Increasing the probability of program success
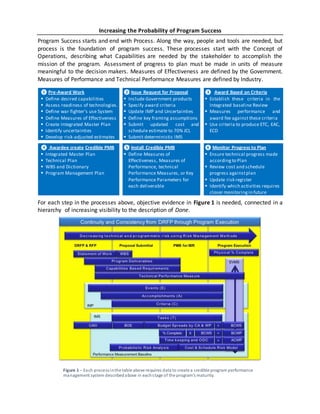
- 1. Increasing the Probability of Program Success Program Success starts and end with Process. Along the way, people and tools are needed, but process is the foundation of program success. These processes start with the Concept of Operations, describing what Capabilities are needed by the stakeholder to accomplish the mission of the program. Assessment of progress to plan must be made in units of measure meaningful to the decision makers. Measures of Effectiveness are defined by the Government. Measures of Performance and Technical Performance Measures are defined by Industry. For each step in the processes above, objective evidence in Figure 1 is needed, connected in a hierarchy of increasing visibility to the description of Done. ❶ Pre-Award Work Define desired capabilities Assess readiness of technologies. Define war fighter’s use System Define Measures of Effectiveness Create Integrated Master Plan Identify uncertainties Develop risk-adjusted estimates ❷ Issue Request for Proposal Include Government products Specify award criteria Update IMP and Uncertainties Define key framing assumptions Submit updated cost and schedule estimate to 70% JCL Submit deterministic IMS ❸ Award Based on Criteria Establish these criteria in the Integrated baseline Review Measures performance and award fee against these criteria Use criteria to produce ETC, EAC, ECD ❹ Awardee create Credible PMB Integrated Master Plan Technical Plan WBS and Dictionary Program Management Plan ❺ Install Credible PMB Define Measures of Effectiveness, Measures of Performance, technical Performance Measures, or Key Performance Parameters for each deliverable ❻ Monitor Progress to Plan Ensure technical progress made accordingto Plan Review cost and schedule progress againstplan Update risk register Identify which activities requires closer monitoringin future Figure 1 ‒ Each processinthe table above requires data to create a credible program performance management system describedabove in eachstage of the program’s maturity.
- 2. In my career, I've worked for a lot of really good managers, and of course, Gene Kranz was one of the best. One of the things I really admired about Gene ... is that of things didn't work out quite right in a project or in a ting that you were doing, Gene would often say, "Well, maybe I didn't explain as clearly as I should have what it was I needed you to do." ‒ Mission Control Center ISS Project Johnson Space Center Without a clear and concise description of Done in units of measure meaningful to the decision makers (Effectiveness and Performance), it's hard to know how to reach Done, how much it will cost to reach Done, and when we will be arriving at Done. This is the purpose of the processes described in this document - to provide the map with the route, cost, and measures of progress along the way to Done, while assuring when we arrive at Done, the deliverables implement the needed Capabilities of the system. These capabilities provide solutions for each process step. With the Roadmap in Figure 2, a credible Performance Measurement Baseline developed to inform the decision makers about progress to plan and corrective action opportunities. To increase the Probability of Program success, three phases of increasing procurement maturity must be in place. Figure 2 – Three Phases neededto construct a credible Performance Measurement Baseline fromthe Concept of Operations.
