PRESENT TENSES AND VERB FORMS
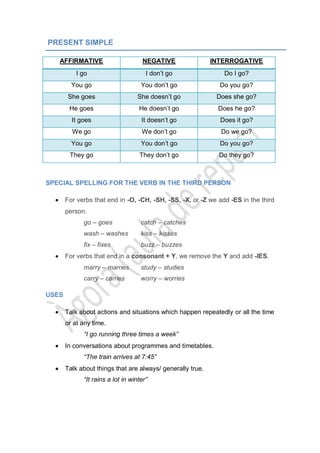
- 1. PRESENT SIMPLE AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE I go I don’t go Do I go? You go You don’t go Do you go? She goes She doesn’t go Does she go? He goes He doesn’t go Does he go? It goes It doesn’t go Does it go? We go We don’t go Do we go? You go You don’t go Do you go? They go They don’t go Do they go? SPECIAL SPELLING FOR THE VERB IN THE THIRD PERSON For verbs that end in -O, -CH, -SH, -SS, -X, or -Z we add -ES in the third person. go – goes catch – catches wash – washes kiss – kisses fix – fixes buzz – buzzes For verbs that end in a consonant + Y, we remove the Y and add -IES. marry – marries study – studies carry – carries worry – worries USES Talk about actions and situations which happen repeatedly or all the time or at any time. “I go running three times a week” In conversations about programmes and timetables. “The train arrives at 7:45” Talk about things that are always/ generally true. “It rains a lot in winter”
- 2. PRESENT CONTINUOUS AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE I‘m running I’m not running Am I running? You’re running You aren’t running Are you running? She’s running She isn’t running Is she running? He’s running He isn’t running Is he running? It’s running It isn’t running Is it running? We’re running We aren’t running Are we running? You’re running You aren’t running Are you running? They’re running They aren’t running Are they running? SPECIAL SPELLING When the verb ends with consonant + vowel + consonant we have to double the last letter. But if the verb ends with –X, -Y. W, we don’t double the last letter. Plan – Planning Row - Rowing If the verb has more than one syllable and the last syllable isn’t stressed, we don't double the last letter. Open – Opening When the verb ends with “e” we omit the “e” and we add –ing. Bake – Baking When the verb ends with “ie” we omit the “ie” and add “-ying”. Die – Dying USES Talk about actions and situations that are already going on at the moment of speaking. “We are all waiting for you” Talk about developing or changing situations. “The weather is getting better and better”
- 3. Talk about temporary situations. “My sister is living at home at the moment” Talk about future happenings. “We are probably spending next weekend at home” PAST SIMPLE AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE I went I didn’t go Did I go? You went You didn’t go Did you go? She went She didn’t go Did she go? He went He didn’t go Did he go? It went It didn’t go Did it go? We went We didn’t go Did we go? You went You didn’t go Did you go? They went They didn’t go Did they go? USES Actions completed in the past at a definite time. For a past action when the time is given “I met him yesterday” When the time is asked about “When did you meet him?” When the action clearly took place at a definite time even thought this time is not mentioned. “The train was ten minutes late” Actions whose time is not given but which occupied a period of time now terminated “He worked in a bank for four years”. Or occurred at a moment in a period of time now terminated “My grandmother once saw Queen Victoria” It’s used for a past habit. “He always carried an umbrella”
- 4. PAST CONTINUOUS AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE I was running I wasn’t running Was I running? You were running You weren’t running Were you running? She was running She wasn’t running Was she running? He was running He wasn’t running Was he running? It was running It wasn’t running Was it running? We were running We weren’t running Were we running? You were running You weren’t running Were you running? They were running They weren’t running Were they running? USES For past action which continued for some time but whose exact limits are not known and are not important. Used with a point in time, it expresses an action which began before that time and probably continued after it. “At eight o’clock she was having brakfast” Used without a time expression it can indicate gradual development. “It was getting darker” If we replace the time expression with a verb in the past. “When I arrived, Tom was walking on the phone” We use the contiunuous tense in descriptions. BE GOING TO (FUTURE FORMS) Intention “I’m going to play football tomorrow” Prediction based on present facts “It’s going to rain soon” Plans “I’m going to work for my father. I’ve already decided”
