2) PHARMACOKINETICS.pptx
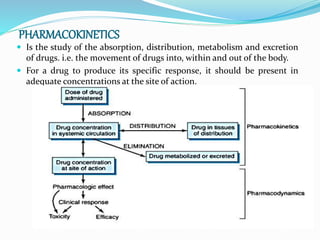
- 1. PHARMACOKINETICS Is the study of the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drugs. i.e. the movement of drugs into, within and out of the body. For a drug to produce its specific response, it should be present in adequate concentrations at the site of action.
- 4. BASIC MECHANISMS OF MEMBRANE TRANSPORT : Transporters versus Channels: Both channels and transporters facilitate the membrane permeation of inorganic ions and organic compounds. In general, channels have two primary states, open and closed. The basic mechanisms involved in solute transport across biological membranes include passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Filtration: The rate of filtration depends both on the existence of a pressure gradient as a driving force and on the size of the compound relative to the size of the pore through which it is to be filtered. In biological systems, the passage of many small water-soluble solutes through aqueous channels in the membrane is accomplished by filtration
- 5. Passive Diffusion: Simple diffusion of a solute across the plasma membrane consists of three processes: partition from the aqueous to the lipid phase, diffusion across the lipid bilayer, and repartition into the aqueous phase on the opposite side. Facilitated Diffusion. Diffusion of ions and organic compounds across the plasma membrane may be facilitated by a membrane transporter. Facilitated diffusion is a form of transporter-mediated membrane transport that does not require energy input. Just as in passive diffusion, the transport of ionized and un- ionized compounds across the plasma membrane occurs down their electrochemical potential gradient.
- 6. Active Transport: Active transport is the form of membrane transport that requires the input of energy. It is the transport of solutes against their electrochemical gradients, leading to the concentration of solutes on one side of the plasma membrane and the creation of potential energy in the electrochemical gradient formed. Active transport plays an important role in the uptake and efflux of drugs and other solutes. Ion Pair Transport: Absorption of some highly ionized compounds is carried here. These compounds are known to penetrate the lipid membrane despite their low lipid– water partition coefficients. It is postulated that these highly lipophobic drugs combine reversibly with endogenous compounds as mucin in the gastrointestinal lumen, forming neutral ion pair complexes; it is this neutral complex that penetrates the lipid membrane by passive diffusion.
- 7. Endocytosis: Endocytosis involves the cellular uptake of exogenous molécules or complexes in side plasma membrane– derived vesicles. This process can be divided into two major categories: (1) adsorptive or phagocytic uptake of particles that have been bound to the membrane surface and (2) fluid or pinocytotic uptake, in which the particle enters the cell as part of the fluid phase. The solute within the vesicle is released intracellularly
- 8. The systemic circulation distributes drugs to various body tissues or target sites. Drugs interact with specific receptors during distribution. Some drugs travel by binding to protein (albumin) in the blood. FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG DISTRIBUTION: Distribution is the delivery of drug from the systemic circulation to tissues.Once a drug has entered the blood compartment, the rate at which it penetrates tissues and other body fluids depends on several factors. These include (1) capillary permeability, (2) blood flow–tissue mass ratio (i.e., perfusion rate), (3) extent of plasma protein and specific organ binding, (4) regional differences in pH, (5) transport mechanisms available, and (6) the permeability characteristics of specific tissue membranes.
- 9. BINDING OF DRUGS TO PLASMA PROTEINS Most drugs found in the vascular compartment are bound reversibly with one or more of the macromolecules in plasma. Although some drugs simply dissolve in plasma water, most are associated with plasma components such as albumin, globulins, transferrin, ceruloplasmin, glycoproteins, and - and -lipoproteins. While many acidic drugs bind principally to albumin, basic drugs frequently bind to other plasma proteins, The extent of this binding will influence the drug’s distribution and rate of elimination because only the unbound drug can diffuse through the capillary wall, produce its systemic effects, be metabolized, and be excreted.
- 10. PHYSIOLOGICAL BARRIERS TO DRUG DISTRIBUTION: Blood-Brain Barrier: The capillary membrane between the plasma and brain cells is much less permeable to water- soluble drugs than is the membrane between plasma and other tissues. Thus, the transfer of drugs into the brain is regulated By the blood-brain barrier. Placental Barrier: The blood vessels of the fetus and mother are separated by a number of tissue layers that collectively constitute The placental barrier. Drugs that traverse this barrier will reach the fetal circulation. The placental barrier, like the blood-brain barrier, does not prevent transport of all drugs but is selective. Blood-Testis Barrier: The existence of a barrier between the blood and testes is indicated by the absence of staining in testicular tissue after the intravascular injection of dyes.
- 11. Both metabolism and excretion can be viewed as processes responsible for elimination of drug (parent and metabolite) from the body. Drug metabolism changes the chemical structure of a drug to produce a drug metabolite, which is frequently but not universally less pharmacologically active. Metabolism also renders the drug compound more water soluble and therefore more easily excreted. Drug metabolism reactions are carried out by enzyme systems that evolved over time to protect the body from exogenous chemicals. The enzyme systems for this purpose for the most part can be grouped into two categories: phase I oxidative or reductive enzymes and phase II conjugative enzymes
- 12. RENAL EXCRETION: Although some drugs are excreted through extra renal pathways, the kidney is the primary organ of removal for most drugs, especially for those that are water soluble and not volatile. The three principal processes that determine the urinary excretion of a drug are glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, and tubular reabsorption(mostly passive back-diffusion). Active tubular reabsorption also may have some influence on the rate of excretion for a limited number of compounds. BILIARY EXCRETION: The liver secretes about 1 L of bile daily. Bile flow and composition depend on the secretory activity of the hepatic cells.
- 13. PULMONARY EXCRETION: Any volatile material, irrespective of its route of administration, has the potential for pulmonary excretion. Certainly, gases and other volatile substances that enter the body primarily through the respiratory tract can be expected to be excreted by this route. The rate of loss of gases is not constant; it depends on the rate of respiration and pulmonary blood flow.
- 14. EXCRETION IN OTHER BODY FLUIDS: Sweat and Saliva: Excretion of drugs into sweat and saliva occurs but has only minor importance for most drugs. The mechanisms involved in drug excretion are similar for sweat and saliva. Excretion mainly depends on the diffusion of the un-ionized lipid-soluble form of the drug across the epithelial cells of the glands. Milk: Many drugs in a nursing mother’s blood are detectable in her milk. The ultimate concentration of the individual compound in milk will depend on many factors, including the amount of drug in the maternal blood, its lipid solubility, its degree of ionization, and the extent of its active excretion.