Model Analysis Methods And Tools For Case Study Research Generic
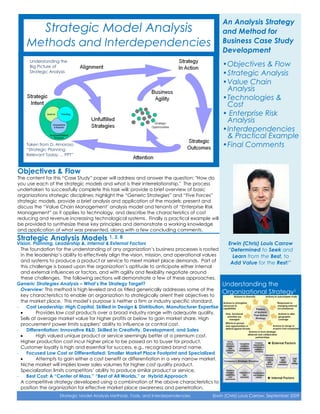
- 1. An Analysis Strategy Strategic Model Analysis and Method for Methods and Interdependencies Business Case Study Development Understanding the Big Picture of • Objectives & Flow Strategic Analysis • Strategic Analysis • Value Chain Analysis • Technologies & Cost • Enterprise Risk Analysis • Interdependencies & Practical Example Taken from D. Amoroso • Final Comments “Strategic Planning Relevant Today … PPT” Objectives & Flow The content for this “Case Study” paper will address and answer the question: "How do you use each of the strategic models and what is their interrelationship." The process undertaken to successfully complete this task will: provide a brief overview of basic organizations strategic disciplines; highlight the “Generic Strategies” and “Five Forces” strategic models, provide a brief analysis and application of the models; present and discuss the “Value Chain Management’ analysis model and tenants of “Enterprise Risk Management” as it applies to technology, and describe the characteristics of cost reducing and revenue increasing technological systems. Finally a practical example will be provided to synthesize these key principles and demonstrate a working knowledge and application of what was presented, along with a few concluding comments. Strategic Analysis Models 1, 2, 8 Vision, Planning, Leadership &, Internal & External Factors Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow The foundation for the understanding of any organization’s business processes is rooted “Determined to Seek and in the leadership’s ability to effectively align the vision, mission, and operational values Learn from the Best, to and systems to produce a product or service to meet market place demands. Part of Add Value for the Rest!” this challenge is based upon the organization’s aptitude to anticipate either internal and external influences or factors, and with agility and flexibility negotiate around these challenges. The following sections will demonstrate a few of these approaches. Generic Strategies Analysis – What’s the Strategy Target? Understanding the Overview: This method is high leveled and as titled generically addresses some of the key characteristics to enable an organization to strategically orient their objectives to Organizational Strategy1 the market place. This model’s purpose is neither a firm or industry specific standard. - Cost Leadership: High Capital, Skilled in Design & Distribution, Manufacturer Expertise Provides low cost products over a broad industry range with adequate quality. Sells at average market value for higher profits or below to gain market share. High procurement power limits suppliers’ ability to influence or control cost. - Differentiation: Innovative R&D, Skilled in Creativity, Development, and Sales High valued unique product or service seemingly better at a premium cost. Higher production cost incur higher price to be passed on to buyer for product. Customer loyalty is high and essential for success, e.g., recognized brand name. - Focused Low Cost or Differentiated: Smaller Market Place Footprint and Specialized Attempts to gain either a cost benefit or differentiation in a very narrow market. Niche market will implies lower sales volumes for higher cost quality product. Specialization limits competitors’ ability to produce similar product or service. - Best Cost: A “Center of Mass,” “Best of All Worlds,” or Hybrid Approach A competitive strategy developed using a combination of the above characteristics to position the organization for effective market place awareness and penetration. Strategic Model Analysis Methods, Tools, and Interdependencies Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow, September 2009
- 2. Generic Strategies Five Forces Strategies Analysis & Success Factors 1, 2, 8 Center of Mass - Best Cost 1, 2 Overview: The following questions highlight the characteristics that are used to identify competitive complementation and distinctions that could threaten or produce an advantage for the organization to gain or lose market share. When assessing the organizations market place strengths and weaknesses the key issues are price and quality, scope of geographical offerings, service or product line distinctions and variety, distributions channel capability, capital, and technological innovations, all to identify cost advantage or differentiation. - Key Success Factors: Questions to ask when forming a strategy What is the basis of the customer choosing between one service or product offerings and another’s’? Why will buyers chose our commodity over others? What capabilities, resources, or distinctions make a product or service superior to another? Does our product or service standout as superior per cost? SWOT Analysis 1, 2 What would need to be changed to ensure sustainable market dominance? What analysis and decisions need to be made to create a market place advantage for our organizations success? - Buyers Analysis: The ability of the buyer to dictate influence or authority Does the industry have a “Buyer versus firm concentration” that affects the potential for market share growth? Does the buyer’s ability to purchase in volume influence cost and profit? Is the buyer’s “switching cost” as relative to the organization’s switching cost and enough to deter loss of revenue or should more emphasis be place in the interoperability of the service or product offerings? Will product or service offerings ability for backward integration influence the buyer’s decision making purchasing process? How is the price of total purchase and brand identity important to the buyer? Example: Contracted government product or service purchase from authorized contractors or vendors. Five Forces Model 1 - Suppliers Analysis: The ability of suppliers to exercise control or influence Will the “differentiation of inputs” increase cost and reduce the product demand? Can “switching cost of suppliers” detract from the organization’s ability to influence the industry market place? Is there a “supplier