Med chem lecture on Antihistaminicdrugs
- 2. Histamine -Pharmacology • Histamine is an Autacoid , which are biological chemicals which act like local hormones, have a brief duration, and act near their site of synthesis. • Histamines has various function in body such as: – Mediator of inflamation and local immune responses – regulating physiological function in the gut and – acting as a neurotransmitter. • .
- 3. • During inflammation Histamine is produced by basophils and by mast cells, found in nearby connective tissues, which increases the permeability of the capillaries to white blood cells and some proteins, to allow them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues • In the gut it is produced by parietal cells and then promotes gastric acid secretion and thus aids in digestion. Here it acts like a local hormone • As a neurotranmitter, it effects sleeping and waking, food intake, thermal regulation, emotions and aggressive behavior, locomotion, memory, and learning
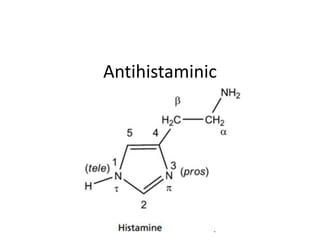
- 4. Histamine - Chemistry • Histamine is a Nitrogenous base. It is composed of an imidazole ring and ethylamine side chain. In Plasma pH of 7.4 is exists in exclusively monocationic form (96.6%). At lower pH higher levels of dication form exist. • In solution form, 80% contain H in Nτ tautamer and 20% in Nπ tautamer • But crystal form consist primarily of Nτ form
- 5. At plasma pH 96.6% is monocationic Lower pH favors dicationic form 80% has H in Nτ 20% has H in Nπ Nτ tautamer Nπ tautamer Note that sp2 N is more basic than sp3 N
- 6. Histamine Biosynthesis Note- There some drugs that can block Histidine Decarboxylase such as Floromethylhistine which in theory can act as direct acting antihistamine but clinically were found to be not useful.
- 7. Storage and release • Stored in mast cells in Complex with Heparin (anticoagulant) • Stored in basophiles in Complex with Chondrotin • Histamine as stored in mast cells are found almost everywhere : skin and the mucosal cells of the bronchi, intestine, urinary tract, and tissues adjacent to the circulation and within neurons of CNS • It is released in response to a wide variety of immune (antigen and antibody) and nonimmune (bacterial products, xenobiotics, physical effects, and cholinergic effects) stimuli
- 8. Histamine receptors Location and function H1, H2, H3, H4; they all are GPCR’s • H1 Location : CNS neurons, the smooth muscle of respiratory, GIT, uterine tissues, epithelial and endothelial cells, immune cells Function: vasodilation, vascular permeability, hypotension, flushing, pain, headache, tachycardia, nasal congestion, bronco-constriction, stimulation of cough receptors, allergic immune response • Therapeutic usage: H1 antihistamine are anti- allergic, and anti-emetic drugs, • H1 receptor is 40% similar to muscarinic receptors (thus some H1 antagonist shows unwanted antimuscaric side effect)
- 9. • H1 receptors belong to the superfamily of G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), and are encoded for by chromosome 3 • these receptors exhibit spontaneous activation of their intracellular messengers, requiring no binding by an agonist at surface level • It exists as a balance between activated (characterized by the production of intracellular second messengers) and inactive (no such intracellular signaling) state. • If the ligand stabilizes the active receptor conformation, making it the predominant form, then the drug is referred to as an agonist, while if the inactive conformation is stabilized the drug is said to be a inverse agonist. In this way, histamine is an agonist, while the antihistamines are presently considered to be inverse agonists instead of antagonists as previously believed
- 11. • H2 function - gastric acid secretion, vascular permeability, hypotension, flushing, headache, tachycardia, broncho-dilation and respiratory mucus production • Therapeutic use – H2 antihistamines are Anti-ulcer drugs • H3 Location : CNS • Function: adrenaline release and autoreceptor of Histamine in CNS • Therapeutic use – potential application against obesity • H4 function : differentiation of hematopoietic cells • Therapeutic use – none yet
- 12. Differentiation • It is a process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type • When cells divide into daughter cells, they are the same exact cells. This is cell division/growth • But differentiation means when cells “divide”, different cell types are formed. • At conception we all were just a single cell but differentiation causes us to have diverse specialized cells that make up different organs
- 13. Undifferentiated cell, called stem cells differentiates into diverse functioning cells RBC WBC Bone Insulin
- 14. Actions of Histamine by receptors
- 15. Adverse effects
- 16. Fig: Effects of H1 antihistamines at histamine, adrenergic, cholinergic, and serotonin-binding receptors. Many second generation antihistamines do not enter the brain and, therefore, show minimal CNS effects.
