Electromagneticinduction
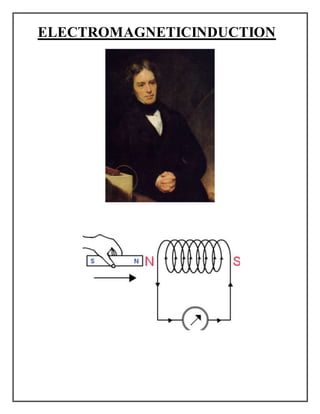
- 3. AIM: To determine the faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction using a copper wire wound over an iron rod and a strong magnet APPARATUS; 1. Insulated copper wire 2. A iron rod 3. A strong magnet and 4. A light emitting diode (LED)
- 4. INTRODUCTION: Faraday's law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism that predicts how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (EMF). It is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors and generators. Electromagnetic induction was discovered independently by Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry in 1831; however, Faraday was the first to publish the results of his experiments. Faraday explained electromagnetic induction using a concept he called lines of force.These equations for electromagnetics are extremely important since they provide a means to precisely describe how many natural physical phenomena in our universe arise and behave. The ability to quantitatively describe physical phenomena not only allows us to gain a better understanding of our universe, but it also makes possible a host of technological innovations that define modern society. Understanding Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction can be beneficial since so many aspects of our daily life function because of the principles behind Faraday’s Law. From natural phenomena such as the light we receive from the sun, to technologies that improve our quality of life such as electric power generation, Faraday’s Law has a great impact on many aspects of our lives. Faraday’s Law is the result of the experiments of the English chemist and physicist Michael Faraday . The concept of electromagnetic induction was actually discovered simultaneously in 1831 by Faraday in London and Joseph Henry, an American scientist working in New York , but Faraday is credited for the law since
- 5. he published his work first . An important aspect of the equation that quantifies Faraday’s Law comes from the work of Heinrich Lenz, a Russian physicist who made his contribution to Faraday’s Law, now known as Lenz’s Law, in 1834 (Institute of Chemistry). Faraday’s law describes electromagnetic induction, whereby an electric field is induced, or generated, by a changing magnetic field. Before expanding upon this description, it is necessary to develop an understanding of the concept of fields, as well as the related concept of potentials. Faraday's first experimental demonstration of electromagnetic induction (August 29, 1831), he wrapped two wires around opposite sides of an iron ring or "torus" (an arrangement similar to a modern toroidal transformer) to induce current Figure 1 Faraday's First Experiment Some physicists have remarked that Faraday's law is a single equation describing two different phenomena: the motional EMF generated by a magnetic force on a moving wire (see Lorentz force), and the transformerEMF generated by an electric force due to a changing magnetic field (due to the Maxwell–Faraday equation). James Clerk Maxwell drew attention to this fact in his 1861 paper On Physical Lines of Force. In the latter half of part II of that paper, Maxwell gives a separate physical explanation for each of the two phenomena. A reference to these two aspects of electromagnetic induction is made in some modern textbooks.
- 6. THEORY: Magnetic flux: The magnetic flux (often denoted Φ or ΦB) through a surface is the component of the B field passing through that surface. The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (Wb) (in derived units: volt-seconds), and the CGS unit is the maxwell. Magnetic flux is usually measured with a fluxmeter, which contains measuring coils and electronics that evaluates the change of voltage in the measuring coils to calculate the magnetic flux. If the magnetic field is constant, the magnetic flux passing through a surface of vector area S is where B is the magnitude of the magnetic field (the magnetic flux density) having the unit of Wb/m2 (Tesla), S is the area of the surface, and θ is the angle between the magnetic field lines and the normal (perpendicular) to S. For a varying magnetic field, we first consider the magnetic flux through an infinitesimal area element dS, where we may consider the field to be constant : From the definition of the magnetic vector potential A and the fundamental theorem of the curl the magnetic flux may also be defined as: where the line integral is taken over the boundary of the surface S, which is denoted ∂S.
- 7. LAW: The most widespread version of Faraday's law states: The induced electromotive force in any closed circuit is equal to the negative of the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit. This version of Faraday's law strictly holds only when the closed circuit is a loop of infinitely thin wire,and is invalid in other circumstances as discussed below. A different version, the Maxwell–Faraday equation (discussed below), is valid in all circumstances. When the flux changes—because B changes, or because the wire loop is moved or deformed, or both—Faraday's law of induction says that the wire loop acquires an EMF , defined as the energy available per unit charge that travels once around the wire loop (the unit of EMF is the volt).Equivalently, it is the voltage that would be measured by cutting the wire to create an open circuit, and attaching a voltmeter to the leads. According to theLorentz force law (in SI units), the EMF on a wire loop is: where E is the electric field, B is the magnetic field (aka magnetic flux density, magnetic induction), dℓ is an infinitesimal arc length along the wire, and the line integral is evaluated along the wire (along the curve the conincident with the shape of the wire).
- 8. The Maxwell–Faraday equation states that a time-varying magnetic field is always accompanied by a spatially-varying, non-conservative electric field, and vice-versa. The Maxwell–Faraday equation is where is the curl operator and again E(r, t) is the electric field and B(r, t) is the magnetic field. These fields can generally be functions of position r and time t. The four Maxwell's equations (including the Maxwell–Faraday equation), along with the Lorentz force law, are a sufficient foundation to derive everything inclassical electromagnetism. Therefore it is possible to "prove" Faraday's law starting with these equations. Faraday's law could be taken as the starting point and used to "prove" the Maxwell–Faraday equation and/or other laws.)
- 9. CONCLUSION Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, first observed and published by Michael Faraday in the mid-nineteenth century, describes a very important electro-magnetic concept. Although its mathematical representations are cryptic, the essence of Faraday’s is not hard to grasp: it relates an induced electric potential or voltage to a dynamic magnetic field. This concept has many far-reaching ramifications that touch our lives in many ways: from the shining of the sun, to the convenience of mobile communications, to electricity to power our homes. We can all appreciate the profound impact Faraday’s Law has on us.
- 11. BIBLIOGRAPHY; www.google.co.in/search?rlz=1C1AOHY_enIN756IN756&biw =1280&bih=582&tbm=isch&sa=1&q=bibliography+for+ELEC TROMAGNETICINDUCTION&oq=bibliography+for+ELECT ROMAGNETICINDUCTION&gs_l=psy- ab.3...109170.110008.0.111387.2.2.0.0.0.0.153.268.0j2.2.0....0. ..1.1.64.psy- ab..0.1.152...0j0i67k1.0.9km55L9MCCg#imgrc=3K4fXLK4D WV9LM: https://www.google.co.in/search?rlz=1C1AOHY_enIN756IN75 6&biw=1280&bih=582&tbm=isch&sa=1&q=bibliography+for +physics+project+class+12&oq=bibliography+for+physics+pro ject+class+12&gs_l=psy- ab.12...0.0.0.47091.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0..0.0....0...1..64.psy- ab..0.0.0....0.4OzAL_rIWxw#imgrc=_ https://www.google.co.in/search?rlz=1C1AOHY_enIN756IN75 6&biw=1280&bih=582&tbm=isch&sa=1&q=bibliography+for +physics+project+class+12&oq=bibliography+for+physics+pro ject+class+12&gs_l=psy- ab.12...0.0.0.47091.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0..0.0....0...1..64.psy- ab..0.0.0....0.4OzAL_rIWxw#imgrc=RY69qiEccBCoKM: