Applications Section 1.3
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•3,820 views
Linear Algebra
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
PR-159 : Synergistic Image and Feature Adaptation: Towards Cross-Modality Dom...

PR-159 : Synergistic Image and Feature Adaptation: Towards Cross-Modality Dom...
Solution of Differential Equations in Power Series by Employing Frobenius Method

Solution of Differential Equations in Power Series by Employing Frobenius Method
Statistics for Management and Economics 9th - Keller.pdf

Statistics for Management and Economics 9th - Keller.pdf
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Ejercicios matriz asociada a una composicion de funciones

Ejercicios matriz asociada a una composicion de funciones
6.4 Graphing Polynomials (Relative Max/Min, Zeros)

6.4 Graphing Polynomials (Relative Max/Min, Zeros)
Matrices conmutable, idempotente, nilpotente, involutiva, elemental y equival...

Matrices conmutable, idempotente, nilpotente, involutiva, elemental y equival...
Similar to Applications Section 1.3
Similar to Applications Section 1.3 (20)
Wk 6 part 2 non linearites and non linearization april 05

Wk 6 part 2 non linearites and non linearization april 05
Matrices and row operations 12123 and applications of matrices

Matrices and row operations 12123 and applications of matrices
بررسی دو روش شناسایی سیستم های متغیر با زمان به همراه شبیه سازی و گزارش

بررسی دو روش شناسایی سیستم های متغیر با زمان به همراه شبیه سازی و گزارش
Wk 6 part 2 non linearites and non linearization april 05

Wk 6 part 2 non linearites and non linearization april 05
1 Part 2 Systems of Equations Which Do Not Have A Uni.docx

1 Part 2 Systems of Equations Which Do Not Have A Uni.docx
Undetermined Mixing Matrix Estimation Base on Classification and Counting

Undetermined Mixing Matrix Estimation Base on Classification and Counting
Transfer Functions and Linear Active Networks Using Operational Amplifiers

Transfer Functions and Linear Active Networks Using Operational Amplifiers
Recently uploaded
💉💊+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHABI}}+971581248768
+971581248768 Mtp-Kit (500MG) Prices » Dubai [(+971581248768**)] Abortion Pills For Sale In Dubai, UAE, Mifepristone and Misoprostol Tablets Available In Dubai, UAE CONTACT DR.Maya Whatsapp +971581248768 We Have Abortion Pills / Cytotec Tablets /Mifegest Kit Available in Dubai, Sharjah, Abudhabi, Ajman, Alain, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Umm Al Quwain, UAE, Buy cytotec in Dubai +971581248768''''Abortion Pills near me DUBAI | ABU DHABI|UAE. Price of Misoprostol, Cytotec” +971581248768' Dr.DEEM ''BUY ABORTION PILLS MIFEGEST KIT, MISOPROTONE, CYTOTEC PILLS IN DUBAI, ABU DHABI,UAE'' Contact me now via What's App…… abortion Pills Cytotec also available Oman Qatar Doha Saudi Arabia Bahrain Above all, Cytotec Abortion Pills are Available In Dubai / UAE, you will be very happy to do abortion in Dubai we are providing cytotec 200mg abortion pill in Dubai, UAE. Medication abortion offers an alternative to Surgical Abortion for women in the early weeks of pregnancy. We only offer abortion pills from 1 week-6 Months. We then advise you to use surgery if its beyond 6 months. Our Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Al Ain, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah (RAK), Sharjah, Umm Al Quwain (UAQ) United Arab Emirates Abortion Clinic provides the safest and most advanced techniques for providing non-surgical, medical and surgical abortion methods for early through late second trimester, including the Abortion By Pill Procedure (RU 486, Mifeprex, Mifepristone, early options French Abortion Pill), Tamoxifen, Methotrexate and Cytotec (Misoprostol). The Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abortion Clinic performs Same Day Abortion Procedure using medications that are taken on the first day of the office visit and will cause the abortion to occur generally within 4 to 6 hours (as early as 30 minutes) for patients who are 3 to 12 weeks pregnant. When Mifepristone and Misoprostol are used, 50% of patients complete in 4 to 6 hours; 75% to 80% in 12 hours; and 90% in 24 hours. We use a regimen that allows for completion without the need for surgery 99% of the time. All advanced second trimester and late term pregnancies at our Tampa clinic (17 to 24 weeks or greater) can be completed within 24 hours or less 99% of the time without the need surgery. The procedure is completed with minimal to no complications. Our Women's Health Center located in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, uses the latest medications for medical abortions (RU-486, Mifeprex, Mifegyne, Mifepristone, early options French abortion pill), Methotrexate and Cytotec (Misoprostol). The safety standards of our Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abortion Doctors remain unparalleled. They consistently maintain the lowest complication rates throughout the nation. Our Physicians and staff are always available to answer questions and care for women in one of the most difficult times in their lives. The decision to have an abortion at the Abortion Cl+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...

+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...?#DUbAI#??##{{(☎️+971_581248768%)**%*]'#abortion pills for sale in dubai@
Recently uploaded (20)
From Event to Action: Accelerate Your Decision Making with Real-Time Automation

From Event to Action: Accelerate Your Decision Making with Real-Time Automation
Top 5 Benefits OF Using Muvi Live Paywall For Live Streams

Top 5 Benefits OF Using Muvi Live Paywall For Live Streams
Workshop - Best of Both Worlds_ Combine KG and Vector search for enhanced R...

