Liver & Liver Diseases
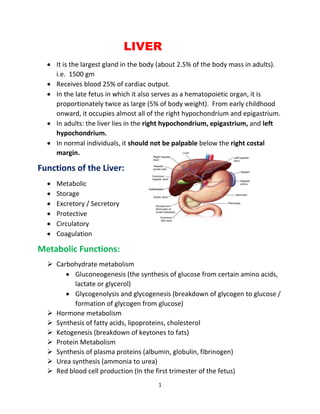
- 1. 1 LIVER • It is the largest gland in the body (about 2.5% of the body mass in adults). i.e. 1500 gm • Receives blood 25% of cardiac output. • In the late fetus in which it also serves as a hematopoietic organ, it is proportionately twice as large (5% of body weight). From early childhood onward, it occupies almost all of the right hypochondrium and epigastrium. • In adults: the liver lies in the right hypochondrium, epigastrium, and left hypochondrium. • In normal individuals, it should not be palpable below the right costal margin. Functions of the Liver: • Metabolic • Storage • Excretory / Secretory • Protective • Circulatory • Coagulation Metabolic Functions: ➢ Carbohydrate metabolism • Gluconeogenesis (the synthesis of glucose from certain amino acids, lactate or glycerol) • Glycogenolysis and glycogenesis (breakdown of glycogen to glucose / formation of glycogen from glucose) ➢ Hormone metabolism ➢ Synthesis of fatty acids, lipoproteins, cholesterol ➢ Ketogenesis (breakdown of keytones to fats) ➢ Protein Metabolism ➢ Synthesis of plasma proteins (albumin, globulin, fibrinogen) ➢ Urea synthesis (ammonia to urea) ➢ Red blood cell production (In the first trimester of the fetus)
- 2. 2 Storage Functions: • Glycogen • Vitamins A, D, E, K (fat soluble) B12 (water soluble) • Iron • Copper Excretory / Secretory: • Bile - Water - Cholesterol - Bile pigments (Bilirubin and Biliverdin) - Anions of the Bile acids - Phospholipids (mainly lecithin) - Bicarbonate and other ions • Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) • Most blood proteins (save antibodies) are synthesis and therefore secreted by the liver • Cholesterol, fatty acids (via lipoproteins) Protective Function • Purification, Transformation, and Clearance - The liver removes harmful substances (such as ammonia and toxins) from the blood and then breaks them down or transforms them into less harmful compounds. In addition, the liver metabolizes most hormones and ingested drugs to either more or less active products. • Kupffer cells - ingest bacteria or other foreign material from the blood Circulatory Function • While the liver is technically part of the gastrointestinal system, it also plays an important role in blood circulation. The liver has been called the "antechamber of the heart" because it collects and processes all of the gastrointestinal blood through the portal vein and delivers it to the right
- 3. 3 side of the heart. The liver receives blood through two vascular systems, the portal vein and hepatic artery. Coagulator Functions ➢ Production and secretion of coagulation factors - fibrinogen I - prothrombin II - Factors (V, VII, IX, X, XI) - protein C - protein S - antithrombin. Common causes of liver disease: • Alcoholic liver disease • Chronic viral hepatitis- C or B • Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) • Autoimmune diseases: autoimmune hepatitis. • Cholestatic liver disease: PBC & PSC • Metabolic and genetic: - Wilson disease - hemochromatosis, - alpha 1- antitrypsin deficiency • Cystic fibrosis Liver fibrosis: Fibrosis is the formation of an abnormally large amount of scar tissue in the liver. It occurs when the liver attempts to repair and replace damaged cells. Many conditions can damage the liver. Fibrosis itself causes no symptoms, but severe scarring can result in cirrhosis, which can cause symptoms. Liver Cirrhosis • Cirrhosis of liver is a chronic, progressive disease characterized by widespread fibrosis (scarring) and nodule formation. • The development of cirrhosis is. insidious, prolonged course, usually after decades of chronic liver disease.
