Plasma membrane -
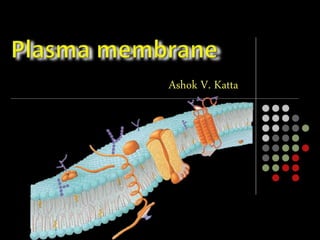
- 2. The plasma membrane, lipid bilayer A flexible yet sturdy barrier that surrounds and contains the cytoplasm of a cell. Is described by the fluid mosaic model.
- 3. The molecular arrangement of the pl. membrane resembles an ever-moving sea of fluid lipids that contains a mosaic of many different proteins. Some proteins float freely like icebergs in the lipid sea, whereas others are anchored at specific locations like boats at a dock. In simple words, Pl. membrane is phospholipids bilayer containing embedded proteins and cholesterol. Carbohydrates are present on the surface as glycoprotein or glycolipids. Cell membrane is selective permeable.
- 5. The basic structural framework is the lipid bilayer. Mead up of 3 macromolecules……… Lipids Proteins Carbohydrate.
- 6. 75% - phospholipids 20% - cholesterol 5% - glycolipids. Mostly lipids are Amphipathic having both polar & nonpolar parts. Acts as permeability barriers. Essential for the maintenance of fluidity of membranes. Membrane lipids:-
- 7. Head Tail “Head” – Polar part – phosphate group “Tail” – Non polar part – long chain fatty acids These includes…… phosphptidylcholine, phosphptidylethanolamine, phosphptidylserine, phosphptidylinositol, plasmalogens & sphingomyelin. Phospholipids Phosphate gr. fatty acid
- 8. Cholesterol molecules are weakly amphipathic & are interspersed among the other lipids in both layers of the membrane. Glycolipids present only in the membrane layer that faces the extracellular fluid.
- 9. Membrane Proteins Two types of proteins are present in membrane Integral proteins peripheral proteins Integral proteins extend through the lipid bilayer are firmly embedded in it. Most integral proteins are transmembrane proteins. Peripheral proteins are not embedded in the membrane. They associate more loosely with the polar heads of membrane lipids at the inner or outer surface of the membrane. Many membrane proteins are glycoproteins.
- 11. Ion channels Carriers (transporters) Receptors Enzymes Cell identity markers (glycoproteins & glycolipids) Membrane Proteins (functions)
- 12. Membrane Carbohydrate Carbohydrate are covalently bound to lipids to form glycolipids And to the protein to form glycoproteins. These are mostly Glucose Galactose Mannose N-acetyl glucosaine N-acetylgalactosamine
- 13. Transport of materials across the plasma membrane is essential to the life of a cell. It also essential to maintain equilibrium of cell Certain substances must move into the cell to support metabolic reactions. Other substances which produced by the cell for export or as cellular waste products must move out of the cell. Transport across Cell membrane
- 14. Passive transport. Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Active transport. Primary Active Transport Secondary Active Transport Bulk Transport Exocytosis. Endocytosis. Transport across Cell membrane
- 15. Passive transport. Simple diffusion :- moment of particles from the area of higher conc. To an area of lower conc. (i.e down the conc. gradient). It does not require energy and membrane transport proteins. Example – Transport of gases, Transport of ions and Transport lipid soluble molecules
- 16. Facilitated diffusion- Diffusion of molecules down the conc. gradient which require carrier protein. It does not require energy. It more rapid than simple diffusion. It works as ping-pong mechanism. Example- Absorption of fructose, Glucose transport.
- 17. Uniport, antiport. Based on direction of moment of molecules, facilitate diffusion can occur by Uniport- transport of single type of molecule in one direction. E.g. absorption of fructose. Antiport - Transport of molecule in opposite direction. E.g. chloride-bicarbonate exchanger. Uniport Antiport
- 18. Osmosis. The diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane. Movement of water molecules occur from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. Clinical Significance- Decreased formation of urine in hypovolemic conditions. Edema due to hypoalbuminemia. Tonicity and its effects on red blood cells (RBCs).
- 19. Two types Primary Active Transport. Secondary Active Transport. Active Transport.
- 20. Primary Active Transport. Transport against conc. gradient in which energy is used directly. It is carrier mediated. It requires energy in the form of ATP & used directly. Example – sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump.
- 21. Sodium-Potassium Pump (Na/K ATPase) Also called Sodium pump. In this pump, 3 sodium ions moves out of the cells and 2 potassium ions moves inside the cell. With consumption of 1 ATP molecule. This is maintain low intracellular Na+ & high intracellular K+.
- 23. Transport against conc. gradient in which energy is used indirectly. The transport of two or three molecules are coupled. This transport is coupled with Na-K ATPase, that requires the ATP. It occurs by symport and antiport. Secondary Active Transport.
- 25. Symport (co-transport) Molecule move in same direction. Example- Sodium-glucose symport Sodium-amino acid symport. Disorders- cystinuria & Hartnup disease (mutations in sod-amino acid symport)
- 26. Antiport (counter transport) Molecule move in opposite directions. Example- Sodium-hydrogen exchanger (Renal tubule) Calcium-hydrogen exchanger (cardiac muscle)
- 27. Also called transport by vesicle formation. It involves formation of membrane bound vesicles. It involves transport of macromolecule. Bulk transport.
- 28. Expulsing out of molecules from the cell. Fate of molecule released by exocytosis may be…….. Peripheral proteins Part of extracellular matrix Release to extracellular medium. Exocytosis.
- 29. Engulfing large molecules by the cell. Two type of endocytosis. Phagocytosis- large substances such as bacteria are taken within cell. (macrophages) Pinocytosis- fluid or fluid contents are taken within the cell. Endocytosis.
- 30. Endocytosis.
- 31. Quick Review Define the Cell. Structural and Functional Unit of Life Which organelle is the control center of the cell? Nucleus Which organelle separates the cell from external environment? Cell membrane Which organelles Detoxifies drugs & harmful substances? Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Which organelle helps in Modification, sorting, packaging, & transportion proteins? Golgi Complex. Niemann pick disease is caused by faulty functioning of which organelles? Lysosomes.
- 32. “THANK U” Contact no. – 07418831766 E mail – ashokktt@gmail.com Ashok Katta Dept. of Biochemistry, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Medical College, Perambalur