- 5. PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE I have gone I haven’t gone Have I gone? You have gone You haven’t gone Have you gone? She has gone She hasn’t gone Has she gone? He has gone He hasn’t gone Has he gone? It has gone It hasn’t gone Has it gone? We have gone We haven’t gone Have we gone? They have gone They haven’t gone Have they gone? USES It used to indicate a link between the present and the past. Is used to discribe: An action or situation that started in the past and continues in the present. “I have lived in Bristol since 1984” An action happening during a period of time that has not finished yes. “She has benn to the cinema twice a week” A repeteated action in an unspeciofied period between the past and now. “We have visited Portugal several times” An action whe the time is not important. “He has read “War and Peace” EVER, NEVER, ALREADY, YET, JUST EVER: Is used in questions “Have you ever been to England?”, negative questions “Haven’t they ever been to Europe?” and in negative statements using “Nobody has ever said that to me before” NEVER: Means at no time before now “I’ve never visited Berlin”
- 6. ALREADY: Something happened sooner than expected. It suggests that there is no need for repetition “I’ve already drunk three coffees this morning” YET: Negative and question, to ask if something that you think is going to happen is happened or to say it hasn’t happened. “I haven’t visited the Lovre museum yet” “Has he arrived yet?” JUST: Affirmative, to express the idea that an action is recently finished. “I’ve just had a lunch” FUTURE FORMS USES Something will automatically happen “She will be 15 years old tomorrow” Unplanned decision, offers, invitations “I will help you/ Shall we go to the cinema?” For uncertain futur with: probably, possibly, perhaps... “He will probably be back at 12:00” Predictions (weather forescat) With time clauses (when, as soon as...) and conditional clases (if, after, before) Type.1 To express opinions with: hope, expect, suppose, believe, think... “I think they will pass the exam” USED TO USE TO + INFINITIVE. (Solía) This structure only exist in the past. It refers to past habits and states. If we say that somebody used to do something, we mean that some time ago he did it habitually, but that he doesn’t do it now. (Habit in the past). “He used to play cards a lot” The structure of questions and negative with used to. “Did you use to play cards a lot?” “I didn’t use to like opera, but now I’m getting interested.”
- 7. RELATIVE CLAUSES Give more information about the subject or the object of a sentence. WHO: Used for people. “The people who work there are all my friends”. WHICH: Used for things and animals. “They enjoy living in the house which tehy rented last year.” THAT: Replace who or which in defining clauses only. “Here is the boy that broke our window.” WHERE: Used for places and replaces words like there, here. “The school where I studied has benn closed.” WHOSE: Used for possession and replaces words. “The man whose car was stolen has called the police” WHEN: Used for time. Often replaces words like the year, the month. “I remember when we first met.” DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES These are clauses that tell us exactly who or what is being referred to. Without the defining relative clause the sentence will not make sense. It needs to be there. PEOPLE THINGS “I hate people who are insincere” For people you can use who or that, but who is more usual. In the above sentence, who is the subject of the relative clause, so it can’t be omimit it. “I enjoyed the books that you lent me” For things you can use that or which, but taht is more usual. In the above sentence, that is the object of relative clause, so in can be ommit it. You cannot miss out the relative pronoun if it the object of the relative clauses. “I hate people are insincere.” The relative pronoun can be missed out if is the object of the relative clause: “She is the girl that I love OR She’s the girl I love” (THERE ARE NO COMMAS IN DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES)
- 8. NON DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES These are clauses that give us extra information about something or someone already mentioned. The sentence will stiill make sense without the non-defining relative clause, but the clause gives you extra information. PEOPLE THINGS “The finance minister, who has been under pressure to resign, will be holding a press conference today.” For people you must use who. “His lastest novel, which is set in India, has received good reviews.” For things you must use which. You cannot leave out the relative pronoun in non-defining clauses. (WHO AND WHICH ARE ALWAYS PRECEDED BY A COMMA IN NON- DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES) QUANTIFIERS SOME, ANY, A, NO We use some and any with plural countable nouns. “some book, any books” The singular of these expressions is a “a book”. We don’t use some and any here. We use some and any with uncountables nouns. “some milk, any milk” We use some in positive statements and positive comands. “Give me some milk” In questions any is more usual than some. “Did she give you any milk?” Sometimes when we are sure the answer will be “yes”, we ask a question with some. “Did she give you some milk?”
