Wet process for it
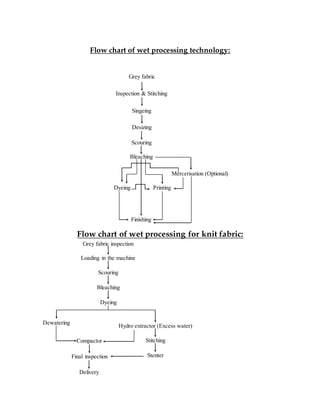
- 1. Flow chart of wet processing technology: Flow chart of wet processing for knit fabric: Grey fabric Inspection & Stitching Bleaching Singeing Desizing Scouring PrintingDyeing Finishing Mercerisation (Optional) Grey fabric inspection Loading in the machine Scouring Bleaching Dyeing Dewatering Hydro extractor (Excess water) Stitching Stenter Compactor Final inspection Delivery
- 2. Singeing: Singeing is a process by which projecting or floating fibres, stand out on the surface of the fabric are burned off. Objects of Singeing: 1 To remove hairy fibres projecting on the surface of cloth and given a smoothen face. 2 Optical levelness of the dyeing and clean-out lines of a printing design. 3 To increase lusture in the finished fabric. 4 To prepare the fabric for next process. Desizing Desizing is the first wet processing textile finishing technology employed to remove the sizing material from the fabric. It depends on 1. The solubility of the film forming polymer. 2. On the effects of numerous subsequent wet processing steps. 3. On the interactions with added chemicals. Objects of desizing: 1. To remove starch from the fabric. 2. To increase absorbency of the fabric. 3. To increase lusture of dyeing and printing. 4. To perfect action of scouring and bleaching. 5. To make the fabric ready for the next subsequent process. Types of De sizing: Methods of De sizing Oxidative method. a. Bromite de sizing. b. Chlorite de sizing. c. Ammonium per sulphate desizing. Hydrolytic method a. Rot Steeping. b. Alkali steeping. c. Acid steeping. d. Enzymatic steeping.
- 3. Scouring: Scouring is the process by which all natural and adventitious impurities such as oil, wax, fat etc. are removed to produced hydrophilic and clean textile material. It is the vital process of wet processing. Objects of Scouring: 1. To make the fabric highly hydrophilic. 2. To remove impurities such as oils, waxes, gum, husks as completely as possible. 3. To increase absorbency of fabric or textile materials without undergoing physical and chemical damage. 4. To produced a clean material by adding alkali. 5. To remove natural colour and make the fabric for next process. 6. To remove non-cellulosic substance in case of cotton. The changes occurring of cotton fibers during scouring: 1. Saponifiable oils and free fatty acids are converted into soaps. 2. Pectins and pectoses are converted into soluble salts of pectic acid. 3. Proteins are degraded to simple soluble amino acids or ammonia. 4. Mineral matters are mostly dissolved. 5. Un saponifiable oils are emulsified by the saponifiable matters. 6. Adventitious dirt are removed and forms in suspension by the soap. 7. Residual sizing materials are broken down into soluble products. Assessmentof scouring:/Absorbency test: 1. Drop test: In a pippet a solution of direct red (Congo red) solution is taken and dispersed on the scoured fabric such that not spread. Then the absorption of the coloured drop is observed visually. The standard time for the absorption of one drop of solution is 0.5-0.8s up to 1 sec. 2. Spot test:- In a pipette a solution of 0.1% direct red or Congo red is taken and droplet of solution put on the different places of the fabric. Then the shape of the absorbed area on the fabric is observed. Good scouring Uniform scouring Uneven scouring
