2 unit ie& v
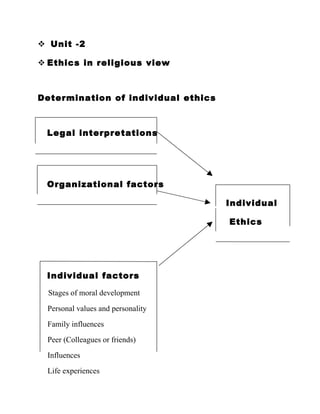
- 1. Unit -2 Ethics in religious view Determination of individual ethics Legal interpretations Organizational factors Individual Ethics Individual factors Stages of moral development Personal values and personality Family influences Peer (Colleagues or friends) Influences Life experiences
- 2. Situational factors Legal interpretation In secular societies, legal interpretations are based upon modern and often short-lived values and standards these values and standards are guided by the collection of previous judgments. The result of this different approach is amazing at one time it was legal and ethical in the United States to differentiate against women and minorities in hiring now positive action laws make it illegal to differentiate against the groups Organizational factors The organization too can affect influence participants behavior. One of the key sources of organizational influence is the degree of commitment of organizational leader to ethical conduct. This commitment can be communicated through a code of ethics, policy statement, speeches, publications etc. For example the Xerox Corporation got 15 pages of ethical code, one section of which states “We’re honest with our customers. No deals no bribes, no secrets, no fooling around with prices. A kick back in any form kick anybody out. Anybody” Individual factors Individual comes to work with different values. Factors affecting one’s ethical behavior include 1. Stages of moral development The stages of development include the minor stage and adult stage. The lunatic, children are not responsible for their behavior
- 3. 2. Personal values and personality An individual values and morals will also influence his or her ethical standards. A person who stresses honesty will behave very differently from another 3. Family influences Individual start to form ethical standards as children. The individual must be rewarded for ethical behavior and punished for the unethical behavior by the family members 4. Peer influences The individuals are influenced by the peers with whom they are interacting daily. The individual should must take only the ethical behavior from peer 5. Life experience The positive and negative key events affect the lives of an individual and determine the ethical behavior and beliefs 6. Situational factors The individuals behave unethically in certain situation because they may see no way out. Christian Business Ethics Principles • Faith in the Workplace
- 4. Which covers the issues: business as missions and (Christian) ethics in business? The issues of Christianity in the workplace and marketplace are both passions of mine. I thought these touch points might be a useful breakdown. • Taking Care of Resources In addition, when we care for our possessions, it gives us opportunity to imitate many other attributes of God, such as wisdom, knowledge, beauty, creativity, love for others, kindness, fairness, independence, freedom, exercise of will, blessedness (or joy), and so forth.” • Greed and materialism We could use our resource to advance our own pride, or we could become greedy and accumulate wealth for its own sake, or we could take wrongful security in riches. We could use our possessions foolishly and wastefully, abounding in luxury and self-indulgence while we neglect the needs of others. These things are rightly called ‘materialism,’ and they are wrong • Buying and selling goods We can imitate God’s attributes each time we buy and sell, if we practice honesty, faithfulness to our commitments, fairness, and freedom of choice.” • Earning Profit The ability to earn a profit it thus the ability to multiply our resources while helping other people. It is a wonderful ability that God gave us and it is not evil or morally neutral but fundamentally good. Through it we can reflect God’s attributes of love for others, wisdom, sovereignty, planning for the future, and so forth.” • Money and Financial Resources Money provides many opportunities to glorify God, through investing and expanding our stewardship and imitating God’s sovereignty and wisdom,
- 5. through meeting our own needs and thus imitating God’s independence, through giving to others and imitating God’s mercy and love, or through giving to the church and to evangelism and thus bringing others into the kingdom • Attitudes of Heart: God knows our hearts, and we glorify him by having attitudes of heart in which he delights….And if others work for us, we need to think of them as equal in value as human beings made in the image of God, and our heart’s desire should be that the job bring them good and not harm • Borrowing and lending In this way, borrowing and lending multiply phenomenally our God-given enjoyment of the material creation, and our potential for being thankful to God for all these things and glorifying him through our use of them. In borrowing and lending, we can reflect many of God’s attributes. We can demonstrate trustworthiness and faithful stewardship, honesty, wisdom, love, and mercy.” Hindus Business ethics principle • Principles of Jewish Business Ethics 1. Accurate weights and measures You shall not falsify measures of length, weight, or capacity. You shall have an honest balance, an honest weight, and the Mishnah spells out how often wholesalers and retailers must clean their weights and measures. The prices must be fixed based on the based. These laws are just as applicable today. Wholesalers and retailers must check their scales and cash registers on a regular basis, not just because civil law demands it, but also because Jewish law requires it.
- 6. 2. Monetary cheating “When you sell anything to your neighbor or buy anything from your neighbor, you shall not mislead one another.” The rabbis of the Talmud used this verse as a basis for a series of specific laws on the subject of monetary cheating. They ruled that if the price charged was more than one sixth above the accepted price, the sale is null and void and the seller must return the buyer’s money, while if it was less than a sixth, the transaction is valid and no money need be returned. Needless to say, these laws are relevant today. It is permissible for a Jew to make a fair profit; it is not permissible to price gouge and rob the customer blind. 3. Verbal cheating Just as there is cheating in buying and selling, there is cheating in words. A person should not say to a merchant: ‘How much does this cost?’ if he has no intention of buying it.” Let us say that Raja goes into a warehouse outlet in order to buy a computer, but he wants a demonstration before he spends $1000. The warehouse outlet is not equipped for demonstrations. The salesman says to Raja: “Go to the IBM showroom down the block and ask for a demonstration, then come back here and buy the computer at our low, low price.” Raja complies and gets a free demonstration plus a discount. When raja asks for the demonstration at the IBM store, he has absolutely no intention of purchasing the computer there. He merely wants a free demonstration. The IBM salesman is being deceived. He either loses a real customer while waiting on raja, or feels badly when Raja walks out on him after a half-hour demonstration. 4. Stealing a person’s mind We would call it false packaging or false labeling. We are all familiar with this kind of ruse. A wholesaler takes an inferior brand of shirt and puts on Pierre Cardin labels. We all know how used cars are touched up and polished for the sole purpose of overcharging the customer.
