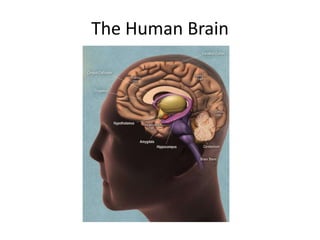
Language and the brain
- 3. Interesting brain facts! • About 1.4 kg (2% of body weight) mass of fat & protein with 75% water content • W = 140 mm, L = 167 mm, H = 93 mm. Left hemisphere is larger than the right • 40% grey matter (outer covering: cerebral cortex) 60% white matter (myelinated fiber tracts traveling to & from the cerebral cortex) • Uses 10 – 23 watt of energy, consuming 20% oxygen from the body. Goes unconscious in 8 – 10 sec. w/o oxygen • 100 billion neurons (166 times human population & would take 171 years to count! (Tony Buzan) • 2,50,000 neurons/ minute in early development & stops growing at 18 • 12 pairs of cranial nerves & 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Thinking initiates electro-chemical-neuro-impulse transmission from 0.5 m/sec - 120 m/sec. (434 km/hr)
- 4. Parts of the brain Keep in mind there are two distinct sides with different functions
- 5. The Brainstem (Pathway to the Body) • Base of brain • Unconscious work • Autonomic functions, e.g., survival, breathing, body functions, etc.
- 6. The Cerebellum (Balance) • ‘little brain’ • Large in size • 11% of brain’s weight • Center of balance
- 7. The brain has 4 areas called lobes • Frontal • Parietal • Temporal • Occipital
- 8. The Frontal Lobes (Problem Solving) • Largest part • Moves your body • Highly developed • Forms your personality
- 9. The Parietal Lobes (Touching) • Two major divisions Anterior and posterior • Senses hot and cold, hard and soft, and pain • Taste and smell • Helps integrate the senses
- 10. The Temporal Lobes (Hearing) • Processes auditory stimuli • Subdivisions into • Wernicke’s Area (associated with speech comprehension) • Broca’s Area (associated with speech production)
- 11. The Occipital Lobes (Seeing) • Located at lower central back of brain • Processes visual stimuli
- 12. Taking sides….two sides that is! • Two sides or hemispheres of the brain: LEFT and RIGHT • We have two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum • This is a bundle of nerves that allows each side of the brain to communicate with each other • Each side of the brain processes things differently • It is an outdated assumption that “artsy” type people are right-brained
- 13. How the two sides process information! Left Brain • Logical • Sequential • Rational • Analytical • Objective • Looks at parts Right Brain • Random • Intuitive • Holistic • Synthesizing • Subjective • Looks at wholes
- 14. Left Hemisphere • processes things more in parts & sequentially • recognizes positive emotions • identified with practicality and rationality • understands symbols and representations • processes rapid auditory information faster than the right (crucial for separating the sounds of speech into distinct units for comprehension) • is responsible for language development. It develops slower in boys, that is why males usually develop more language problems than females
- 15. Right Hemisphere • recognizes negative emotions • high level mathematicians, problem solver like chess playing • the “non-verbal” side • responds to touch & music (sensory) • intuitive • responsive to color & shape • emotional & creative
- 16. Taking sides…. what information the two sides recognize! Left Brain • Letters • Numbers • Words Right Brain • Faces • Places • Objects based on Sousa (1995, p. 88)
- 17. Taking sides….take the test! http://capone.mtsu.edu/studskl/hd/hemispheric_dominan ce.html
- 18. Aphasia
- 19. • Aphasia is defined as an acquired impairment in the use of language due to damage to certain parts of the brain • This damage could be caused by injury, stroke, or seizures • The language deficits include difficulties in language comprehension and execution
- 20. Major Types of Aphasias All aphasias can be classified into two groups • Fluent aphasias – The inability to understand the language of others and the production of less meaningful speech then normal • Non-fluent aphasias – Difficulty producing fluent, articulated, or self- initiated speech
- 21. Types of Fluent Aphasias • Wernicke’s aphasia – People with this type of aphasia have difficulty or inability understanding others speech, and produce meaningless speech – They generally do not realize their speech is meaningless and are surprised when others cannot understand them – They may demonstrate paragrammatical speech, which means they use inappropriate morphemes. For instance a person my say to you instead of for you or substitute the word pork for fork – This type of aphasia is produced by damage to Wernicke’s area of the brain Video of someone with Wernicke’s aphasia
- 22. More Types of Fluent Aphasia • Conduction aphasia – The main symptom of this type of aphasia is difficulty repeating something someone has just said – People with this condition have relatively good language comprehension and their conversational speech is only mildly impaired – This type of aphasia is produced by damage to the left temporoparietal region – It has been suggested that this type of aphasia could come about because of deficits in short term memory or phoneme selection
- 23. More Types of Fluent Aphasia • Anomic aphasia – This aphasia is characterized by difficulty finding names and difficulty substituting indefinite nouns and pronouns with substantive words. For instance, people with this affliction will use words like, thing, stuff, or it instead of automobiles, groceries, or furniture. – There are very few cases of pure anomic aphasia and it is therefore difficult to find the area of the brain responsible – Some have suggested that it is a mild form of Wernicke’s aphasia
- 24. More Types of Fluent Aphasia • Transcortical sensory aphasia – Symptoms of this type of aphasia are fluent speech with some anomia, poor language comprehension, and echolalia. – Echolalia is the tendency to repeat something someone has just said. For instance, if a person with this type of aphasia was asked, “What is your name?” they are predisposed to repeat the question over and over instead of answering it. – This aphasia may be caused by damage surrounding and including Wernicke’s area
- 25. Non-Fluent Aphasias • Broca’s aphasia – This type of aphasia manifests with difficulties initiating well-articulated conversational speech – The language that is produced is slow, labored, and agrammatical, which means words like a, an, or the and verb tense is left out of their speech – This aphasia is produced by damage to Broca’s area of the brain Video of someone with Broca’s aphasia
- 26. More Types of Non-Fluent Aphasia’s • Transcortical motor aphasia – People with this aphasia do not speak unless they are strongly encouraged to do so and when they do speak it is labored and non-fluent – Interestingly enough when these people are verbally presented with long complicated sentences they are able to repeat them fluently – This aphasia is produced by damage to the premotor cortex anterior and superior to Broca’s area
- 27. More Types of Non-Fluent Aphasia’s • Global aphasia – As the name suggests, this type of aphasia is characterized by a severe depression of all language functioning – The people with this affliction have poor language comprehension and speak in slow, labored jargon – This aphasia is caused by damage around and to Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas of the brain
- 28. Other Interesting Facts About Aphasia The handwriting of a person with an aphasia reflects their speech impediment. There was an experiment done where people with Broca’s and Wernicke’s aphasias were presented with a picture and then asked to write down a description of what they say in the picture.
- 29. This is the picture
- 30. A patient with Broca’s aphasia wrote this Notice the use of very few words, but the words do make some sense
- 31. A patient with Wernicke’s aphasia wrote this Notice here that there are many, less forced, words, but they don’t make much sense. Also because they’re not struggling to find their words, the handwriting is better.