LH and FSH are secreted from the Gonadotropes of the Anterior Pituitary.LH and FSH are secreted from the Gonadotropes of the Anterior Pituitary. CG secreted by the placenta.CG secreted by the placenta. Regulation:Regulation: Stimulation:Stimulation: Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone from theGonadotropin-Releasing Hormone from the hypothalamus (Gn RH).hypothalamus (Gn RH). Inhibition:Inhibition: Feed back mechanism by sex hormones.Feed back mechanism by sex hormones. CG produced by placenta after fertilization.CG produced by placenta after fertilization. Physiological effects:Physiological effects: In Males:In Males: LH:LH: Stimulate production of androgens by Leydig cells.Stimulate production of androgens by Leydig cells. FSH:FSH: Enhance normal sperm production by Sertoli cells.Enhance normal sperm production by Sertoli cells. In Females:In Females: LH:LH: Induce Ovulation and stimulate Progesterone production.Induce Ovulation and stimulate Progesterone production. FSH:FSH: Enhance production of Estrogen and development of follicles.Enhance production of Estrogen and development of follicles.
- 15. ■ Uses:Uses: Diagnostic uses:Diagnostic uses: Diagnosis of Pregnancy: CG in Urine or Blood.Diagnosis of Pregnancy: CG in Urine or Blood. Prediction of Ovulation: LH 36 hr before Ovulation.Prediction of Ovulation: LH 36 hr before Ovulation. Reproductive system disorder in males and females.Reproductive system disorder in males and females. Therapeutic uses:Therapeutic uses: Male infertility.Male infertility. Female infertility.Female infertility. Cryptorchidism.Cryptorchidism. Antagonists:Antagonists: Used as contraceptives.Used as contraceptives.
- 16. Gonadotropin-Releasing HormoneGonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH, LHRH)(GnRH, LHRH) Structure:Structure: Polypeptide composed of 10 amino acid residues.Polypeptide composed of 10 amino acid residues. Secretion:Secretion: Hypothalamic neurones with onset of puberty.Hypothalamic neurones with onset of puberty. Uses:Uses: Stimulation of Gonadotropin Secretion:Stimulation of Gonadotropin Secretion: Long-term pulsatile administration in cases of deficiency.Long-term pulsatile administration in cases of deficiency. Suppresion of Gonadotropin Secretion:Suppresion of Gonadotropin Secretion: Log-acting GnRH in a continuous fashion. This is required in:Log-acting GnRH in a continuous fashion. This is required in: Prostate cancerProstate cancer Estrogen dependent breast cancers.Estrogen dependent breast cancers. Endometriossis.Endometriossis. Gonadotropin-dependent precocious puberty.Gonadotropin-dependent precocious puberty. Analogs:Analogs: Gonadorelin HCl (Synthetic Human GnRH).Gonadorelin HCl (Synthetic Human GnRH).
- 17. Adrenocorticotropic HormoneAdrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)(ACTH) Structure:Structure: Peptide hormone composed of 39 amino acid residues.Peptide hormone composed of 39 amino acid residues. Function:Function: Stimulate the secretion of Corticosteroids.Stimulate the secretion of Corticosteroids. Necessary for the adrenal gland otherwise atrophy of the gland takes place.Necessary for the adrenal gland otherwise atrophy of the gland takes place. Control:Control: Feed-back inhibition by corticosteroids.Feed-back inhibition by corticosteroids. Uses:Uses: Diagnoses of Adrenal insufficiency.Diagnoses of Adrenal insufficiency.
- 18. Steroidal HormonesSteroidal Hormones (Adrenocorticosteroids, Adrenocorticoids,(Adrenocorticosteroids, Adrenocorticoids, Corticosteroids, Corticoids)Corticosteroids, Corticoids) Secretion:Secretion: Adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland.Adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland. Regulation:Regulation: Stimulation:Stimulation: ACTH.ACTH. Inhibition:Inhibition: Feed back Mechanism.Feed back Mechanism.
- 19. Classification of corticosteroidsClassification of corticosteroids They are all C21 hormones.They are all C21 hormones. Corticosteroids Glucocorticoids Regulate carbohydrates, lipids and proteins metabolism e.g. Hydrocortisone Mineralocorticois Control electrolytes and water balance e.g. Aldosterone.