- 7. 5. Putting a stumbling block before the blind We would call it “giving someone a bum steer.” This law is based on Vayikra Chapter “You shall not curse the deaf nor put a stumbling block before the blind, but you shall fear your God, I am the Lord.” Our Sages interpreted this verse in a very broad fashion “You shall not put a stumbling block before the blind” – before someone who is blind in that particular matter… don’t say to your neighbor ‘sell your field and buy a donkey,’ when your whole purpose is to deceive him and buy his field. This law can be readily applied to modern situations: A real estate agent should not dupe a young couple into buying a home with structural faults simply in order to make a fast buck. A stockbroker should not sell his client a bad investment just to collect the commission. A salesman should not convince his customer to buy an expensive item he really has no use for. About such behavior we are warned: “and you shall fear your God, I am the Lord.” 6. Tax avoidance Eighteen hundred years ago, the l established the legal principle that in civil matters “dina d’malkhuta dina - the law of the land is the law” . In its discussion of this principle, the Talmud specifically includes taxation as a secular law that must be followed. This, for example, is the way Maimonides summarizes this law “but a tax fixed by the king of 33% or 25% or any fixed sum… a person who avoids paying such a tax is a transgressor because he is stealing the king’s portion, regardless of whether the king is Jewish or not.” Jewish law requires us to pay our taxes in a scrupulous fashion because in civil matters “the law of the land is the law.” Principles of Buddhism 1. Right views As ignorance with its consequences, namely, wrong views about the self and the world is the root cause of our suffering it is natural that the first step to moral reformation should be the acquisition of right views or the knowledge about
- 8. the four noble truths. It is the knowledge of these truths alone that helps moral reformation and leads us towards the goal. 2. Right determination Mere knowledge of the truths would be useless unless one determination to reform life in its light. The moral aspirant is asked to renounce all attachment to the world, to give up ill feeling towards others and desist from any harm to them. These three constitute the contents of right determination 3.Right speech Right determination should not remain a mere pious wish but must issue forth into action. Right determination should be able to guide and control our speech. The result would be right speech consisting of abstention from lying, slander, unkind words and merry talk 4.Right conduct Right determination should end in right action or good conduct and not stop merely with good speech. Right conduct consists therefore of desisting from destroying life, from stealing and from improper gratification of the senses 5.Right living Reject bad speech and bad actions, one should earn one’s living by honest means. Right living entails that one’s means of living should not be dishonest or otherwise cause suffering to other living beings. 6. Right effort While a person tries to live a reformed life, through views, resolution, speech action and living, he is constantly knocked off the right path by old evil ideas that were Dee rooted in the mind as also by fresh ones that constantly arise. Once cannot progress unless he maintains a constant effort to root out old evil thoughts and prevent fresh evil thoughts from arising. Moreover as the mind cannot be kept empty he should constantly endeavor to fill the mind with good ideas and retain such ideas in the mind. This fourfold constant endeavor is called right effort 7. Right mindfulness The necessity of constant vigilance is further stressed in this rule that lays down that the aspirant should constantly bear in mind the things he has already learnt.
- 9. 8. Right concentration One who has successfully guided his life in the light of the last seven rules and thereby freed himself form all passions and evil thoughts is fit to enter step by step into four deeper stages of concentration that gradually take him to the goal of his long and arduous journey- cessation of suffering. He concentrates his pure mind on reasoning and investigation regarding the truths and enjoys the joy and ease born of detachment and pure thought. Principles of Muslim religious in business ethics Freedom of Enterprise Islam gives complete freedom to economic enterprise. Each individual in an Islamic society enjoys complete freedom in the earning of his livelihood. He can start, manage and organize any kind of business enterprise within the limits set by the Islamic. However, freedom does not and must not operate without a sense of responsibility. An individual is free to pursue his economic activities provided he respects the code of conduct prescribed for the profession, which broadly means choosing things lawful and shunning matters unlawful. Islam, as a matter of principle, prohibits all activities which may cause harm either to the traders or the consumers in the market. It encourages the prevalence of free market where everyone earns his sustenance without government intervention. However, it puts certain restraints in order to eliminate the incidence of injustice and check malpractices and unlawful operations Concerning Business Transactions An Islamic market is characterized by certain norms that take care of the interests of both the buyer and the seller. There are a number of rules of ethical discipline in Islamic commercial transactions without which business contract would be regarded as lacking perfection in the light of the code of good manners, decency and ethical excellence
- 10. Earn lawful Earnings Islam places great emphasis on the code of lawful and unlawful in business transactions. It disapproves the wrongful taking of the property. Muslim trader must be determined to earn only through lawful means Trade through Mutual Consent Mutual consent between the parties is a necessary condition for the validity of a business transaction. It, therefore, follows that a sale under coercion is not acceptable in Islam. A sale transaction is to be regarded as legal only if it is made through the mutual consent of the parties concerned. Truthfulness in Business Transactions Islam encourages truthfulness in business transactions and raises the status of a truthful merchant so much so that he will be at par with the holy warriors and martyrs, in the Hereafter. The seller and the buyer have the right to keep or return the goods as long as they have if both the parties spoke the truth and described the defects and qualities of the goods then they would be blessed in their transaction, and if they told lies or hid something, then the blessings of their transaction would be loss Trustworthiness in Business Transactions Trustworthiness is one of the most important principles of ethical discipline in commercial transactions. It demands sincerity in work and purity of intention from every believer. A true Muslim trader will avoid fraud, dishonesty, and other dubious means in selling his merchandise. Honouring and fulfilling Business Obligations Islam attaches great importance to the fulfilment of contract and promises. Islamic teachings require a Muslim trader to keep up his trusts, promises and contracts. The basic principles of truth, honesty, integrity and trust are involved