- 4. Souring: The treatment/the process by which the fabric, after processing with alkali or scouring, is treated with Hydrochloric acid or dilute H2SO4 for removing alkali or neutralization of alkali is scouring. Bleaching: Bleaching of textile material is a chemical or commercial process which can be defined as – Destruction of natural coloring matters to impart a pure permanent and basic white effects suitable for the production of white finishes, level dyeing and desired printed shade with the minimum or no tendering(degradation) or without diminishing the tensile strength. Object: To ensure a pure and permanent basic white color fabric. Destruction of natural coloring matters from the fabric. To increase absorbing for dyeing operation. To ensure level dyeing property. To make the textile materials suitable for subsequent processing (dying printing etc.) I) Oxidizing bleaching agent i.e 1. Ozone(O3) 2. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) 3. Calcium hypochlorite [Ca(OCl)2] 4. Sodium hypochlorite [NaOCl] 5. Sodium Chlorite (NaClO2) 6. Potasium Permanganate (KMnO4) 7. Per acetic acid 8. Bleaching powder[Ca(OCl2).2Ca(OH)2] generally [Ca(OCl)Cl] 9. Potasium di- Chromate(K2Cr2O7) 10. Sodium di Chromate(Na2Cr2O7) 11. Potasium chlorate(KClO3) 12. Sodium per oxide (Na2O2) II) Reducing bleaching agent 1. Zinc dust(Zn) 2. Staneous chloride (SnCl2) 3. Ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) 4. Sulphar di-oxide(SO2) 5. Sodium bi- Sulphate(NaHSO4) 6. Hydrogen Sulphide(H2S) 7. Sodium Sulphite formaldehyde 8. Sdium sulphate (Na2SO4)
- 5. 9. Hydrogen (H2) Dyestuff: Dyes are colored, unsaturated organic chemical compounds capable of giving color to substrate (textile) i.e. coloring or dyeing it. Dyes can be formed synthetically from relatively cheap basic products where specific functional groups in the dyes which determine or affect the applicability and fastness. Characteristics of dyestuff: Must containing chromophore groups. This chromophore groups may be different types. Example; -NO2, -NH2, -CO-, -N=O etc. Must able of preparing dilute solution by dissolving water i.e. solubility Must be power of entering dyestuff to fibre from dye bath i.e. substantivity. Should have fastness property. Dyeing: The process by which a textile material is changed physically or chemically so that it looks colourful is called Dyeing. Pigments: Insoluable coloring matters, mostly of mineral origin, have been used from earliest times for the coloration of metal, wood, stone and other surfaces as paints in association with oil or water. The pigments which are applied by means of binding agent. Such insoluable colorents or pigments i.e. certain oxides presented a limit range of hues generally of very fastness to light but of variable behaviour towards other agent. The more important criteria by which pigments are evaluated are fastness to light, heat, solvent, acids, alkali and other chemical agencies. Advantage: Light fastness very high. Disadvantage: Harsh fabric, Rubbing. Required criteria of pigments: Pigments should have good covering power. Pigments should have freely mixing properties. Pigments should be chemically inert. Pigments should have good resistance to Acid. Pigments should be resistance to solvent. Pigments should have suitable brilliance , hardness, and stability.