concentration” or lack that will deter or increase product or service cost and impact revenue? How is volume purchasing for the supplier important and can it be an advantage or disadvantage, or affect organizations’ cost negotiation capabilities? Do the suppliers cost influence the total purchase or the industry’s market? Example: Silicon availability for memory chip suppliers for critical part relationship with computer manufacturers. No silicon – no memory – no computer production. - Substitutes Analysis: The threats of substitution for a service or product Are there similar products or services available from competitors that could Buyer and Supplier Power 2 potentially affect market share? Will the price and performance of substitute products or services potentially displace an organization’s market share? What is the likelihood or impact of the buyer’s tendency to substitute another product or service – can a substitute be offered and what is the expected impact? Example: A TV’s versatility or capability to support computer based video technology. - New Entrants Analysis: The potential of new competitors to usurp market share Does the competition have the ability to exercise “economies of scale” and adversely influence the market and reduce the organizations market share? Are there “proprietary product difference” that limit or inhibit entrance of competitors? Is “brand identity” a maintainable advantage and deterrent for new entrants? Are there switching costs that would deter or encourage competitors’ capability to enter into the market place? Will capital revenue requirements and access to distribution channels limit or encourage competition Decision Making Process to enter into the market place? Example: Government imposed legal compliance or limitations for distribution of various sensitive or confidential technologies to other countries that potentially may undermine national security. - Rivalry Determinants Analysis: The level of intensity that may limit competitors What is the “potential of industry growth” for the current market? What “product differences” and “brand identity” limit rivalry influence? Can the industry’s “intermittent overcapacity” affect the market growth? Is there a “concentration or balanced” level of competition that would require a change in strategy, and what are the “barriers to an exit strategy? Does the “diversity of competitors” limit or adversely influence market share success? Example: Organization could temporarily raise or lower prices to gain an advantage or change product or services by improving innovation or more differentiation. Page 2 “Strategic Model Analysis Methods … “ Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow, Erwin.carrow@usg.edu September 2009
- 3. Value Chain Management Analysis (VCM) 3, 5, 7 Overview: The value chain model is an analysis tool for identifying an organization’ “core competencies” and the needed actions for a competitive edge. Analysis of the value chain management consists of: 1) evaluation of the purchasing process from suppliers and the inbound logistics for cost reduction and mitigating potential threats; 2) operations’ focuses on assessing business functional processes to increase efficiency, productivity, and lower cost; 3) distribution and outbound logistical considerations are critical, and require the evaluation of the product order to delivery “life cycle” to ensure effectiveness; 4) sales and marketing activities are assessed to make sure that necessary investments are made in sales channels to support potential buyers; and finally, 5) services demands analysis that assess the various processes to support customers after a purchase has been made. An organization’s success is dependent on having a thorough understanding of all these factors to ensure they remain competitive in whatever industry they have invested or market strategy they support. Primary & Support Activities: The logistics and behind the scene requirements to produce a service or product Procurement: Assesses purchasing efforts of materials, supplies, and equipment for the various activities needed to produce a product or provide a service. This task is essential to controlling cost and supporting general business operations. Technology Development: Considers research and development of technological capabilities to support value- creating systems to lower production cost. Ensures all operations and product or service order fulfillment work efficiently. Human Resource Management: All organization processes for employee recruiting, hiring, training, development, and compensation. No industry can afford to not invest in people to support the people who buy their products or services. Firm Infrastructure: organizational structure, control systems, company culture, and the typically industry focus, etc. - Inbound Logistics Analysis: Receiving, Raw Product Warehousing, and Inventory Control The receiving and warehousing of raw materials and their distribution to manufacturing as they are required. An effective control may be to move manufacturing processing closer to the raw products needed, to limit inbound logistical handling and transportation cost. Development relations with key suppliers to ensure demanded resources are always available and that agreements can be made to decrease purchases when buyer demands is lessened. Technologies used are Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems that monitor and manage all facets of the supply progression and logistics. - Operations Analysis: Key Activities, What’s Required to Transform Input to Final Product The processes of transforming inputs into finished products and services for the life cycle of key business functions. Various types of business functions exist that need to be managed and monitored to ensure products are effectively being produced. Technological systems are needed for material handling, maintenance, packaging, machinery, building design and operations, and information and information systems. Technology used is an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system that manages and monitors all facets of