- 11. in all business dealings. Each business contract should clearly specify the quality, the quantity and the price of the commodity. Thus, in a business contract the offer and acceptance should be made between the parties concerned on a commodity which is with the buyer and, which he is able to deliver. Any commodity which is non-existent or not deliverable is not allowed to be transacted. Fair Treatment of Workers Islam puts certain conditions and restrictions to obviate the chances of bitterness between the employer and employees. Islam encourages and promotes the spirit of love and brotherhood between employer and employees. According to the Islamic teachings it is the religious and moral responsibility of the employer to take care of the overall welfare and betterment of his employees. Fair wages, good working conditions, suitable work and excellent brotherly treatment should be provided to the workers Dealing in Prohibited items Dealing in unlawful items such as carrion (dead meat), explosive etc are strongly prohibited in Islam Fixing the Prices Islam grants absolute freedom to traders provided they adhere to the code of lawfulness. It does not, therefore, encourages the practice of price–fixing and leaves the traders to earn the profits from each other within the lawful limits Cheating and Fraud in Business Transactions Islam strongly disagrees all such practices in business transactions. The Messenger of Allah has commanded the believers not to indulge in cheating and fraudulent practices in business transactions. Ethical Policy
- 12. Identify the impact its actions and policies have on the environment and society it prescribe a range of guidelines and aims that will limit the actions have on the environment and society. The policies of ethics in business • Statement of Policy The Code of Business Conduct was prepared to provide Associates, as well as those with whom we do business and the general public, with a formal statement of the Company’s commitment to the standards and rules of ethical business conduct. All Associates are expected to review this Code, and in so doing, agree to comply with its principles. This Code should be considered the basis on which each Associate conducts business on behalf of, and is the cornerstone of ethical business practices. A code of conduct cannot cover all circumstances or anticipate every situation. Associates encountering situations not addressed specifically by this Code should apply the overall philosophy and ethical standards observed by honorable people everywhere. Situations that are not covered may be reviewed with your manager, or as appropriate, senior management of the Company. • Use of Company Funds and Assets The assets of the Company are to be used solely for the benefit of the Company and only for valid business purposes. The assets are much more than our physical plants, equipment, inventory, company funds, or office supplies. They include technologies, concepts, business strategies and plans, financial data, and other information about our business. These assets may not be improperly used to provide personal gain for Associates or others. Associates may not transfer any of the assets to other people, except in the ordinary course of business. On occasion, some assets of the Company no longer needed in the business may be sold to Associates. Such sales must be supported by properly approved documentation signed by an appropriate authority other than the Associate.
- 13. • Confidential Information As part of a business may have access to confidential information about the customers, suppliers and competitors. Until material information has been made public, this information is not to be disclosed to coworkers who do not have a business need-to-know, nor to non-Associates (including former Associates) for any reason except in accordance with established corporate procedures, which may include confidentiality agreements when appropriate. Associates may not use confidential information obtained on the job for personal financial gain through the trading of securities or other personal financial transactions. "Confidential information" includes information or data on products, business strategies, company manuals, material, processes, systems, procedures, etc., as well as all financial data. If there is any question as to whether information is confidential material or whether it has been publicly disseminated, Associates should take the initiative to consult with a Company officer or director prior to initiating any securities trade, or discussing any significant information with anyone outside the Company. • Agreement with Laws The business of the Company must be conducted in compliance with all applicable laws, rules and regulations at all federal, state and local levels of government in the United States and at all levels of government in any non-U.S. jurisdiction in which we do business. In some cases, the interpretation of laws, rules and regulations may be difficult, but we have access to legal advice and will furnish such advice as necessary to enable you to comply with this policy. • Dealing With Suppliers and Customers Obtain and keep our business because of the quality and value of our products and services, and the respect and confidence we instill in our customers. Conducting business with suppliers and customers can pose ethical or
- 14. even legal problems, especially in cross-border transactions where local laws and practices may be different from those with which we are familiar. The following guidelines are intended to help all Associates to make the "right" decision in potentially difficult situations. • Payments to Agents, Representatives or Consultants Agreements with agents, sales representatives, or consultants must be in writing in corporate standard format, and must clearly and accurately set forth the services to be performed, the basis for earning the commission or fee involved, and the applicable rate or fee. Any such payments must be reasonable in amount, not excessive in light of the practice in the trade, and commensurate with the value of the services rendered. The agent, sales representative or consultant must be advised that the agreement may be publicly disclosed and must agree to such public disclosure. In some countries, local laws may prohibit the use of agents or limit the rate of commissions or fees. • Communications with Competitors It is not illegal and may be appropriate for representatives of and its competitors to meet and talk from time to time. In such conversations, you should scrupulously avoid comment on such topics as pricing, production levels, marketing methods, inventories, product development, sales territories and goals, non-public market studies, and any proprietary or confidential information. Discussions regarding customers must be limited to the exchange of credit information. • Information about Competitors As a business that competes in the marketplace, we seek economic knowledge about our competitors. However, we will not engage in illegal or improper acts to acquire a competitor's trade secrets, customer lists, and information about company facilities, technical developments or operations. In addition, we will not hire a competitor's employees for the purpose of obtaining confidential