Workshop - Best of Both Worlds_ Combine KG and Vector search for enhanced R...
ProductAnonymous-April2024-WinProductDiscovery-MelissaKlemke

ProductAnonymous-April2024-WinProductDiscovery-MelissaKlemke
Tata AIG General Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Tata AIG General Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Apidays Singapore 2024 - Building Digital Trust in a Digital Economy by Veron...

Apidays Singapore 2024 - Building Digital Trust in a Digital Economy by Veron...
Apidays New York 2024 - Scaling API-first by Ian Reasor and Radu Cotescu, Adobe

Apidays New York 2024 - Scaling API-first by Ian Reasor and Radu Cotescu, Adobe
Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...

Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...
Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)

Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)
Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood

Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood
Axa Assurance Maroc - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Axa Assurance Maroc - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
How to Troubleshoot Apps for the Modern Connected Worker

How to Troubleshoot Apps for the Modern Connected Worker
+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...

+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...
Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business

Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business
Applications Section 1.3
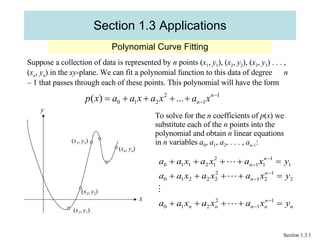
- 1. Section 1.3 Applications Polynomial Curve Fitting Section 1.3.1 Suppose a collection of data is represented by n points ( x 1 , y 1 ), ( x 2 , y 2 ), ( x 3 , y 3 ) . . . , ( x n , y n ) in the xy -plane. We can fit a polynomial function to this data of degree n – 1 that passes through each of these points. This polynomial will have the form y To solve for the n coefficients of p ( x ) we substitute each of the n points into the polynomial and obtain n linear equations in n variables a 0 , a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n -1 : ( x 1 , y 1 ) ( x 2 , y 2 ) ( x 3 , y 3 ) ( x n , y n ) x
- 2. Section 1.3 Applications Polynomial Curve Fitting Section 1.3.2 Example 1 : The graph of a cubic polynomial has horizontal tangents at (1, – 2) and (– 1, 2). Find the equation for the cubic and sketch its graph. Solution : The general form for a cubic polynomial is The derivative of this function is We know the derivative is zero at the given points so we obtain the equations
- 3. Section 1.3 Applications Polynomial Curve Fitting Section 1.3.3 Example 1 : These substitutions lead to the following system of equations Which in turn leads to the augmented matrix We now solve this system:
- 4. Section 1.3 Applications Polynomial Curve Fitting Section 1.3.4 Example 1 : From this matrix we have a 2 = 0 and a 1 = – 3 a 3 . Now using the given points and the solutions from the above system we substitute into equation (1) to obtain: or This is a new system of equations with augmented matrix:
- 5. Section 1.3 Applications Polynomial Curve Fitting Section 1.3.5 Example 1 : We now solve this system: From the last matrix we see that a 0 = 0 and a 3 = 1, and consequently a 1 = – 3. The equation of the polynomial is p ( x ) = – 3 x + x 3 . We can now sketch the graph of the third degree polynomial that goes through these points and has horizontal tangents at these points.
- 6. Section 1.3 Applications Polynomial Curve Fitting Example 1 : We now graph the polynomial p ( x ) = – 3 x + x 3 : ( – 1, 2) ( 1, – 2) Section 1.3.6
- 7. Section 1.3 Applications Network Analysis Section 1.3.7 Networks composed of branches and junctions are used as models in fields as diverse as economics, traffic analysis, and electrical engineering. It is assumed in such models that the total flow into a junction is equal to the total flow out of the junction. For example, because the junction shown below has 30 units flowing into it, there must be 30 units flowing out of it. We show this diagrammatically as and can be represented by the linear system Since we can represent each junction in a network gives rise to a linear equation we can analyze the flow through a network composed of several junctions by solving a system of linear equations. 30 x 1 x 2
- 9. Section 1.3 Applications Network Analysis Section 1.3.9 Example 2 : We label each junction appropriately as shown. We then establish the equations: Junction 1 Junction 2 Junction 3 Junction 4 These equations lead to the following system of linear equations: 200 100 100 200 x 1 x 3 x 2 x 4 1 2 3 4
- 10. Section 1.3 Applications Network Analysis Section 1.3.10 Example 2 : This system of linear equations leads to the following matrix representation: We now use the Gauss-Jordan elimination technique to solve this system.
- 11. Section 1.3 Applications Network Analysis Section 1.3.11 Example 2 : From the fourth row we see that x 4 can be any real number, so letting x 4 = t we have the following general solution: x 4 = t , x 3 = 200 + t , x 2 = t – 100 , x 1 = 100 + t where t is a real number. Thus this system has an infinite number of solutions. This is the solution to part (a) of the question.
- 14. Section 1.3 Applications Analysis of an Electrical Network Section 1.3.14 Example 3 : Determine the currents I 1 , I 2 , and I 3 or the electrical network shown below. 1 2 Path 1 Path 2 8 Volts 7 Volts R 3 = 4 R 2 = 2 R 1 = 3 I 1 I 2 I 3