- 3. Concept of Operations (ConOps) A Concept of Operations (CONOPS) is a document describing the characteristics and intended usage of a proposed or existing system from the viewpoint of its users. Its purpose is to communicate the quantitative and qualitative system characteristics to all stakeholders and serve as a basis for stakeholder discussions about the system. Moreover, the CONOPS can help reach a “meeting of the minds” before the requirements process begins. Generated effectively, it may convey a clearer statement of intent than the requirements themselves. 1 Our approach to developing the Concept of Operation starts with a verbal or graphicalstatement that clearly and concisely expresses what the program intends to accomplish and how it will be done based on DoDAF V2.02 framework. The Concept of Operation includes: Current System or Situation - Background, mission, objectives, scope, operational policies and constraints - Operational environment and its characteristics with major system components and interconnections, Interfaces to external systems and processes - Capabilities or Functions of the current system - Performance characteristics needed to fulfill the planned system with their quality attributes needed to fulfill the planned system Concept for new or modified system - Background, objectives, and scope of new system with Operational policies and constraints of the new system. - Technical policies and constraints that impact the new system and operational environment and its characteristics for the major system components and interconnections - Capabilities or function for the new or modified system including activities and relationships WBS/CWBS/WBS Dictionary The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) defines the products and the services that produce those products in a Mutually Exclusive and Exhaustively Complete structured decomposition. Constructing the WBS starts with the Concept of Operations for the deliverables that implement that ConOps.The work breakdown structure’s define and organizing the project’s work. A project budget is allocated to the elements of the work breakdown structure. When the Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS) is defined, the staffing budgets are defined based on the each project's work breakdown structure. Allocating time and cost estimates to work breakdown elements, the project schedule and budget can be developed. As the project executes, specific sections of the WBS can be tracked to identify project cost performance and identify issues and problem areas in the project organization. The WBS identifies potential technical and programmatic risks. These risks are tracked and reviewed as the project executes. By integrating the WBS with an OBS, the project manager identifies communication points and formulate the communication plan across the project organization. 1 “Developing a Stakeholder-AssistedAgile CONOPS Development Process,” Ali Mostashari, Sara McComb, Deanna Kennedy, Robert, Cloutier, andPeter Korfiatis, Systems Engineering, Volume 15, Issue 1, 2012, pp. 1-13.
- 4. Operational and Technical Requirements Operational requirements are statements that identify the essential capabilities, associated requirements, performance measures, and the process or series of actions to be taken in effecting the results that are desired in order to address mission area deficiencies, evolving applications or threats, emerging technologies, or system cost improvements. 2 The operational requirements assessment starts with the Concept of Operations (CONOPS) and goes to a greater level of detail in identifying mission performance assumptions and constraints and current deficiencies of or enhancements needed for operations and mission success. Operational requirements are the basis for system requirements. Elicitation of these requirements starts with users' needs based on an operational needs assessment. Analysis of the needs identifies capability gaps and defines the operational and top- level characteristics and requirements of the system. Using CONOPS the operational needs, desires, visions, expectations, performance requirements, and challenges of the system are captured from the users, developers, and integrators, to define the system operational requirements, ensuring each requirement maps to an operational need in CONOPS. Integrated Master Plan Successful Program Management developing and maintaining plans and schedules for all program processes needed effective Government ‒ Industry interaction. With the contract in place, schedule, cost, and resources from the contractor established, the program plan accounts ‒ at an appropriate level of detail ‒ the contractor's strategy for the successful delivery of the programs outcome. The IMP, with its hierarchy of Significant Accomplishments (SA) and Accomplishment Criteria (AC), documents that the program is properly structured and executable within schedule and cost constraints with an acceptable level of risk. During the proposal evaluation and source selection phases, the IMP and IMS are critical components of the offeror's proposal; identifying the offeror's ability to decompose a program into tasks and phases to be successfully executed to deliver the needed capabilities. After contract award, the IMP and IMS are used by the contractor and the government as the day-to-day tool for executing the program and tracking program technical and schedule status, including significant risk mitigation efforts. The IMP is a Systems Engineering activity. describing the programmatic architecture in the same way the hardware and software are described in the technical architecture. A poor, weak, or unstructured Programmatic Architecture reduces the visibility to the Product Architecture’s cost and schedule performance measures and their connections with the Technical Performance Measures. 2 Kossiakoff, A., andN. Sweet, 2003, Systems Engineering Principles and Practices, Hoboken, N.J., JohnWiley& Sons.