- 15. information, or urge competitors' personnel, customers, or suppliers to disclose confidential information. The Role of Business Ethics Today Business people and their corporations need to be reminded about their role and responsibilities. The following issues need special attention today: 1. Globalization should mean that all people are considered to comprise one family. All human beings should be treated with respect, equality, and fairness. Exploitation of one group by another should stop. There should not be any division among people because of their race, color, nationality, gender, or faith. 2. The resources of the Earth are not only for us, we share this biosphere with other species, and so we take care not to waste or destroy them. 3. We should use the Earth's resources with great care and should remember that we have a duty to leave this world in a better condition for the generations to come after us. 4. Human beings are one family, although we have our differences. Diversity is natural and beautiful. We should try to understand other people's religions and cultures and we should be sensitive to their feelings and emotions. 5. The universal golden rule states, "Love for others what you love for yourself." We should try to empower others and work to eradicate poverty, hunger, illiteracy, disease, and unsanitary conditions in the world in order that all people can live in peace and happiness. 6. Businesses should promote ethical and moral behavior in their corporations, as well as in the world at large. People involved in business should always be
- 16. honest, truthful, and fulfill all promises and commitments. We must eliminate fraud, cheating, and cut-throat competition. 7. We should also promote more political freedom, open debates, participatory democracies, and representative governments. 8. We must encourage and support an educational system that promotes openness, dialogue and that guard against fanaticism. Our educational system should not teach every view in the absolutist terms. Our children should be taught about the multitude of perspectives and one should be open to other points of view. Principles for Positive Business Ethics • Business Ethics are built on Personal Ethics Business Ethics are built on Personal Ethics. There is no real separation between doing what is right in business and playing fair, telling the truth and being ethical in your personal life. • Business Ethics are based on Fairness Business Ethics are based on Fairness. Would a dis-interested observer agree that both sides are being treated fairly are both sides negotiating in good faith. Does each transaction take place on a "level playing field. If so, the basic principles of ethics are being met. • Business Ethics require honesty. Honesty refers to wholeness, reliability and consistency. Ethical businesses treat people with respect, honesty and integrity. They back up their promises, and they keep their commitments • Business Ethics require Truth-telling
- 17. Business Ethics require Truth-telling. The days when a business could sell a defective product and hide behind the "buyers beware" defense are long gone. You can sell products or services that have limitations, defects or are out-dated, but not as first-class, new merchandise. Truth in advertising is not only the law, business ethics require it. • Business Ethics require Dependability Business Ethics require Dependability. If your company is new, unstable, about to be sold, or going out of business, ethics requires that you let clients and customers know this. Ethical businesses can be relied upon to be available to solve problems, answer questions and provide support • Business Ethics require a Business Plan Business Ethics require a Business Plan. A company's ethics are built on its image of itself and its vision of the future and its role in the community. Business ethics do not happen in a vacuum. The clearer the company's plan for growth, stability, profits and service, the stronger its commitment to ethical business practices. • Business Ethics apply internally and externally Business Ethics apply internally and externally. Ethical businesses treat both customers and employees with respect and fairness. Ethics is about respect in the conference room, negotiating in good faith, keeping promises and meeting obligations to staff, employers, vendors and customers. The scope is universal. • Business Ethics require a Profit Business Ethics require a Profit. Ethical businesses are well-run, well-managed, have effective internal controls, and clear expectations of growth. Ethics is about how we live in the present to prepare for the future, and a business without profits (or a plan to create them) is not meeting its ethical obligations to prepare for the future well-being of the company, its employees and customers. • Business Ethics come from the Boss
- 18. Business Ethics come from the Boss. Leadership sets the tone, in every area of a business. Ethics are either central to the way a company functions, or they are not. The executives and managers either lead the way, or they communicate that cutting corners, deception and dis-respect are acceptable. Line staff will always rise, or sink, to the level of performance they see modeled above them. Business ethics starts at the top. 18 Rules of International Business Ethics Rule 1: If you strive to understand the values of different cultures, you will find common points. Rule 2: if you analyze the facts, you will realize that honesty and reliability benefit you. Rule 3: if you analyze case studies from different perspectives, you will discover the benefits of fair play. Rule 4: Respecting your colleagues is the smartest investment you can make. Rule 5: To increase productivity, provide safe and healthy working conditions. Rule 6: To inspire trust, make your performance transparent. Rule 7: Your loyal dissent can lead your institution in the right direction. Rule 8: Downsizing your labor force is only beneficial when you respect each stakeholder. Rule 9: To establish your brand name, act as a fair competitor. Rule 10: Reduce the gap between the rich and poor by developing a new social security system. Rule 11: if you act against discrimination, you will increase your productivity and profitability. Rule 12: If you protect intellectual property, all stakeholders will receive their due share.