- 20. Numbering System of Steroidal ring:Numbering System of Steroidal ring: HO 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 89 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
- 22. Physiological Functions and Pharmacological Effects:Physiological Functions and Pharmacological Effects: Carbohydrates and Proteins Metabolism:Carbohydrates and Proteins Metabolism: Stimulate glucose formation in the brain.Stimulate glucose formation in the brain. Decrease peripheral utilization of glucose.Decrease peripheral utilization of glucose. Promote storage of glucose in the liver.Promote storage of glucose in the liver. Promote gluconeogenesis.Promote gluconeogenesis. Lipids Metabolism:Lipids Metabolism: Redistribution of body fat (Buffalo hump, Moon face).Redistribution of body fat (Buffalo hump, Moon face). Enhance lipolyses of Triglycerides.Enhance lipolyses of Triglycerides. Electrolyte and Water balance:Electrolyte and Water balance: Enhance reabsorption of sodium and water into plasma.Enhance reabsorption of sodium and water into plasma. Increase urinary excretion of potassium.Increase urinary excretion of potassium.
- 23. Blood Picture:Blood Picture: Increase hemoglobin and Red blood cells.Increase hemoglobin and Red blood cells. Decrease white blood cells.Decrease white blood cells. Anti-inflammatory effects:Anti-inflammatory effects: Suppress inflammations regardless to their cause.Suppress inflammations regardless to their cause. Immunosuppressive Effects:Immunosuppressive Effects: Decrease immunity as a result of decrease the WBC’s.Decrease immunity as a result of decrease the WBC’s. Cell Growth:Cell Growth: Retardation of cell division and cell growth.Retardation of cell division and cell growth.
- 24. Disease States:Disease States: Addison’s disease:Addison’s disease: Rare syndrome 1/100,000 due to Hypoadrenalism.Rare syndrome 1/100,000 due to Hypoadrenalism. Causes:Causes: Atrophy of adrenal gland.Atrophy of adrenal gland. Tuberculoses.Tuberculoses. Low level of ACTH.Low level of ACTH. Symptoms:Symptoms: Weakness, fatigue, apathy, depression and irritability.Weakness, fatigue, apathy, depression and irritability. Anemia and low blood pressure.Anemia and low blood pressure. Loss of sodium and dehydration.Loss of sodium and dehydration. Hypersensitivity to Insulin.Hypersensitivity to Insulin. Hyper pigmentation.Hyper pigmentation. Nausea and vomiting.Nausea and vomiting.
- 25. Cushing’s disease:Cushing’s disease: Rare syndrome 2- 5/Million due to Hyperadrenalism.Rare syndrome 2- 5/Million due to Hyperadrenalism. Causes:Causes: Tumor of the Adrenal Cortex.Tumor of the Adrenal Cortex. Tumor of the Pituitary gland.Tumor of the Pituitary gland. Symptoms:Symptoms: Alteration of fat distribution.Alteration of fat distribution. Hypertension.Hypertension. Osteoporosis.Osteoporosis. Growth retardation.Growth retardation. Decrease Immunity.Decrease Immunity. Conn’s syndrom:Conn’s syndrom: Causes:Causes: Inability of adrenal cortex to carry out 17Inability of adrenal cortex to carry out 17αα-hydroxylation of pregnenolone. That-hydroxylation of pregnenolone. That leads to low level of Cortisol and high level of Aldosterone.leads to low level of Cortisol and high level of Aldosterone. Symptoms:Symptoms: Hypertension.Hypertension. Alkalosis.Alkalosis. Polyuria.Polyuria. Edema.Edema.
- 26. Pharmacokinetics:Pharmacokinetics: Absorption:Absorption: Well absorbed from all sites of administration.Well absorbed from all sites of administration. Plasma Protein binding:Plasma Protein binding: 90% to albumin or globulin.90% to albumin or globulin. Half life (tHalf life (t1/21/2):): 1- 1.5 hr.1- 1.5 hr. Metabolism and Excretion:Metabolism and Excretion: Excreted in urine after glycosylation with glucuronic acid.Excreted in urine after glycosylation with glucuronic acid.
- 27. O O OH HO HO A B C D Structure-Activity Relationship Essential for activity 1 2 3 4 5 9 10 19 18 11 13 14 16 17 1, 2 Double bond improve carbohydrate metabolism to Na+ retention α-CH3 increase glucocorticoid activity 6 α-CH3 in Cortisol increase all activities α-CH3 in Prednisolone increase antiinflammatory activity &Decrease Na + retaining activity 9α-Fluoro increase all activities F Br Cl Essential for antiinflammatory activity & carbohydrate regulatory activity 12 12α-F increase all activities if no OH at C-17 12α-F with 16α,17αdihydroxy--inactive compounds CH3 or OH eleminate Na+ retention activity Essential for activity Essential for antiinflammatory activity Ether & esters increase antiinflammatory & glucocorticoid activities 21 Halogen & halomethylene greatly increase Topical antiinflammatory activity