- 6. Pigments should have good wet , light, and abrasion resistance. Pigments should have good characteristics for excellent dispersion including : Particle size and distribution Electrical charge Specific gravity Purity and crystalline structure Condition of Precipitation Should be applied to all fibre Should be cheap. Classification of coloring matter/dyes/dyestuff: Classification of colouring mtls: Dyestuffs are classified on different bases: 1. Physical form 2. Application form 3. Chemical form Colouring mtls Dyes (Organic Pigments (Organic + Inorganic) Chromophore Auxochromes Chromogen Chromophore Chromogen
- 7. Green Blue green Yellow Blue Purple Red 1. Physical form: Theory of color: 1. Thomas Young(1801): Proposed thatthe eye perceive color interms of three colour stimuli, these are Red, Green, Blue. 2. Helmholtz theory (1852): First recogise the difference between the additive and subtractive color mixing. Additive or Light theory: Physical form Powder form Lump form Solution form Pasteform Grain form Fine powder Micro or Ultra fine powder form Application form Ready made dye Ingrain dye Water soluable dye Water insoluable dye Azoic dye Oxidation color Direct dyes Acid dyes Basic dyes Reactive dyes Vat dyes Sulpher dyes Mordant dyesDisperse dyes Mineral color
- 8. Yellow Green Orange Blue Violet Red Red +Blue+ Green= White Subtractive or Pigment theory: Red +Yellow+ Blue=Black Printing Defn: The textile printing is the art of design by mechanical and chemical application. It entails the localised of dye of pigment the design being created by different colour or motives. OR By the term “ Textile printing” we mean the localised application of dyes or pigments and chemicals by any method which can produce particular effect of colour on the fabric accurding to the design. Steps/stages of printing: Grey textiles / Raw materials ↓ Preparation of textile mtls ( singening, desizing , bleaching scouring) Preparation of printing paste Printing (with a certain style and method) Drying of the printed fabric (in the drier)
- 9. Steaming of the printed fabric (to transfer dye into fibre, 100-1020 C, 15 min in a steamer) After treatment (Soaping of washing) Styles of printing: Style refers to the manner by which particular action is performed. It is chemical operation. Styles of printing means the manner in which a printed effect is produced- 1. Direct style. 2. Dyed style. 3. Discharge style 4. Resist style 5. Raised “ 6. Azoic “ 7. Metal “ 8. Flock “ 9. Creap “ Methods of printing: 1. Block printing---(i)By hand (ii) By machine 2. Stencil printing (i) Metal stencil (ii) Screen stencil 3. Roller printing 4. Screen printing (i) Hand screen (ii) Semi-Automatic flat screen printing (iii) Fully Automatic flat screen printing (iv) Rotary screen printing 5. Transfer printing (i) Flat bed press transfer printing m/c (ii) Continuous transfer printing m/c (iii) Vacuum transfer printing m/c
- 10. Thickener Definition: Thickener is a thick mass which imparts stickness and plasticity to the print paste so that it may be applied on the fabric surface without bleeding or spreading and be capable of maintaining the design out lines. Function or Object or Purpose of Thickener: To give the required viscosity to the printing paste. To prevent premature reactions between the chemicals contained in the print paste. To hold the ingredients of the print paste on the fabrics. Difference bet Dyeing & Printing : Dyeing Printing 1. There is no localized application 1. This is the localized application of dyes/pigments on the fabric according to design. 2. Colour is applied in form of soln 2. Colour is applied in form of thick paste. 3. Fabric, yarn and fibres are dyed. 3. Fabric is only printed 4. Generally a colour is used. 4. One or more colour is used. 5. Thickener is not used. 5. Thickener is used. 6. Steaming is not required on dyed mtl. 6. Steaming is used in the printed fabric for fixation. 7. More time is required 7. Less time is required. 8. Less expensive. 8. More expensive 9. Much amount of water is used 9. Less amount of water is used. 10. Liquor ratio is high. 10. Liquor Ratio is less. Finishing:
- 11. In general, before marketing, all the process which are applied on the fabric after knitting or weaving is called finishing. In broad sense, the term finishing covers all the processes which the fabric undergoes after leaving the loom or knitting m/c to the stage at which enters the market. Process Sequence: In short sense, finishing is the process by which the fibres, yarns, fabrics are made as presentable to the customer and these process are implemented after coloration. Classification of Finishing: Pretreatment (Scouring, bleaching) Coloration After Treatment Washing Softenings or other Chemical finishing Hydroextractor Drying Calendering / Compacting or Sanforzing Packing Delivery to market
- 12. Physical / Mechanical finishing : The finishing process which is per formed by m/cs but not using of chemicals is called finishing. Used to control dimension To improve appearance and handle etc. Less expensive. Example: Calendaring, embossing, raising , sanforizing, beething etc. Chemical finishing: The finishing process which is performed by application of chemicals which reacts with fibres is termed as chemical finishing. Used to make glossy protection To improve performance Finishing Physical (Mechanical) Chemical Temporary e.g. Calendering Embossing Beetting etc Permanent e.g. Raising Sanforizing Temporary e.g. Starching Weighting Softening Permanent e.g Mercerising Resin finishing etc.