- 17. H1 antihistamines • Their main application is as anti-allergic, anti-emetic and • The first generation of H1 antihistamines has sedative effect due to effect on H1 receptor in brain. Structurally this effect is linked to their high lipophilicity induced BBB penetration and also they are poor substrate for brain’s endothelial P- glycoprotein efflux pumps, thus can’t exist the brain once they enter. • They also antagonize cholinergic receptors which causes dry mouth, dizziness, fatigue and are alpha adrenergic blockers which can cause cardiotoxicity by prolonging the QT interval • The second generation are more selective for H and don’t penetrate brain and thus has no sedation or cardiotoxicity • MOA: They bind and stabilize the inactive form of H1 receptors onto which Histamine is not capable of binding.
- 18. Therapeutic Uses:H1 blockers 1. dermatosis 2. allergic rhinitis 3. motion sickness & emesis 4. Parkinson’s disease 5. EPS 6. Insomnia
- 19. ECG of heart and prolonged QT interval •The QT interval denotes time period taken by heart to empty it’s blood. •Prolonged QT interval Suggests problem in cardiac muscle’s repolarization mechanism after each contraction. •It is a dangerous side effect that can cause ‘Ventricular Fibrillation' which will lead to sudden death unless a defibrillator is used to reset heart’s normal rhythm
- 20. Classification First Generation 1) Propylamines - Chlorpheniramine, Phenindamine 2) Ethanolamines - Diphenhydramine, Clemastine 3) Ethylenediamines - Pyrilamine, Tripelennamine 4) Phenothiazines - Promethazine, Trimeprazine 5) Piperazines - Cyclizine, Meclizine 6) Heptanes – Azatadine, Cyproheptadine 7) Phthalazinone – Azelastine Second Generation (Peripherally Selective) 1) Piperazine- Cetirizine/Levocetirizine 2) Piperidines - Fexofenadine, Loratadine /Desloratadine Note: Antihistamines have a lot of structural diversity
- 22. SAR of H1 antihistamines (1st gen only) General framework of Anticholinergics C X (CH2) N substituent R1 R3 R2 n Note the similarity in H1 antihistamines and Anticholinergics (this explains the origin of Anticholinergic side effect of H1 antihistamines) General framework of AntiHistamine (Ethanolamine based)
- 23. 1. It needs a tertiary amine which is mostly di- methyl substituted or part of cyclic ring 2. The methylene (-CH2-)groups can be about 2 or 3 3. The oxygen can be removed or replaced with C 4. The terminal carbon must have two aromatic groups and R group is mostly H but can be CH3 too
- 24. 5) Alkyl Substitution in these aromatic rings influence selectivity • Increasing alkyl substituions at C4 increases anticholinergic activity and decreases antihistaminic activity • Increasing alkyl substituions at C2 decreases anticholinergic activity and modestly increases antihistaminic activity 6) Presence of halogen at C4 position enhances potency 7) Replacement of one of the aromatic rings with 2-pyridyl group increases histaminic selectivity 8) For max potency, the terminal carbon must have R configuration. R/S configuration at amine is less important
- 25. C O CH2 CH2 R1 N 1 2 3 4 5 6 2C2C2C 2C CH CH3 CH3 C CH3 CH3 CH3 C2H5 CH3 Methyl Ethyl i-propyl t-butyl Alkyl position Anticholinergic Antihistaminic At C2 Increases Decreases At C4 Decreases Increases Effect of increasing Alkyl group at C2 or C4
- 26. Halogen at C4 increases potency 2-pyridyl ring increases histaminic selectivity
- 27. Importance of stereomeric consideration Clemastine has two chiral centres, terminal carbon and amine ED50 reflect potency. Entry 1st and 3rd are most potent. Both contain R configuration at terminal carbon. Conversely Entry 2nd and 4th with S configuration at terminal carbon are the least potent Configurati on (C,N) ED50 mg/kg R,R 0.04 S,S 5.0 R,S 0.28 S,R 11.0
- 29. Chlorpheniramine • It is a propylamine based 1st generation H1 antihistaminic • It is chlorinated pheniramine which improves potency 10 times and changing toxicity • It’s Dextro isomer has S configuration and called DexChlorpheniramine is more potent • It also acts as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor or SNRI • It is combined with opiods for cough medicine because it can potentiate action of opiods • It causes drowsiness by penetrating into brain and acting on H1 receptor • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, in cough medicines • MOA (from above)
- 30. Draw dextro isomer of Chlorpheniramine in fisher projection