- 19. Rule 13: Ongoing changes in information technology require new forms of loyalty. Rule 14: Your public relations strategy will only secure your reputation if it witnesses your drive for quality and excellence. Rule 15: Your economic achievements will only stand on firm ground if you diminish corruption. Rule 16: Long-term success urgently calls you to constantly care for the environment. Rule 17: To become a refined player, sharpen your discernment and cultivate good manners. Rule 18: Care for your business by caring for society. Contentious rules of Business ethics OR Theory of ethics OR decision making to mattered equally
- 20. Cultural environment .Religion Perceived ethical Legal system problem Political system Professional environment Deontological Deontological Action control Informal norms norms evaluation Formal codes Code enforcement Perceived Industry environment alternatives Informal norms Formal codes Code enforcement Probabilities of Ethical Intentions Behavior Organizational environment Consequences judgments Informal norms Formal codes Desirability of Code enforcement Consequences Personal characteristics perceived Teleological Religion consequences Importance of evaluation Actual Value system stakeholders Consequences Belief system Strength of moral character Cognitive moral development Ethical sensitivity Ethics The ethics is a set of moral principles which guides the code of conduct and behavior of a human being in his life and in society Determinants of ethics
- 21. 1. Value and morals The code of conduct is based on the value and morals of a person or a society, which leads to setting of goals and objectives and the effort for achieving these levels 2. Family, schools and religions: The learning of behavior starts in the beginning of one’s life. In the family one learns what is good or bad, what ought to do or not to do. The parents and family members inculcate the value the value, morals and ethical standards among their children by rewarding good behavior and controlling unacceptable manners. In the same way, a student learns several behaviors from school and religious society. It may be in terms of truthfulness, honesty, sincerity, tolerance 3. Peers, colleagues and superiors A person learns most of the behavior of life form his workplace. This friends, team members and superior people promote, rewards and control the different behavior which develops a pattern of working 4. Social pressure There is considerer able influence of social pressure on the life style of a person. The different customs, norms, culture, beliefs of a society. Discrimination based on caste system, different boycotts, prevention for the construction of any such thing like nuclear power plant, ban on adoption for social reformation restrict the thoughts as well as actions in one’s life 5. Experiences from life One learns so many lessons from his own experiences from his own life. There may be so many bitter or sweet experiences depending on the ability of a person or expectation. Success or failure teach how to do or act next in an individual life 6. Organizational demand and ethical codes The organizations have their specific guidelines for the managers as well as employees. The employees as ethics of the organization follow these codes of
- 22. behavior. All the top, middle and first level management compromise their personal principles to meet the organizational demand the corporate goals and objectives exert considerable pressure of the executive to change their ethical views 7. Legislation Govt, legislation, rules and regulations guide the code of conduct about standards, social responsibilities, exploitation, corruption in public life, product safety, working condition; statutory warning etc.these guidelines helps in determining what are acceptable standards and practices 8. Threatened situations There are several situations in person’s life where he or she faces several threats. It may be loss of job, social boycott, critical disease, loss of wealth etc which bounds human behavior and sets the new path of conduct for personal and professional life Objectives of ethics 1. To set the standards of personal life and norms of behavior 2. To define the working pattern of professional life 3. To set a standard for do’s and don’ts 4. To develop a value system 5. To create strong work culture 6. To set the mission of life 7. To inculcate good behavior in children 8. To improve the social life 9. To balance the need and wishes of human being 10. To prevent the social evils
- 23. Ethics in teaching Teaching ethics means to teach the ethics of business in the school or colleges or in university Principles of Ethical education 1. Content Competence A university teacher maintains a high level of subject matter knowledge and ensures that course content is current, accurate, representative, and appropriate to the position of the course within the student's program of study. 2.Academic Competence - A pedagogically competent teacher communicates the objectives of the course to students, is aware of alternative instructional methods or strategies, and selects methods of instruction that are effective in helping students to achieve the course objectives. 3. Dealing with Sensitive Topics - Topics those students are likely to find sensitive or discomforting are dealt with in an open, honest, and positive way. 4. Student Development - The overriding responsibility of the teacher is to contribute to the intellect development of the student, at least in the context of the teacher's own area of expertise, and to avoid actions such as exploitation and discrimination that detract from student development. 5. Dual Relationships with Students - To avoid conflict of interest, a teacher does not enter into dual-role relationships with students that are likely to detract from student development or lead to actual or perceived favoritism on the part of the teacher. 6. Confidentiality - Student grades, attendance records, and private communications are treated as confidential materials and are released only with
- 24. student consent, for legitimate academic purposes, or if there are reasonable grounds for believing that releasing such information will be beneficial to the student or will prevent harm to others. 7. Respect for Colleagues - A university teacher respects the dignity of her or his colleagues and works cooperatively with colleagues in the interest of fostering student development. 8. Valid Assessment of Students - Given the importance of estimation of student performance in university teaching and in students' lives and careers, instructors are responsible for taking adequate steps to ensure that assessment of students is valid, open, fair, and congruent with course objectives. 9. Respect for Institution - In the interest of student development, a university teacher is aware of and respects the educational goals, policies, and standards of the institution in which he or she teaches. Visit the Association for Practical and Professional Ethics' Web site to learn more about ethics in college teaching Regulating ethics 1. Market systems Most of the recent ethical writings on integrating greed, Pleasure, efficiency, privacy and free choice rely on the existence of a market system considered to be a profoundly ethical instrument. Its ethical use has been accepted by many ancient cultures including India but with less enthusiasm and greater constraints. Market system can be viewed as value neutral as they can only be vehicles for transactions. However the relationships they generate have strong ethical overtones and therefore the system can be treated as value in ethics. 2.Respect for processes of social adaptation
- 25. Respect for family and other institutions for socializing individuals in their ethical evolution is now understood as an important ethical value equally valid for business. In fact Alacrity foundation of tamilnadu has made it a motto in the advertisements. 3. Respect for law Institutionalizing ethics through laws that can be enforced is a process as old as civilization itself. Hosmer (1995) accords high value to this process. Thomas Hobbes and john Locke in England and kautilya, Thiruvalluvar and Manu in India have also been its proponents. The overzealous concern for the value of protecting the institutional means should not supersede the basic need for ensuring that the outcomes are by themselves ethical 4. Respect for professional codes A major development in the ethical movement in the US is the mobilization of professions through professional councils who develop professional codes which make it easier to reach across to organization and provide a countervailing force to greed. This path of ethical control through professional guilds was quite common in ancient India. Professional councils and codes have played a major role in the ethical revival in the west. 5. Organizations as vehicles of ethical synergy Large organizations that were not extensions of the state apparatus are relatively new to civilization. An emerging ethical value in business is that they must synergies ethics such that their actions are the summation of individual ethical values and not of ethical disvalues. The respect for ethical frameworks and consequently becomes an ethical value by itself 6. Respect for rituals and symbols The last of the values is an enigma. A growing number of people now feel that rituals and symbols of every culture are strong emotional and psychological supports for ethical sustenance. There are strong ancient Indian traditions both for and against this
