Networking notes part2 final
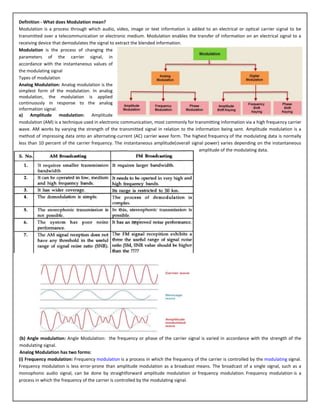
- 1. Definition - What does Modulation mean? Modulation is a process through which audio, video, image or text information is added to an electrical or optical carrier signal to be transmitted over a telecommunication or electronic medium. Modulation enables the transfer of information on an electrical signal to a receiving device that demodulates the signal to extract the blended information. Modulation is the process of changing the parameters of the carrier signal, in accordance with the instantaneous values of the modulating signal Types of modulation Analog Modulation: Analog modulation is the simplest form of the modulation. In analog modulation, the modulation is applied continuously in response to the analog information signal. a) Amplitude modulation: Amplitude modulation (AM) is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a high frequency carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent. Amplitude modulation is a method of impressing data onto an alternating-current (AC) carrier wave form. The highest frequency of the modulating data is normally less than 10 percent of the carrier frequency. The instantaneous amplitude(overall signal power) varies depending on the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating data. (b) Angle modulation: Angle Modulation: the frequency or phase of the carrier signal is varied in accordance with the strength of the modulating signal. Analog Modulation has two forms: (i) Frequency modulation: Frequency modulation is a process in which the frequency of the carrier is controlled by the modulating signal. Frequency modulation is less error-prone than amplitude modulation as a broadcast means. The broadcast of a single signal, such as a monophonic audio signal, can be done by straightforward amplitude modulation or frequency modulation. Frequency modulation is a process in which the frequency of the carrier is controlled by the modulating signal.
- 2. (ii) Phase modulation: Frequency Modulation and the Phase Modulation are the two forms of the angle modulation. The main characteristic of the angle modulation is that the amplitude of the carrier frequency is maintained constant, whereas the frequency or phase is changed. In the phase modulation, the phase of the carrier wave is shifted in accordance with the amplitude of the modulating frequency. Phase modulation is a form of modulation that can be used for radio signals used for a variety of radio communications applications. (2) Digital Modulation: Digital communication is the process of communication in which, the signals are transferred in the form of discrete formats rather than the continuous analog forms. Digital communication is very common in the present day communication systems and the signals are normally transmitted in binary formats. It is always easy to process the digital information as compared to the analog signals, because of their discrete nature and hence they have become more popular in the electronic communication. Advantages of Digital Communication 1. Reliable communication 2. Less sensitivity to changes in environmental conditions (temperature, etc.) 3. Easy multiplexing 4. Easy signaling 5. Voice and data integration 6. Easy processing like encryption and compression Analog to Digital Conversion: An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D) is a device that converts the input continuous physical quantity to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude. Instead of doing a single conversion, an ADC often performs the conversions ("samples" the input) periodically. The result is a sequence of digital values that have converted a continuous-time and continuous- amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signals. The most commonly employed A/D converter is the Ramp based circuit. It uses a comparator to compare the voltage levels Digital to Analog Conversion: Digital to analog converter is the electronic circuit, which takes digital input and converts this into an analog waveform. A common use of digital-to-analog converters is generation of audio signals from digital information in music players. Digital video signals are converted to analog in television and cell phones to display colors and shades. (a) Amplitude Shift Keying: Frequency Shift Keying Phase Shift Keying 1) Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) is a type of Amplitude Modulation which represents the binary data in the form of variations in the amplitude of a signal. Any modulated signal has a high frequency carrier. The binary signal when ASK modulated, gives a zero value for Low input while it gives the carrier output for High input.
- 3. 2) Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) is the digital modulation technique in which the frequency of the carrier signal varies according to the digital signal changes. FSK is a scheme of frequency modulation. The output of a FSK modulated wave is high in frequency for a binary High input and is low in frequency for a binary Low input. The binary 1s and 0s are called Mark and Space frequencies. 3) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) or BPSK( Binary Phase Shift Keying): Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation scheme that communicates the data by changing, or modulating, the phase of the carrier wave. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern in the form of a binary code. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase. It determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the phase of the received signal to a reference signal.