operations. System is used to support all activities used to produce a commodity. - Outbound Logistics Analysis: Warehousing, Order Fulfillment, and Customer Product Delivery The warehousing and distribution of finished goods to ensure the finished product is successfully delivered. Requires the evaluation of how transportation, material handling, packaging, communications, and information and information systems are being used to get the product or service to the customer. Key tasks ensure the necessary inventory is always available. - Marketing & Sales Analysis: Channel Selection, Advertising, and Pricing The identification of customer needs, the generation of sales, and includes timing of market entry for new product lines. Assesses public media promotion, employs the use of audio/video communications and Customer Relations Management (CRM) technological information system. Key tasks ensure market place awareness and penetration to increase sales. - Service Analysis: Value Enhancement, Customer Support, and Repair Services The support of customers needs after the products and services are sold. Uses surveys and tests consumer feedback, communications, and uses a Customer Relations Management (CRM) technological information system to manage and monitor business functional processes. Key tasks include developing innovative approaches to gaining additional sales. Cost advantage: Is gained by having an understanding of costs and limiting unnecessary loss through value-adding activities. Once value chain is defined, cost analysis can then justify expenses associated with each of the phases and specific tasks. Differentiation: Is achieved by focusing on activities associated with the organization’s core competencies and strengths in order to perform them more effectively than their competitors. Organization looks at policies and decisions, business interrelationships, integration issues, quality of scale, and other institutional factors to determine distinctions and efficiency. Enterprise Resources Planning, Supply Chain Management, and Customer Relations Management - Decision Systems 1,5 Page 3 Strategic Model Analysis Methods … “ Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow, erwin.carrow@usg.edu September 2009
- 4. Data Value Chain Technology and Cost Considerations 8 Systems used to manage and mitigate unexpected cost through the use of advance Diagram technological systems to provide more predictability for corporate solvency. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) - System manages the organizations’ integration of high level business functional and operational requirements to ensure success. Without a clearly defined plan and ERP system the functional capability of the organizations general operations is unpredictable and will contribute to revenue losses. Areas of Enterprise Resource Planning and a brief description are: Research and Development, Product Production and Fulfillment Management, Human Resource Management, Fiscal Resource Management. Accounts for the organization’s operations and is used to define, manage, and monitor product and service orders, shipping, billing, and miscellaneous operational needs to reduce product managing errors and provide real- time awareness of business transactions. System improves accuracy for understanding the organizations business rules and requirements and how to sustain the needed Business Intelligence infrastructure resources and improve associated business functional and operational processes. The system helps to improve process efficiency and limit unnecessary cost. Transactional System5 Supply Chain Management (SCM)3 - System manages the organizations’ integration of manufacturing processes, non-integrated distribution processes and relationships with suppliers to ensure success. Without a clearly defined plan and SCM system the impact on the whole supply chain becomes unpredictable and will contribute to revenue losses. Areas of supply chain and a brief description are: Procurement and Material Management, Manufacturing, Inventory and Warehouse Management, and Transportation, Distribution, and Coordination Management. Accounts for various demands and is used to plan objectives to reduce forecast error and create buffers regarding the demand variability. System is used to improve accuracy of forecasting and collaborative forecasting for all logistical requirements. Processes provides multi- site planning for usage of material, capacity capability, transportation and other constraints, simultaneously. Assesses the procurement constraints of vendor capacities, costs and lead times, to be modeled for incorporation into a supply chain plan. System considers the dynamics of transportation requirements and optimizing logical support accordingly. Identifies materials, capacity and other constraints which impact on manufacturing and suggests adjustments accordingly and is cost reduction focused. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) - System manages the organizations’ Ansoff Matrix and “business face” and provides market penetration tools to ensure their success. The Innovation2 CRM system’s functional capability for the organization is to generate market share influence and support customer requirements that could contribute predictable revenue gains. Areas of Customer Relations Management and a brief description are: Sales Management, Service and Support Management, and Product and Service Marketing. Accounts for customer demands and is used to assist product sales and marketing objectives. System is used to track and organize contacts for current and prospective customers and improve relations. Processes provide a method for storing customer interactions that can be accessed by employees or different department or organizational entities. Provides an analytical resource for understanding customer needs and influences for potential use and exploitation of market place environment variables. Assess sales and market place constraints that deter integration of product offerings and the dynamics of the buyers’ environment. Innovates incentives for promotions to