- 26. Principles of business ethics 1. Stimulating morale thoughts 2. Developing problem solving skill 3. Creating a sense of moral commitment 4. Recognizing the ethical problem 5. Reducing hesitation Code of conduct in ethical education The ethical education is given in the following things 1. Truthfulness The truthfulness is the corner stone of all values. A business manager honorably straight. It is the characteristic that distinguishes a professional manager from mercenary 2. Fairness A manager should look at and treat all aspects of an issue in a fair and balanced manner. 3. Responsiveness to the public interest Though a manager is paid to serve the interest of the stock holders of the company, public interest is no less important. In fact mangers should consider it as of paramount importance, if they have to successful in their tasks 4. Accountability
- 27. Accountability is one of the basic characteristics of a good business managers are responsible for all their actions and are accountability to all the stakeholders- stockholders, creditors, employees, consumers, government and the society at large 5. Honesty A cardinal ethical value that a manager should possess is this quality. Managers should be fair, just and sincere both in character and behavior. They should not indulge in cheating or stealing and should be free of deceit and untruthfulness 6. Clearness Good business managers should be clear and set standards for others to follow. They should be frank and open. Their actions should be easily discussed and understood by others Benefits of learning Business ethics The benefits of learning business ethics 1. Aware of the moral principles Young mangers should understand and be aware of the reasons that underlie moral principles. These are helpful in fostering ability to reason when applying these principles it is vital part of ensuring compliance by managers with company standards for conduct 4. Determine ethical issues Knowledge of business ethics will help mangers in determining the ethical issues 5. Responsible tone for the organization Knowledge will help mangers in setting highly responsible tone for the organization in individual judgments’ and decisions whether ethical or not
- 28. 6. Provide hard-working managers The study of business ethics will provide hard working managers with morally responsible approach to business. The need for responsible managers is acute as questions of business ethics cannot wholly be determined by law or government regulations but means remain the concern of individual manager. 7. To realize their social responsibility It helps to realize their social responsibility. Many organizations find it wise to go beyond their primary mission and take into account needs of the community. Business ethics makes managers more accountable for social responsibility 6. High level of honesty in managers The study of business ethics inculcates high level of honesty in managers. Goal of ethics education to his share knowledge, build skills and develop minds. It helps to gain clarity and insight into business ethics and avoid business misconduct in organizations. The study of business ethics helps to arrive a decision that he feels to be right and proper .It facilitates individual to understand their moral standards and ethical norms, beliefs and values so that they can decide when faced with business dilemma Types of values Values can be divided into two classes Instrumental values Are those values regarding the way we approach end states These relate to means for achieving desired results. Assertiveness Dependability
- 29. Hard work Obedience Open mindedness Self sufficient Truthfulness Good manners Terminal values refer to beliefs about ultimate good or end results while instrumental values refers to beliefs about desirable modes of behavior that are instrumental to the attainment of ultimate of goals. Satisfaction Peace and harmony Pride in accomplishment Prosperity Recognition Security Theoretical values Interest in the discovery of truth through reasoning and systematic thinking Economic values Interest is usefulness and partiality including the accumulation of wealth Social values Interest in gaining power and human relationships Political values Interest in gaining power and influencing other people Religious values
- 30. Interest in unity and understanding the cosmos as a whole The following list shows several instrumental and terminal values Value formulation 1. Genetic source A significant portion of our value is genetically determined 2. Environmental source Environmental factors like natural environment, culture, friends circle, educational institutions, and religious faith help in formulation of values 3. Influence of superiors Parents, elders, teachers, religious leaders, all such persons help us in the formulation of our values 4. Media News papers, journals, magazines, film, radio, cinema go long way to formulate our values 5. Value forming institutions The development of a human life and society is based on values. There are various institutions in the society which inculcates values. There are four major institutions which provide the basic sources of values: - family, school, state and religion. These institutions teach the individuals what is good or bad for them. Good behavior is rewarded
- 31. and bad behavior is punished. It develops and inculcates a particular behavior 6. Organizational values The organization where an individual works affects the behavior and shape value in working life. The different organizations have their own value system and behavioral pattern which shapes human life 7. Peers and colleagues An individual learns different behavior from his peers and colleague. In a work group an individual learn the group’s norms and values. Organization or group value strengthen and protect the membership status in that group 8. Work and career The model of work in an individual career includes the task or responsibilities associated with a particular job in a period of time. It follows a related progressive of job career over a period of time. Relevance of values in management: • worth of values in management Our effectiveness at work is tied to exercising intrinsic human values i.e., moral or ethical values. These human values support established
- 32. business values such as service, communication, excellence, credibility, innovation, creativity and coordination. The human values help in self development. Managerial function such as direction, control, supervision and communication, integration and coordination are much easier. The human values help good interpersonal interactions. They reduce conflicts and disputes. They are part and parcel of achieving accelerated process of improvement and customer’s workers and citizen satisfaction. They enhance reputation and good will of the organization In the view of management and organizational work we can say that: • Value system influences choice of organizational goals and strategies adopted to achieve those goals • Value influences the way in which an individual looks at other individual and its group of individuals that is interpersonal relationship. Value becomes basis of such interpersonal interactions. • Individuals judge organizational success as well as its achievement on the basis of their value system • Individuals set limit for the determination of ethical behavior for themselves as well as for others • Values determine the extent to which individuals accept organizational pressure and goals. • Values helps in decision making
