Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
To understand construction of outside micrometer and calculate its least count

To understand construction of outside micrometer and calculate its least count
Viewers also liked
Temperature plays an important role in many industries both electrical & non-electrical for analyzing properties and behavior of various objects.
Industrial Instrumentations.
Hot Wire Anemometers.
Lab Quality Measurements.
�WHEATSTONE BRIDGE CIRCUIT DESIGN AND SIMULATION FOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR�

WHEATSTONE BRIDGE CIRCUIT DESIGN AND SIMULATION FOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR�Technische Universität Chemnitz
Viewers also liked (20)
WHEATSTONE BRIDGE CIRCUIT DESIGN AND SIMULATION FOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR�

WHEATSTONE BRIDGE CIRCUIT DESIGN AND SIMULATION FOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR�
Similar to MET 102 Module 6 review-questions_solved
Similar to MET 102 Module 6 review-questions_solved (20)
Mechanical Engineering Technical Interview Q & A Metrology and precision inst...

Mechanical Engineering Technical Interview Q & A Metrology and precision inst...
Design & development of multi orientation drilling special purpose machine su...

Design & development of multi orientation drilling special purpose machine su...
IRJET- Design and Manufacturing of Relation Gauges

IRJET- Design and Manufacturing of Relation Gauges
More from Ibrahim AboKhalil
More from Ibrahim AboKhalil (20)
MET 102 Module 6 review-questions_solved
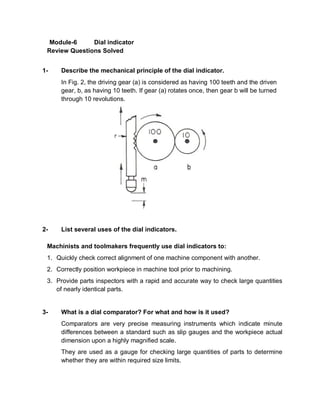
- 1. Module-6 Dial indicator Review Questions Solved 1- Describe the mechanical principle of the dial indicator. In Fig. 2, the driving gear (a) is considered as having 100 teeth and the driven gear, b, as having 10 teeth. If gear (a) rotates once, then gear b will be turned through 10 revolutions. 2- List several uses of the dial indicators. Machinists and toolmakers frequently use dial indicators to: 1. Quickly check correct alignment of one machine component with another. 2. Correctly position workpiece in machine tool prior to machining. 3. Provide parts inspectors with a rapid and accurate way to check large quantities of nearly identical parts. 3- What is a dial comparator? For what and how is it used? Comparators are very precise measuring instruments which indicate minute differences between a standard such as slip gauges and the workpiece actual dimension upon a highly magnified scale. They are used as a gauge for checking large quantities of parts to determine whether they are within required size limits.
- 2. 4- Describe how a dial comparator is used? The comparator shown in Fig. 12 has a rigid construction, a large easily visible indicating scale. An adjustable worktable is provided and the indicating head can be raised or lowered by means of the large diameter back screw pillar. Range magnification is 300-500. 5- Explain the difference between the balanced dial indicator and the continuous reading type? 1. The balanced type has figures in both directions from the zero as in Fig. 3. 2. The continuous reading type is numbered continuously as in Fig. 4. Figure 3 Balanced Typed Figure 4Continuous Typed 6- List several kinds of dial indicating gauges and briefly describe their use. 1. Dial indicator gauges Numerous special gauges are equipped with dial indicators. These gauges are used widely for determining whether parts are within required size limits. 2. Dial indicating depth gauges Fig. 7 is used for gauging or testing the depth of holes, slots, shoulders, recesses, and keyways. Extension points increase the measuring depths at which the gauge may be used. 3. Dial indicating snap gauges Fig. 8, are used for gauging diameters of parts to determine whether they are within the size limits specified. In use, the gauge is snapped over the diameter of
- 3. the part being gauged. Snap gauges are efficient for checking parts which are produced in large numbers, and they are available in a wide range of sizes. 4. A retractable contact snap gauge Is shown in Fig. 9, the contactor point is opened with a button located conveniently for thumb operation. This type of gauge is available in sizes which gauge, within certain ranges, from 0 -112 mm (0″ - 4 1/2″). 5. Dial indicating caliper gauges Fig. 10, have revolution counters which make it possible to measure directly through their complete range of 75 mm (3”). Calipers of this type are available with 0.02 mm (0.0008”) graduations. 6. Dial indicating hole gauges, Fig. 11, are used to gauge or test holes for size, taper, out-of-roundness, or other irregular conditions. They are available in a wide range of sizes.