facilitate the capabilities of organization’s product to increase revenue. Key Success Factors 1, 2 Enterprise Risk Management Analysis (ERM) 6 Scope, Size, Experience, and Associated Volatility? The ERM process is where an organization sets the level of risk tolerance to sustain, and attempts to identify and prioritize potential risks as related to the business goals, objectives, or functional and operational business processes. ERM utilizes internal controls to manage, monitor, and mitigate risk throughout the organization. A Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) system is often used to analyze, manage, and monitor Enterprise Risk. This system was not addressed in class. - Strategic: Affects the organization’s ability to achieve goals and objectives Each organization must contextualize a long and short term strategy to determine what potential risks may deter or inhibit product success. It is typically dependent upon leadership and results are often from adverse business decisions or improper implementation of decisions. Example: Failure of leadership to plan and budget expenditures for new innovative technology to lower cost and increase sales revenue could produce risk. Page 4 “Strategic Model Analysis Methods … “ Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow, erwin.carrow@usg.edu September 2009 Page 3
- 5. Compliance: Affects are from the lack of compliance with laws and regulations, safety Strategic Planning and environmental issues, litigation, conflicts of interest, etc. Process 2 Arises from an organizations’ failure to create and enforce appropriate policies, procedures, or controls to ensure it conforms to laws, regulations, or organizational constraints. If often interdependent with cultural values, ethics, and governance. Example: Non effective technologically automated controls for PCI DSS, FERPA, or HIPAA privacy of information compliant, which can influence either Reputational Risk or Financial Risk, e.g., someone’s personal information gets stolen from the organization. - Reputational: Affects are loss of reputation, public perception, political issues, etc. This risk is difficult to categorize, predict, control, or mitigate Affect can be immediate or overnight and difficult to recover from, often can quickly undermine the organizations stability and solvency. An organizations reputational value is difficult to calculate. Example: Organization’s security of information or information systems breached and exploited by hackers and the event gets public attention. Financial: Affects are loss of assets, resource procurement, technology, etc. Risk base of influencing factors is broad and often not clearly defined or predictable, but results in fiscal loss. Example: Lack of proper technological tools to audit financial transactions or controlled bookkeeping practices to identify problems. Operational: Affects are often the loss of effective or efficient on-going management processes and procedures These losses occur from inadequate or poorly controlled internal processes associated with people and systems, or external influences and events. Example: Poor Risk Life Cycle 6 implementation or antiquated ERP, SCM, CRM, or GRC systems that fail to provide efficient and effective cost savings support. Interdependencies and Practical Example 3, 5 Overview: A competitive business environment requires more than the standard budget- oriented planning or forecast-based planning method to ensure success. Strategic planning must be undertaken to define the goals, objectives and associated business rules and requirements for all internal and external organizational circumstances that might be encountered in their industry market place. Once developed and implemented, the strategy should to be periodically evaluated to ensure progress, and adjusted as necessary to maintain market relevance. This strategy should always align with the organization’s essential characteristics. Some of these basic essentials are exemplified in a vision and mission statement which describes the organizations long term to short term values, ethics, purpose, and practical operational ideals documented in a strategic, tactical, and Potential Risk 6 operational set of plans. From these key elements, the organizations leadership should identify measurable financial and strategic objectives. These objectives should include sales, earnings, market share growth, and how to position the organization for future success for their industry. Effective Leadership is critical to the entire processes success! Key Strategic Processes: Critical to this process requires that the organization conduct a self-evaluation and analysis, to identify internal strengths and weaknesses and any external opportunities and / or threats. This evaluation includes the aforementioned areas of Generic Strategic Analysis, Five Force Analysis, Value Chain Management and Analysis, Cost and Technology considerations, and a definable Enterprise Risk Management and analysis process. After having assessed and provided the analysis this information should identify organization’s strengths in direct proportion to the potential opportunities, and address similar internal weaknesses or external threats that might deter success. Therefore to achieve consistent profitability, the organization must develop a competitive advantage that is based on cost and /or differentiation. This selected set of strategies should be the Transition Management basis for all the organization’s programs, budgets, and functional operational procedures, Strategy 2 and the implementation involve all of the organization’s resources and be effectively communicated to achieve the identified goals or objectives. Simple Practical Example: The following example is an exposition of a study conducted. The process will highlight the following steps: 1) define factors to be measured, 2) define target values for those factors, 3) conduct measurements, 4) compare measured results to the pre-defined strategic factors, 5) demonstrate how to make necessary changes or adjustments. The factors that are to be measured are the various technological systems used to manage, monitor, and optimize the processes and outcomes of various business functions, e.g., ERP, SCM, CRM, and GRC. The target to be achieved is real-time business intelligence information to assist an automated response to changes from environmental factors. These types of influences identified from the Value Chain Management or Enterprise Risk Management systems can impact an organization’s cost and profit. Target values are determined per the organizational goals, business strategy analysis (Generic and Five Force), value chain management analysis, and these then baselined with preset Page 5 “Final Exam – Strategic Model Analysis Methods … “ Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow, ecarrow@gmail.com IS-8950, Spring 2009