- 33. It helps in better decision making because respect for moral principles l from a management eye view to take all aspects into consideration, both the economical aspects and social and ethical aspects • Essential for long term success of organization An organization not responding the values and ethics can survive only for a short period but not for long period. An organization is required to build up a strong image for long term survival • Value creates credibility among share holders If values are properly followed it would create a good image of company and it would help in attracting an immediate response of shareholders • Value creates credibility (reliability) with the public A company having the ethical and social value will be honored and respected by even those who have no knowledge of its actual working. There will be an intuitive prejudice in favor of its product, since people believe the company gives for money Some additional Relevance of values in management 1. Managerial effectiveness based on value based management can solve problems irritating the economy in all countries. Such management offers human welfare, nature welfare the quality of life and quality of work. 2. Selfless action purifies our mind/ intellect. Purer mind concentrate, contemplate and mediate to approach perfection i.e., pure consciousness 3. Self surrender to god and emotionally we can reach the goal of pure consciousness
- 34. 4. Value based management provide proper use of valuable human and material resources offered by the mother earth 5. Value based management promotes work culture, self discipline and consciousness among the employees 6. Value based management helps in bringing the human agreement and happiness in the organization 7. Value based management cares for its people. People are protected from unwanted stresses and strains, unrest and adverse organizational work life 8. Value based management reduces the conflict and disputes Factors that guide managers to take ethical decisions 1. A man’s personal code of ethics 2. The company’s formal policy 3. The ethical climate in the industry 4. Government regulations 5. Behavior of mangers with the society 6. The organization becomes larger their standards of ethical conduct tend to rise because of greater public exposure/ image Teaching ethics to management students: • Management knowledge
- 35. Management knowledge is like physical body to which soul is provided by ethics. Without ethics knowledge of management is just like meals without salt and the body without soul. • Essential power of differentiate right and wrong Knowledge of ethics will equip students of management with an essential power of discriminate right and wrong. It will make them wisdom decision makers or leaders. They will set good examples through their ethical decisions, conduct and behavior before their subordinates. This will improve effectiveness of individuals, departments and organization as a whole. • Serve as standard on the basis of which quality of management Ethics serve as standard on the basis of which quality of management. Good management or mismanagement can be determined, quality of decisions can be examined and quality of individual conduct can be examined. Mis conduct can be penalized. Good management good decisions and good conduct may be appreciated and rewarded • Key issue in corporate governance Ethics are the key issue in corporate governance debate. Without atmanushashan there can’t be good corporate governance and without that there can’t be good administration. • Solid foundation to corporate laws Ethics provide solid foundation to corporate laws, code of conduct; corporate social responsibility etc. there is corporate ethics committee at board level as part of corporate governance. Socially responsible corporate entity can be conceived on the basis of ethical framework • Boundaries of corporate behavior and conduct Ethics define boundaries of corporate behavior and conduct. What will amount to compliance with corporate laws. What will amount to corporate misconduct
- 36. are the critical issues which managers can better understand through knowledge of ethics • Ethics determine human values General ethics determine human values. A manager committed to ethics will have due respect for human values or human rights. He will never think about exploitation of anybody or showing disrespect to others Importance of teaching ethics There is a study carried out a Harvard business school by three of its faculties. One of the researchers tells us of the response of the students to the required ethics module at H.B.S 1.One student says that earlier he didn’t consider ethical issues as important ones but after taking course on ethics, he has become aware of the need to ask the question of what is going to be the impact of this decision on the people that live in that area and environment 2. Another student says that the difference such as course has made is in level of analysis. When you talk about whom are all people involved 3. Ethical consciousness and commitment can continue to undergo transformation at least throughout formal education has to be the foundation of any program of teaching ethics 4. An overemphasis of SWM (shareholders wealth Maximization) objectives of managers on a mis understanding of its true implication and theoretical foundation means that if these are misunderstood then it can lead to dangerous or disastrous consequences for consumer’s employees in the general population. So teaching ethics is extremely necessary in present scenario Barriers to teaching ethics
- 37. 1. According to some research in the H.B school some faculties feared that they would be asked to teach ethics as a distinct subject 2. Some faculties feared that teaching a course on ethics would bring very few professional rewards 3. Many faculties felt that integration of ethics into the class soon can threaten their self confidence who identify strongly with their role as experts in their professional field without giving or having the same confidence on ethics issues 4. Some teachers as well as some students felt that they need to pay some attention to ethics in their own lives before they can talk it in the classroom 5. Some faculties raised a number of teaching questions like how should a faculty respond to a student’s behavior that appears very much unethical Ethical as a tool for moral training in the organization The ethics program is essentially useless unless all staff members are trained about what it is how it works and their roles in it. The nature of the system may invite suspicion if not handled openly and honestly. In addition no matter how fair and up to date is a set of policies; the legal system will often interpret employee behavior (rather than written policies) as de facto policy. Therefore all staff must be aware of and act in full accordance with policies and procedures (this is true, whether policies and procedures are for ethics programs or personnel management). This full accordance requires training about policies and procedures 1. Orientation of new employees to the organization’s ethics program during new employee orientation 2. Review the ethics management program in management training experiences 3. Involving staff in review of policies (ethics and personnel policies) is strong ethics training
- 38. 4. Involving staff in review of policies ( ethics and personnel policies) is strong ethics training 5. One of the strongest forms of ethics training is practice in resolving complex ethical dilemmas. Have staff use any of the three ethical dilemma resolution methods in this guidebook and apply them to any of the real to life ethical dilemmas also listed in this guidebook 6. Include ethical performance as a dimension in performance appraisals 7. The best ethics trainer; Bill goodman chief human resource officer at Aveda describes, we start our training even in our job ads, but the best trainer is the behavior of our leaders 8. Give all staff a copy of this free complete guide to ethics managemet Values in management Values A value is a belief on which a person acts by preference. A value is a perspectives belief. The word values means the worth, merit, usefulness or importance of a thing. Everyone does not hold the same value. The value of the thing varies from person to person and it is more relative concept few of the Trans culture values come to us by our relatives is not due to the culture we follow but due to the humanity, mankind and soft corner of an individual Cultural values in management 1. Credibility among stakeholders These are individuals which are directly or indirectly affect by decision of the organization. Stakeholders, customers, suppliers, employers, shareholders etc. 2. Corresponds to human values Managers know that his decisions can affect the thousands of individual. So there should not be any place for biasness. One should not think of individual interest.