- 31. Zimelidine is an anti-depressent. It is a derivative of brompheniramine Note how a simple addition of double bond completely altered pharmacology of drug. But was this structural alteration randomly discovery or fully Intended? Brompheniramine H1 antihistaminic/Antiallergic Zimelidine Selective Serotonin reuptake inhibitor/ Antidepressent
- 32. Clemastine • It is a ethanolamine based 1st generation H1 antihistaminic • This class has a longer duration of action (10-12 hrs) • It causes drowsiness by penetrating into brain and acting on H1 receptor • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, urticaria (itchy skin rash), anti-emetic • MOA (from above)
- 33. Pyrilamine • It is a ethylenediamine based 1st generation H1 antihistaminic • They are among the weakest antihistamines • It is combined with opiods for cough medicine because it can potentiate action of opiods • It causes drowsiness by penetrating into brain and acting on H1 receptor • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, incest bites (topically) • MOA (from above)
- 35. Promethazine • It is a phenothiazine based 1st generation H1 antihistaminic • It’s sedative action is strong to be used clincally • It causes drowsiness by penetrating into brain and acting on H1 receptor • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, motion sickness, anti-emetic, sedative • MOA (from above)
- 36. Meclizine • It is a Piperazine based 1st generation H1 antihistaminic • It has weak antihistaminic activity • It causes drowsiness by penetrating into brain and acting on H1 receptor • Uses – anti-emetic and motion sickness • MOA (from above)
- 37. Cyproheptadine • It is a Heptane based 1st generation H1 antihistaminic • It possesses both antihistamine and anti- serotonin activity and is used as an anti-itch agent • It causes drowsiness by penetrating into brain and acting on H1 receptor • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, allergic skin urticaria, hypersensitivity reactions • MOA (from above)
- 38. 2nd generation H1 antihistamines • They don’t act on H1 receptor in brain because their lower lipophilicity doesn’t allow them to penetrate the BBB • They have low lipophilicity due to addition of hydrophilic groups OH, and COOH in the 1st gen molecules. (other hydrophilic groups can be NH2,NO2,SO4,PO4) • They have low affinity for off-targets such as muscarinic, adrenergic, and serotonergic receptors • Advantage – negligible sedation, no cardiotoxicity • Limitation – high selectivity for H1 prevents their use as anti-emetic, during motion sickness, potentiate cough medicines • MOA – same as above
- 40. Fexofenadine • It is a piperadine based 2nd gen H1 antihistaminic • It produces no clinically significant Anticholinergic or α1-adrenergic blocking or sedative effect at therapeutic doses and is safe even in higher doses • It needs only single dosing daily • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, chronic urticaria • MOA (from above)
- 41. Cetirizine/Levocetirizine • It is a Piperazine based 2nd gen H1 antihistaminic • It produces no clinically significant Anticholinergic or α1-adrenergic blocking or sedative effect at therapeutic doses • It needs only single dosing daily • It’s R-enantiomer, called Levocetrizine, has 30- fold higher affinity than the S-enantiomer • Uses – Allergic rhinitis, relief from urticaria, water eyes caused by hay fever • MOA (from above)
- 42. Wilson and gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry
- 43. Prospect of β3 agonist as anti-obesity drug • Around 1980’s, Agonists of β3 adrenergic receptor was found to cause lipolysis, fat oxidation, energy expenditure and insulin action • This lead to hopeful research into anti-obesity and type 2 diabetics • In vivo effect in rodents was also confirmed • However as of 2014 no good drug has ever cleared human testing Beta 3-adrenoceptor agonists as anti-diabetic and anti-obesity drugs in humans. Curr Pharm Des. 2001 Sep;7(14):1433-49
- 44. • The failure has been attributed to – Compounds that succeeded in rodent, such as CL- 316,243, did not perform in same way in human due to pharmacological differences – the lack of selectivity of previous compounds for the beta(3)-AR over beta(1)-/beta(2)-ARs, and – Newer compounds have unsatisfactory oral bioavailability and pharmacokinetic properties – Newer compounds did not lose weight when used chronically
- 45. History of anti-obesity drugs • The last anti-obesity drug was approved in 1999 was olristat • Recently 3 new drugs have been approved • Contrave • Qnexa/Qysmia • Belviq • Future possibility : GLP-1 agonist