- 9. Any is not negative, but with not it is used in negative statements and negative commands. “Don’t give me any milk” No is used with a positive verbs. “There is no sugar in the bowl.” MUCH, MANY, A LOT OF. We use much only with uncountable nouns (air, help, sugar, hair, information, money...) We must always use a singular verb with these nouns. We use many only with plural countable nouns (apples, houses, girls, ideas...) Many and much are normal in questions and negative statements. “Have you got many records?” “She didn’t give me much bread” In positive statements we very often use a lot of instead of many and much. “We eat a lot of potatoes” “She gave me a lot of bread” ENOUGH, TOO. Enough comes before a noun but after an adjective or an adverb. “I haven’t got enough money to buy the dress” “I’m not strong enough.” Too always comes before and adjective or adverb. “I’m too weak to lift all those suitcases”
- 10. EXERCISE 1: Present Simple and Present Continuous. 1) Cuckoons ..................................... (not build) nests. They ................... (use) the nests of other birds. 2) You can’t see Tom now: He ................................ (have) a bath. 3) He usually ......................... (drink) coffee but today he ................................. (drink) tea. 4) What ............................ (she do) in the evenings? She usually .................... (play) cards or ................................. (watch) TV. 5) The last train ............................ (leave) the station at 11:30. 6) I won’t go out now as it .................................. (rain) and I ............................ (not have) an umbrella. 7) Why ......................................... (you put) on your coat? I ............................ (go) for a walk. .............................................. (you come) with me? Yes, I’d love to come. .................................... (you mind) if I bring my dog? 8) I ........................ (hate) you and ......................... (wish) you would go away! 9) You look worried. What ........................................... (you think) about? EXERCISE 2: Past Simple and Past Continuous. 1) I lit the fire at 6:00 and it ............................................... (burn) brightly when Tom came in at 7:00. 2) When I arrived the lecture had already started and the professor .................................... (write) on the overhead projector. 3) I didn’t want to meet Paul so when he entered the room I .......................... (leave). 4) He ................................ (have) a bath when the phone rang. Very unwillingly he ......................... (get) out of the bath and ................................ (go) to answer it. 5) He suddenly .................................... (realise) that he ................................... (travel) in the wrong direction. 6) I .................................... (just open) the letter when the wind ....................... (blow) it out of my hands. 7) When I came in they ................................. (sit) round the fire and Mr.Pitt ................................ (do) a crossword puzzle.
- 11. EXERCISE 3: Choose the correct answer. 1) Computers ................................. more and more efficient. A. are becoming B. Become C. Is becoming 2) Paul ................................. to Tina when I saw him. A. is talking B. Was talking C. Talks 3) Richard ........................... very hard at the moment. A. is working B. Works C. Has worked 4) Sam ............................... to school every day. A. was walking B. Is walking C. Walks 5) We ................................ to Austria last winter. A. have gone B. Went C. Go 6) Tina ........................... while Bob was watering the plants. A. cooked B. Was cooking C. Has cooked 7) Jason ............................. Amanda since he was five years old. A. has known B. Knows C. Have known 8) The River Amazon .......................... into the Atlantic Ocean. A. is flowing B. Flows C. Flowed 9) They often .................................. on holiday abroad when they were single. A. went B. Go C. Have gone 10) They ........................................ in that house for five years. A. have lived B. Are living C. Live 11) Mary .................................... to Singapore at 3:00 tomorrow morning. A. flies B. Was flying C. Is flying
- 12. EXERCISE 4: Present Perfect and Past Simple. 1) This is my house. How long ……………………………………… (you live) here? I ………………………….. (live) here since 1970. 2) He ………………………….. (live) in London for two years and then …………………….. (go) to Edinburgh. 3) ……………………………….. (you wear) your hair long when you were at school? Yes, my mother …………………………… (insist) on it. 4) But when I ………………………. (leave) school I …………………………… (cut) my hair and ……………………………… (wear) it short ever since. 5) My brother ……………………………….. (write) several plays. He …………………………….. (just finish) his second tragedy. 6) I …………………………….. (not see) him for three years. I wonder where he is. 7) He …………………………… (not smoke) for two weeks. He is trying to give it up. 8) Chopin ……………………… (compose) some of his music in Majorca. 9) I …………………………. (read) his books when I was at school. I ……………………… (enjoy) them very much. 10) I can’t go out because I …………………………. (not finish) my work. 11) I ………………………. (never drink) whisky. Well, have some now. 12) The clock is slow. It isn’t slow, it ………………………….. (stop). 13) I ………………………………. (leave) home at 8:00 and …………………….. (get) here at twelve. 14) ………………………. (you have) breakfast yet? Yes, I ……………………… (have) it at 8:00. 15) ………………………….. (you be) there before? Yes, I ……………………… (spend) my holidays here last year. ……………………………. (you have) a good time? No, it ………………………… (never stop) raining.