- 4. 4 • Cirrhosis is a consequence of. chronic liver disease, characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules leading to loss of liver function. Causes: - Chronic alcohol abuse - Chronic viral hepatitis ( Hep B, Hep C) - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Types of Cirrhosis: a. Alcoholic Cirrhosis (Laennec's Cirrhosis) - micronodular, portal cirrhosis. - Men are more likely to have alcoholic cirrhosis. - Fibrosis occurs mainly around central veins and portal areas. - It is associated with chronic alcoholic abuse. - Small nodules forms as a result of some offending agent. b. Post-necrotic cirrhosis - Late result of a previous bout of acute viral hepatitis - Macronodular cirrhosis, toxin-induced cirrhosis. - Most common worldwide form. - Broad bands of scar tissue. - Caused by post-acute viral B, C hepatitis, Post intoxication with industrial chemicals. - More common in women. c. Biliary cirrhosis - Scaring around bile ducts and lobes of the liver. - It results from chronic biliary injury and obstruction of the intrahepatic or extrahepatic biliary system. - Primary biliary cirrhosis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis are biliary causes of cirrhosis. d. Cardiac cirrhosis - It is rare. - It is chronic liver disease associated with long term severe right sided heart failure.
- 5. 5 - It is caused by AV valve disease, constrictive pericarditis Stages of liver Cirrhosis: Formatin of fibrosis : Fibrosis is the prosses mediated by these special cells called Stellate cell that sites betwwen sinusoid and Hepatocytes known as the perisinusoidal space. At the basic layout of the basic functional unit of the liver portal vain and hepatic artery that combine into sinusoid which then goes into central vein and these are all line with hepatocytes. Along these there’s bile duct (central vein+ hepatocytes+ bile duct= Portal triad). In healthy tissue stellate cell store Vitamin-A and dormant quiescent. When hepatocytes are injured, they secrete factors that activates and sort of change stellate cells. When activated these cells loss Vitamin-A and start secreting Transforming growth factor beta-1 Which then causes them to produce collagen which is the main ingredient in extra cellular matrix gradually fibrosis then Scar tissues. As these fibrotic tissues builds up it start to compress the central vein in Sinusoid. Complications:
- 6. 6 • Portal hypertension: Coagulopathy • Gastroesophageal varices: Factor deficiency • Portal hypertensive gastropathy: Fibrinolysis • Splenomegaly, hypersplenism: Thrombocytopenia • Ascites disease: Bone disease • Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Osteopenia • Hepatorenal syndrome: Osteoporosis - Type 1: Osteomalacia - Type 2 Hematologic abnormalities • Hepatic encephalopathy Anemia • Hepatopulmonary syndrome: Hemolysis • Portopulmonary hypertension: Thrombocytopenia • Malnutrition: Neutropeni Signs and symptoms ➢ Some of the following signs and symptoms may occur in the presence of cirrhosis or as a result of the complications of cirrhosis. Many are nonspecific and may occur in other diseases and do not necessarily point to cirrhosis. Likewise, the absence of any does not rule out the possibility of cirrhosis. ➢ Spider angiomata or spider nevi. Vascular lesions consisting of a central arteriole surrounded by many smaller vessels due to an increase in estradiol. These occur in about 1/3 of cases. ➢ Palmar erythema Exaggerations of normal speckled mottling of the palm, due to altered sex hormone metabolism. ➢ Gynecomastia Benign proliferation of glandular tissue of male breasts presenting with a rubbery or firm mass extending concentrically from the nipples. This is due to increased estradiol and can occur in up to 66% of patients. ➢ Hypogonadism
- 7. 7 Manifested as impotence, infertility, loss of sexual drive, and testicular atrophy due to primary gonadal injury or suppression of hypothalamic or pituitary function. ➢ Liver size. Can be enlarged, normal, or shrunken. ➢ Splenomegaly (increase in size of the spleen). Due to congestion of the red pulp as a result of portal hypertension. ➢ Ascites Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity giving rise to flank dullness (needs about 1500 mL to detect flank dullness). It may be associated with hydrocele and penile flomation (swelling of the penile shaft) in men. ➢ Caput medusa In portal hypertension, the umbilical vein may open. Blood from the portal venous system may be shunted through the periumbilical veins into the umbilical vein and ultimately to the abdominal wall veins, manifesting as caput medusa. ➢ Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur Venous hum heard in epigastric region (on examination by stethoscope) due to collateral connections between portal 'system and the remnant of the umbilical vein in portal hypertension. ➢ Fetor hepaticus Musty odor in breath due to increased dimethyl sulfide. ➢ Jaundice Yellow discoloring of the skin, eye, and mucus membranes due to increased bilirubin (at least 2-3 mg / dL or 30 mmol / L). Urine may also appear dark. ➢ Asterixis Bilateral asynchronous flapping of outstretched, dorsiflexed hands seen in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. ➢ Other Weakness, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss. Diagnosis • The gold standard for diagnosis of cirrhosis is a liver biopsy
