Gel chromatography, Introduction, Theory, Instrumentation, Applications .pptx
- 1. Mrs Vandana Sharma Assistant Professor
- 2. Introduction Theory Instrumentation Applications
- 4. As a technique, size exclusion chromatography was first developed in 1955 by Lathe and Ruthven. Gel chromatography is a type of partition chromatography used for separating different sized molecules. Gel chromatography is also called Gel permeation chromatography or gel filtration or gel exclusion, size exclusion, molecular- sieve chromatography. The separation is based on the analyte molecular sizes since the gel behaves like a molecular sieve. In size exclusion chromatography, the stationary phase is a porous matrix made up of compounds like cross-linked polystyrene, cross-like dextrans, polyacrylamide gels, agarose gels, etc. The gel structure being used contains pores of different diameters upto maximum size. 1.The test molecules are washed through a gel column and molecules larger than the largest pores in the gel are excluded from the gel structure.
- 5. 2. Smaller molecules penetrate the gel and the extent of penetration depends on the molecular size----- This delay their movement through the column This technique is used for the separation of proteins, polysaccharides, enzymes, and synthetic polymers.
- 6. In gel chromatography- molecules are separated based on their size 1. A column is filled with swollen gel beads or porous glass beads- this column is serves as a molecular sieve 2. A mixture with molecules with of different sizes is poured over the column. 3. The larger molecules are collected first as they pass through the spaces between the gel or glass beads. Because the pores of beads are smaller and the large molecules cannot pass through them. 4. The small molecules enter the beads through the pores and get separated from the solvent 4a. Small molecules slowly travel down the beads and collected in the separated stream means collected latter 4b. Large molecules cannot pass through the pores, and are excluded from the beads means collected first. hence, this technique is also called exclusion chromatography.
- 8. In short
- 9. Only for explanation (not compulsory to write in exam paper Add with principle in last if asked about Theory
- 10. A. Stationary phase It is composed of semi-permeable, porous polymer gel beads with a well-defined range of pore sizes. It has the following properties: 1. Chemically inert 2. Mechanically stable 3. With ideal and homogeneous porous structure (wide pore size give low resolution). 4. A uniform particle and pore size. Examples of gel: Dextran (Sephadex) gel: An α 1-6-polymer of glucose natural gel Agarose gel: A 1,3 linked β-D-galactose and 1,4 linked 3,6- anhydro-α, L-galactose natural gel Acrylamide gel: A polymerized acrylamide, a synthetic gel
- 11. 1. Matrix choice- The gel filtration matrices compromise of porous beads containing cross linked polyacrylamide, agarose, dextran or combination of these. These matrices are supplied in suspended form or as dry powders. Desirable properties of matrix 1. They should be compatible with the molecules to be separated and should be stable in organic solvents, pH, and temperature 2. They should be inert when molecules undergoing separation so that the molecule don't get partially adsorbed to the matrix – if this will happens the migration of molecules through the column will be retarded. Eg Sephadex- Original medium based on dextran (a linear polymer)- that has been modified to offer varying degree of cross linking to determine the material pore size
- 12. sephadex is a strongly hydrophilic polymer and swell in aqueous solutions, like dextran Polyacrylamide beads- Like dextran- hydrophilic and swell in aqueous solution. Chemically more stable than dextran gels. Agarose gels- Hydrophilic and used when very large pore sizes is needed Polystyrene gels- hydrophobic in nature, used with non-aqueous solvents for organic chemical applications 2. sample size and concentration- sample is applied in small volume (1-5% of the total bed volume) The sample viscosity -(increase with the sample concentration) A high viscosity- irregular sample migration through the column and reduce the column flow rate= loss of resolution 3. Column parameters- use long column, ratio of column diameter to column length (1:20 to :100)
- 13. Dry gel powder (A weighted amount)- Mixed with solvent (to be used as eluent ) and made to swell The resultant mixture is kept aside till equilibrium is attained Then the column slurry warmed at 100 o C in a water bath The gel swells in a few days. The slurry is cooled and packed in column The method or steps used for gel preparation Type of column packing 1. Porous glasses or silica and 2. Porous cross-linked organic gels eg- dextrans, methylate acrylic based gels, polyvinyl alcohal based gels, Hydroxyethyl cellulose gels Detectors- based on –UV fluorescence, -UV absorption or -Change in refractive index