- 13. EXERCISE 5: Write sentences or questions with already, just or yet. 1) I / have / breakfast (just) …………………………………………………………………………………..... 2) You / finish your homework? (yet) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 3) The film/ start (already) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 4) I/ not meet/ his girlfriend (yet) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 5) They / get married (just) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 6) You’re too late. He/ go home (already) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 7) You/ speak to him? (yet) ……………………………………………………………………………………. 8) I/ not read his new book (yet) ……………………………………………………………………………………. EXERCISE 6: Make sentences with used to, didn’t use to, or did…..use to. 1) Where/ you/ go to school ? …………………………………………………………………………………..... 2) I/ like vegetables when I was a child. - ……………………………………………………………………………………. 3) My sister/ hate maths at school. + .................................................................................................................... 4) What/ you do in the summer ? ……………………………………………………………………………………. 5) They/ live near here. – ……………………………………………………………………………………. 6) This building/ be a cinema. + …………………………………………………………………………………….
- 14. EXERCISE 7: Circle the best answer. (Future forms) 1) A. …………………? B. Tomorrow. My flight is in the morning. a. When will you leave b. When are you leaving c. When are you going to leave 2) A. You must bring the money tomorrow. B. Don’t worry, ……………………………. a. I’m not forgetting. b. I’m not going to forget. c. I won’t forget. 3) A. This suitcase is too heavy for me. B. …………………………. a. I’ll carry it for you. b. I’m carrying it for you. c. I’m going to carry it for you. 4) A. What would you like to drink? B. …………………………… a. I’ll have a cappuccino, please. b. I’m going to have a cappuccino, please. c. I’m having a cappuccino, please. 5) A. Here’s my email address. B. Thanks. …………………………………….. tomorrow. a. I’m going to send you the photos b. I’m sending you the photos c. I’ll send you the photos 6) A. England are playing Brazil tomorrow. B. I’m sure ……………………………………. a. They’ll lose. b. They’re losing. c. They’re going to lose.
- 15. EXERCISE 8: Quantifiers. Circle the correct answer for each gap. 1) After four years in government, what have you done? Look at the state of the country: There isn’t …(a)…. money for pensions, there’s …(b)… Unemployment, and …(c)…. children are failing at school. a. no / enough b. too many / too much c. a lot of / a lot 2) Nonsense! You don’t know what you’re doing! And …(a)… people in your own party are now saying that, too. You said you haven’t had ….(b)…? I say you don’t have ….(c)… ideas! a. much / a lot b. enough time / time enough c. any / no EXERCISE 9: Complete the jokes using much, many or a lot of. 1) We don’t have ………………… beautiful women in our town. Why do you say that? Well, we had a beauty contest, and nobody won. 2) How …………………….. money do you have in the bank? I don’t know. I haven’t shaken it recently. 3) John is so stupid. He thinks a football coach has four wheels. Well, how …………………… wheels does it have? 4) A horse walked into a bar and said to the barman, same as usual, Sam. Look, said the barman. I serve ……………….. costumers in this bar every day. How do you expect me to remember what they all drink! 5) What do you take for a headache? I drink ………………… beer the night before! 6) I don’t have ……………… hair and I’d like to buy a wig. Certainly, sir. That’s 50€ plus tax. Forget the tacks. I’ll use glue.
- 16. EXERCISE 10: Choose the correct options (more than one is possible) 1) The man ………….. is marrying Suzanne is very lucky. a. who b. which c. that d. – 2) The house – I used to live – was demolished yesterday. a. in which I used to live b. (which/ that) I used to live in c. where I used to live d. in that I used to live 3) Pablo Picasso, …….. father was also an artist, spent his early childhood In Malaga. a. who b. that c. whose d. – 4) The city ……… I most enjoyed visiting in Belgium was Brussels. a. which b. that c. where d. – 5) Usain Bolt, …….. won three gold medals at the Beijing Olympics, is a Jamaican runner. a. who b. where c. that d. – 6) When I was a child, my auntie gave me a puppy ……… I decided to call Boney. a. that b. who c. which d. – EXERCISE 11: Complete these sentences with all the possible relative pronouns THAT; WHO; WHICH; - or WHOSE 1) Thank you very much for the present ……………………….. you sent me. 2) She was dancing with a student, ………………………… had a slight limp. 3) I’m looking after some children ……………….…………. are terribly spoilt. 4) Romeo and Juliet were two lovers ………………… parents hated each other. 5) There wasn’t any directory in the phone box ………………..……. I was phoning from. 6) The chair …….………………………. I was sitting on, suddenly collapsed. 7) The Smiths, ……………………… house had been destroyed in the explosions, were given rooms in the hotel.