- 39. We should help and cooperate everybody without any favor. Opportunities and responsibilities should be same for all employees at same level. 3. Helpful in decision making Another point of great importance is the Trans cultural values help the managers make better decisions. I.e. the decisions which are in the interest of public their employees and the company’s own long term good. This is so because respect for ethics will force a management to take various aspects – economic, social and ethical in decision making 4. Profit earning A company which is inspired by cultural values is also a profitable one. Value driven companies are sure to be successful in the long run, though in the short run, they may lose money 5. Management credibility with employees Cultural values are supported to be common language to bring leaderships and its people together organization values when perceived by employees as genuine create common goals, values and culture 6. Clear objective The organization should make clear the objective of the company so that even a layman can understand it. If the objectives are not clear then the lower management cannot achieve these objectives efficiently. It can affect the productivity of the employees at operational level. Clear objectives are helpful in reducing disputes and conflicts 7. Self discipline It is important to control one’s own mind before controlling others. A manger should take decisions with cool mind and self discipline. A manger should be properly disciplined which includes arriving on the time in the organization,
- 40. optimum use of working hours, Not wasting other’s time. If a manger expects discipline form others, he must demonstrate first. Features of values: 1. Values are the core of personality and are a powerful force affecting behavior 2. Values contain judgmental elementals 3. Values are fixed they change over time 4. Many values are relatively stable and enduring. This is because of the way of which they are originally learned 5. We have a hierarchy of values that form our value system. But everyone does not hold the same value 6. Values has both comfortable and strength Values for managers 1. Fearlessness 2. Purity of mind and hearts 3. Integration of thoughts 4. Inspired deals and vision 5. Creativity 6. Understanding 7. Love and affection 8. Patience
- 41. 9. Friendship with all 10. Spirit of sacrifice 11. Non violence 12. Harmlessness 13. Gentleness Styles of values 1. Performer Be conscientious and live by the ethical values and principles. Treat others with fairness and objectivity. Be fair and precise at improving products or services. 2. Helper Act as a team player and support others and make them feel welcome in group. Be of service to clients and customers 3. Producer Realistic with resources and people. Delegate responsibility and divide work components into small manageable teams. 4. Animator Be positive and flexible. Adapt to an ever new and changing work situation. Give others the freedom to grow and build positive morale among co workers 5. Expressionist Very clear with their feelings and emotions. Constantly remain in which with coworkers feeling quotient. Create the feeling of being valued being valued among the employees. Respect every person as a unique individual.
- 42. Features of values in global change 1. Managerial decision making requires an inter play of both reasoned and holistic facilities 2. Key to cooperation and team work 3. The creative energies of human being are derived from global changes 4. The effective leadership skill needs purity, strong living, selfishness terms 5. The effectiveness of such decisions depends critically on the purity of the decision maker Needs for values in global change 1. Value creation for work force An organization culture v should create a sense of commitment in the workforce. They must love their job and should be dedicated to their work. For this dedication a personal should feel as a member of family where there is no bounding but freedom and opportunity to develop him as well as the organization. In consideration of this view the management should take some steps as • Taking the initiative to implement a meaningful that address personal basis and values that foster harassment of individuals 1. Liberalization In the new economy there have been much more liberal policies. It means removing all necessary controls and restrictions. It means removing all necessary controls and restrictions like permits, license, quotas etc imposed by the government. Earlier because was required to establish majority of the industries but now the license requirement has been reduced. The above control and restrictions resulted in a) Consumption delays
- 43. b) Losses c) High cost economy Liberalization resulted in industrial sector reforms, tax reforms, foreign exchange reforms, tradepolicy reforms all of which resulted in boosting the Indian economy 2. Privatization It means transfer of functions, activity or organization form public to private sector. It indicate the beginning of the new culture in the society in which marketization, competition, efficiency become the guiding principle in economic decision making 3. Globalization It refers to entrance of private /government players in the foreign markets or independence among countries with regard to capital, goods, and technology restriction on the extension of business outside the geographical boundaries of the country 4. Participative style of management This is followed by the organization in which all the employees are invited in the meeting for suggestions in order to improve the productivity of the organization 5. Competition Earlier their used to be monopoly but not competition has become intense due to privatization and globalization. Perfect competition exists in the market. There is lots of brand available in the market in every product category. 6. Decentralization Now a day to make the implementation process faster, authority of decision making is transferred to subordinates. They know the problem and solution well. Responsibility is also transferred to subordinates
- 44. 7. Conservation of natural resources In today’s scenario companies are using natural resources without thinking of future requirements. The companies are not socially responsible towards natural resources. The concept of sustainable development should be followed and optimum utilization of resources is the need of the day