- 6. settings in the various aforementioned information technology systems. These systems’ performance measurements are then gathered, and the information stored in both an archival historical trending analysis data warehouse system and a real-time transactional Basic Strategic information cached system. From these systems and through analysis on the data Building Blocks2 warehouse and cached systems’ information, performance measurements can be conducted for both long and short term objectives. Business Intelligence (BI) reporting can Vision and Mission then be done to assist leadership in making good decisions. More importantly, real-time Statement Constructs procurement, product creation, inventory control, warehousing, distribution, and other logistical or customer oriented service and support can be automated for immediate response and tempered from the historical trending and analysis. Changes or adjustments can be both immediate and evaluated to anticipate seasonal trends to meet business objectives and improve efficiency. This process cuts cost and anticipates potential needs. How It Works: The process involves multiple tiers of technology, the first tier would be client access by the user to input relevant real-time data through a portal based application. From the data inputted, a second tier or middleware application would forward the data to the appropriate system, e.g., ERP, SCM, CRM, or GRC. These systems would then perform per their designated function and typically store their data in third tier transactional databases. From these transaction databases an Extract, Translation, and Load (ETL) would be conducted to replicate information into both a data warehouse and data cached systems for immediate analysis by the transactional caching system and long term trending by the data warehouse system. Various methods and tools would interface with the Diamond of National information to automate both types of responses to facilitate good business decisions Advantage (fourth and fifth tier). Human intervention could also be included for automated responses to the Business Intelligence reports that were out of the predefined scope of “acceptable change” to any of the key business functions previously mentioned, e.g., procurement, product creation, etc. The significance is that viable relevant information is timely presented to leadership based upon their strategy and organizational objectives with real- time business information for critical decision making that is immediate and tempered with historical trended analysis. Several diagrams illustrate this process and are presented on pages 4 and 5. Operational and strategic risk is mitigated by real-time decision making. Summary of Functionality: Clearly we can see from this process that strategy and market influence is calculated into the various technological systems to provide an automated response to real-time events from systems throughout the business life-cycle of an organizations’ product or service. Knowledge is power and this application provides the organization the ability to respond with flexibility and agility. With this advantage, more differentiation and cost savings can be used to position an organization to be more effective for their industry market penetration and the sustainment of a competitive edge. Value Creation Final Comments As demonstrated in the preceding example and earlier analysis, this paper has addressed and answered the question: "How do you use each of the strategic models and what is their interrelationship." I have explained in detail the various facets of the: foundational business concepts, generic strategies, Porter’s Five forces, value chain management and analysis processes, technology and cost factors, and a high level application of enterprise risk management for technology. And finally, all of these components were interconnected to demonstrate how an organization could process and apply these to increase their market potential and capability to achieve strategic outcomes. References 1. Various graphs and diagram taken from D. Amoroso Instructional strategic models.pdf COBIT – Business’ and class notes and readings Functional Goals or 2. Various strategies models and diagrams taken from Objectives http://www.quickmba.com/strategy 3. “Supply Chain Modeling using Simulations” by Yoon Chang and Harris Makatsoris; I. J. Dependencies4 of SIMULATION Vol. 2 No. 1. ISSN 1473-804x online, 1473-8031 4. COBIT - www.isaca.org/cobit 5. “Real Time Business Intelligence in Supply Chain Analytics” by Sahay, B.S. & Ranjan, J. in Information Management & Computer Security(2008). ; Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 28-48. 6. ERM definitions and standards were taken from University System of Georgia Board of Regents Office of Internal Audit, Institute of Internal Auditors, and Information Systems Audit and Control Association 7. “Benefits, barriers, and bridges to effective supply chain management” by Fawcett, S. E., Magnan, G., & McCarter, M. W., from Supply Chain Management: An International Journal; Vol. 13, No. 1 pp. 35–48 (2008) 8. “Corporate Information Strategy and Management: Text and Cases” by Applegate, Austin, & McFarlan Eighth Edition, Boston: McGraw-Hill Irwin(2009) Page 5 6 “Strategic Model Analysis Methods … “ Erwin (Chris) Louis Carrow, erwin.carrow@usg.edu September 2009