- 14. 4. Choice of eluent/mobile phase- In gel chromatography, the molecules are separated based on their relative sizes. Due to this reason, the technique is independent of the of type of eluent used. The elution conditions (pH, essential ions, cofactors, protease inhibitors etc) that will fulfill the requirements of desired molecule should be selected Mobile phase: Buffers Ex- Phosphate buffer pH 7, NaCl solution, Ammonium acetate (CH3COO - NH4 + ), Ammonium bicarbonate (NH₄HCO₃) ethylenediamine acetate 5. Effect of Flow rate- maintain with the help of pump Maximum separation in gel chromatography- can be achieved by low flow rate indicate longer separation time Higher flow rates can be used with rigid material such as Sephacryl HR range Elution carried out with buffer at optimal flow rate (Eg- 0.25- 5ml/min) to give maximum resolution with optimal separation time
- 15. 6. Separation of components from the sample- Separation of component from mixture is achieved with the help of column Separation mechanism- In gel chromatography, the polymer molecules are separated based on their molecular size. Separation is achieved when the polymer molecules elute through the column(s) packed with a porous material Smaller molecules are retained in the pores while the larger ones are excluded. Thus, first the largest molecule (having the greatest hydrodynamic volume) elutes from the column and then the smaller molecules. The retention volume (VR) - The volume of liquid at which a solute elutes from a column or the volume of liquid corresponding to the retention of a solute on a column is the retention volume (VR), which is related to the void volume (Vo) and internal pore volume of the column
- 16. 7. Detection- Using UV absorption detectors A graph of Elution Volume (ml) Vs Molecular weight For calibration of the gel in column – Calibrators - (Proteins of known molecular weight) like- Yeast alcohal dehydrogenase (1,50,000 Daltons), Bovine serum albumin (66,000 Daltons), carbonic anhydrase (29,000 Daltons) and Cytochrome C (12,400 daltons) are used A graph of MW vs elution volume – plotted For unknown compounds – separation is carried out using the same column of gel, elution volume is determined – and FROM THE GRAPH- the molecular weight of each compound is determined 10,00,000 1,00,000 10,000 1,000 10 15 20 M.W. in Daltons Elution volume (ml) Calibration curve
- 17. Easy Diagram
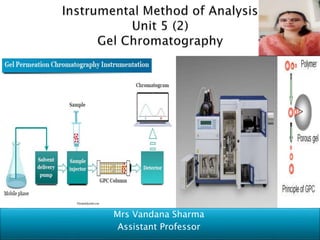
- 18. A generic size exclusion chromatography Explained Diagram of Gel Chromatography
- 20. Steps 1. Preparation of column- slurry of stationary phase with the help of mobile phase – allow to become gel After sufficient time – in column (made of glass or inert material) is filled to get packed bed of gel. Stationary phase- porous beads containg cross linked poly acrylamide, agarose, dextran or combination of these 2. Washing of the column- The packed bed is equilibrated with buffer, which fills the pores in the beads as well as the space between the beads. Now the packed bed of column is ready for separation. NOTE- The buffer is not required to improve resolution- but buffer is used at the end of separations to remove any molecules which are present in the column to facilitate next separation.
- 21. 3. Loading of the sample- The compounds to be separated, in the form of solution is charged into the column, followed by flow of mobile phase with a specific flow rate. 4. Elution using mobile phase (buffers)- Elution is carried out with buffer at optimum flow rate (eg- 0.25-5ml/min) to give maximum resolution of peaks and small volume fractions are collected for detection of individual component. Depending upon separation – a pressure upto 350 psi (Pounds per square inch0 are used 5. Detection of compounds – Detection of compound is carried out by connecting outlet of column to detector. Usually UV detector monitored at 214nm or 280nm and a chromatogram is obtained
- 23. Separation of protein in mixtures- Molecular weight of each protein is different – gels for required specification is used to separate – mixture of proteins into pure component This technique is frequently used for – 1. The separation of small proteins, large proteins 2. Polynucleotides 3. DNA fragments 4. Small virus particles 5. Peptides 6. Globular proteins 7. Peptide hormones 8. Monoclonal antibiotics etc Determination of approximate molecular weight of unknown sample- The gel column is calibrated, followed by separation of unknown compounds in the same column
- 24. From the elution volume, and calibration graph- the approximate MW of given unknown sample is determined Purification of macromolecules, proteins, enzymes, amino acids, polysaccharides When impurities are present, they can also be separated as the molecular sizes of impurities are different when compared to components of interest. Each fraction is collected separately and detected using suitable technique Desalting of proteins- When salts are used in the separation of proteins in to fractions- to remove these salts for purification of proteins- gel filtration is used Salts travel slower in the gel ( smaller size) and proteins excluded from the column faster ( due to larger size)