- 5. Integrated Master Schedule Starting with the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), the Integrated Master Schedule summarizes the work and the order of the performance of the work for the Accomplishment Criteria (AC) in the IMP. 3 A well-constructed IMS contains distinct tasks summarized by WBS identifiers so the program can track progress and measure schedule performance. Risk mitigation and handling activities are included in the program IMP and IMS and resourced in the IMS. The IMP and IMS should be traceable to the program and contractor WBS and Statement of Work. Starting with the IMP’s top-down planning, the IMS bottom-up execution tool assures visibility to several critical success factors for the program. Measurable Criteria ‒ established by IMP Significant Accomplishments including accomplishment of critical performance requirements (Key Performance Parameters and Technical Performance Measures). Stakeholder Involvement ‒ including user organizations, financial managers, and sustainment organizations are involved in the work planning process from alllife-cyclephases to ensure that technical and support activities are adequately addressed in program plans in the IMP and IMS. Communication of Progress to Plan ‒ through the IMS with stakeholders on a regular basis. For enterprise systems with largenumbers of external interfaces and programs, the IMS is used as the integration tool to indicate and track milestones relevant to the other programs. Technical Performance Measures Technical Performance Measurement (TPM) are used to predict the future value of a key technical performance parameter of an end product under development based on current assessments of products lower in the system structure. TPMs define the planned progress of a selected technical parameter defined as the expected performance at specific points in the program as shown in the WBS, IMS, IMP. These connections start with Systems Engineering – where Measures of Effectiveness (MOE), Measures of Performance (MOP), Technical Performance Measures (TPM), and Risks are identified. TPMs are derived from MOPs and characterize the physical or functional attributes relating to the execution of the mission or function. TPMs may also be derived from Measures of Effectiveness (MOE) to become system cost and effectiveness metrics. The TPMs Performance parameters significantly qualify the entire system, with the parameters derived from analyses, demonstrations, or tests. The measure of value is the result of analyses or tests and is used to predict future values. Each parameter is periodically measured and profiled to compare with predicted values and tolerances over the project life cycle. 3 Air Force Pamphlet 63-128, “Integrated LifecycleManagement,” 10 July 2014
- 6. Technical and Programmatic Risk Management Risks are future uncertainties relating to achieving program technical and programmatic performance goals. 4 Uncertainty comes in two forms – reducible uncertainty (epistemic) and irreducible uncertainty (aleatory). These uncertainties create risk. Epistemic uncertainty can be handled with specific work, redundancy, testing, alternative plans. Aleatory uncertainty can only be handled with margin ‒ cost, schedule, and technical margin. Both handling methods must be defined in the Integrated Master Schedule ‒ risk buy down tasks and margin. Starting with a risk adjusted Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB), the information is needed to inform program performance using both reducible and irreducible risk. Statusing the reducible risks at the planned reduction date is similar to a Technical Performance Measure, where the target measure is improved as the program proceeds. Irreducible risks require schedule margin to protect contract events or end item deliverables. The connections between the program’s Technical Plan (delivery of technical outcomes compliance with needed MOE, MOP, and TPM) and the Programmatic Plan (Cost and Schedule) is the role of the Risk Management Plan. These risk management activities include standard risk processes with their risk reduction efforts as well as application of Management Reserve and Schedule Margin to assure acceptable program performance is met. Management of the Performance Measurement Baseline Performance measurement is the ongoing monitoring and reporting of program accomplishments, particularly progress toward pre-established goals. Performance measures may address the type or level of program activities conducted (process), the direct products and services delivered by a program (outputs), or the results of those products and services (outcomes). The Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) is a time–phased schedule of all the work to be performed, the budgeted cost for this work, and the organizational elements that produce the deliverables from this work. The PMB provides an integrated view of three project constraints: scope, time, and cost, and establishes a means to measure project’s performance in units of measure meaningful to the decision makers. There are three PMB’s: 1. The scope baseline from the WBS, projects specifications, design elements and deliverables 2. The time baseline in the approved project schedule, showing the planned start and finish of the work needed to produce the scope 3. The cost baseline for the budget and spend plan used to monitor cost performance Managing the PMB is part of Program Performance management ‒ a process for making course corrections to achieve an organization's goals by using performance information to adjust resources and activities. Focusing on Program Performance Management (PPM) is to focus on the future. Program Performance Management techniques track the progress and status of the project and forecast the likely future performance of the project. Information from the PMB’s performance provides corrective actions needed to Keep the Program Green. 4 “DOD Risk Management Guide,” V7, December 2014