- 13. Highly expensive. eg Straching, weighting, mercerizing, resin finishing etc. Temporary Finishing: The finishing process by deposition of different materials on the fabric where the finishing materials may be removed by easy washing or clearing is called temporary finishing. This finishing is only achieved on the surface of the mtls. Permanent / Durable finishing: In this finishing process, the finishing mtls stables up to the last position of using the mtl and not damage in any clearing process. It is of 2 types – Physical finishing – Milling of wool, raising Chemical finishing – mercerizing, resin finish. Effect of finishing on Fabric Properties/ Object of finishing: (1) To improve attractiveness. If can be done by- I) Modification of fabric appearance e.g. calendering or ironing, optical brightening or whitening, delusturing, mercerizing. II) Alternation of fabric handle e.g. softening, stiffening, weighting etc. III) Control of fabric dimension e.g. shrinkage resistant, chemical setting, thermo setting. (2) To improve serviceability. It can be done by- I) Improve performance e.g. flame proofing, not proofing, Antibacterial II) Improve performance e.g water proofing, antistatic finish, coating. III) Easy care properties. e.g. soil and oil repellency,resin finishing etc.
- 14. Mercerisation: Mercerisation is a physio-chemical process where cotton/yarn is treated with 15-25% (55- 65oTw) caustic soda solution at a temperature of 20o-30oC. It is necessary to hold the fabric under tension and wash thoroughly. Benefit obtained by Mercerisation/Objects: I) Increase tensile strength. II) Improved hygroscopicity. III) Improved dye afeinity. IV) Improved smoothness. V) Improved luster. VI) Improved dimensional stability and physical compactness. VII) 20-30% dye and chemical save while dyeing after mercerising. Mercerising Process: Calendaring: After a grey fabric is subjected to scouring, bleaching, mercerizing etc. It is finally dried to retain its true shape and dimensions. But in this state the fabric becomes least lustrous. Because, for those operations the threads in fabric become wavy and crimped. But if a fabric is to appear highly lustrous then its surface should be perfectly flat and fibres appeared on the surface should be parallel to each other and all should lie in the length direction. To fulfill this object cotton, linen, rayon, silk materials are applied a temporary physical finish which is known as calendaring. In this process fabric is passed through a series of healed rollers under pressure in open width form. Objects of calendaring: Mercerising process Yarn mercerising Fabric/Cloth mercerising Hank form (Generally) Continuous yarn mercerising Grey fabric mercerising Mercerizing after scouring, bleaching
- 15. The main objects or purpose of calendaring process are mentioned below:- 1. To cause a closing together of the threads of the fabric by flattening them and thus tending to fill up the interstices between warp and weft. 2. To produce a smooth, glossy and highly lustrous appearance on the surface of the cloth. 3. To reduce fabric thickness. 4. To reduce air permeability and water permeability of fabric by changing its porosity. Raising: Raising is a permanent mechanical finishing process of lifting a layer of fibres from the body of the fabric which stand out from the surface. Rising may be done either in wet stage (for woolen) or dry stage (for cotton). For example, i) Funnel fabric (woven raised fabric) ii) Fleece fabric (knitted raised fabric) Raising causes a ‘Lofty’ handle effect on fabric. Objects of raising: The objects of raising are mentioned below: i) To obtain a lofty handle effect in fabric. ii) To obtain fleecy appearance. iii) To create pile or cover on fabric surface. iv) To produce a heavier surface made of fibers. v) It is used to develop some structural features. vi) To produce warm cloth as well as a soft one.