- 8. 8 • Histologically cirrhosis can be classified as micronodular, macronodular, or mixed, but this classification has been abandoned since it is nonspecific to the etiology • Diagnosis Lab findings: The following findings are typical in cirrhosis: ➢ Aminotransferases - AST and ALT are moderately elevated, with AST> ALT. However, normal aminotransferases do not preclude cirrhosis. ➢ Alkaline phosphatase - usually slightly elevated. ➢ GGT - correlates with AP levels. Typically much higher in chronic liver disease from alcohol. ➢ Bilirubin - may elevate as cirrhosis progresses. ➢ Albumin - levels fall as the synthetic function of the liver declines with worsening cirrhosis since albumin is exclusively synthesized in the liver ➢ Prothrombin time- increases since the liver synthesizes clotting factors. ➢ Globulins - increased due to shunting of bacterial antigens away from the liver to lymphoid tissue. ➢ Serum sodium - hyponatremia due to inability to excrete free water resulting from high levels of ADH and aldosterone. ➢ Thrombocytopenia - due to both congestive splenomegaly as well as decreased thrombopoietin from the liver. However this rarely results in platelet count <50,000 / mL. ➢ Leukopenia and neutropenia- due to splenomegaly with splenic margination. • ➢ Coagulation defects - the liver produces most of the coagulation factors and thus coagulopathy correlates with worsening liver disease. • Liver biopsy. • Liver scan. • Upper GI barium swallow. • Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen • Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen • Ultrasound of the abdomen.
- 9. 9 Treatment • All patients with cirrhosis can benefit from certain lifestyle changes, including: • Stop drinking alcohol. • Limit salt in the diet. • Get vaccinated for influenza, hepatitis A and hepatitis B, and pneumococcal pneumonia (if recommended by doctor). • Generally, liver damage from cirrhosis cannot be reversed, but treatment could stop or delay further progression and reduce complications. • A healthy diet is encouraged, as cirrhosis may be an energy-consuming process. • Antibiotics will be prescribed for infections, and various medications can help with itching. • Laxatives, such as lactulose, decrease risk of constipation. • Alcoholic cirrhosis caused by alcohol abuse is treated by abstaining from alcohol. • Treatment for hepatic cirrhosis involves medications used to treat the different types of hepatitis, such as interferon for viral hepatitis and corticosteroids for autoimmune hepatitis. • Liver transplant. Viral Hepatitis ➢ Viral hepatitis is a systemic disease with primary inflammation of the liver by any one of a heterogeneous group of hepatotropic viruses. ➢ The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic viruses Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D, and Hepatitis E. among them Hep B & C are most common ➢ In addition to the nominal hepatitis viruses, other viruses that can also cause liver inflammation include Herpes simplex, Cytomegalovirus, Epstein- Barr virus, or Yellow fever. Hepatitis B V
- 10. 10 • Hepatitis B (formerly known as "serum" hepatitis) is an acute systemic infection with major pathology in the liver, caused by hepatitis B virus. • Transmitted by the Parenteral route. • The acute illness causes liver inflammation, vomiting, jaundice, and, rarely, death. Chronic hepatitis B may eventually cause cirrhosis and liver cancer. • Hepatitis B is endemic throughout the world, especially in tropical & developing countries. Epidemiology Determinants ➢ Agent factor a) AGENT: Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) - It is a complex, 42 nm double-shelled DNA virus originally known as "Dane Particle". - It replicates in liver cell. HBV occurs in 3 morphology form in serum: I. Small spherical particles with an average Diameter of 22nm. II. Filamentous or Tubules of varying length & of 22 nm diameter. III. Dane particle. Out of 3 morphology forms, only the Dane particle is considered infectious, other circulating morphology forms are not infectious. b) RESERVOIR OF INFECTION: -Men is the only reservoir of infection which can be spread either from carriers or from cases. c) Infective material: - Contaminated blood is the main source, - Virus has been found in body secretion such as saliva, vaginal secretion & Semen in infected material. d) Resistance: -Readily destroyed by sodium hypochlorite, as is by heat sterilization in an autoclave for 30-60 min. ➢ Host factor a) AGE: - 1. Acute hepatitis B 2. Chronic hepatitis is B
- 11. 11 b) High Risk Group: - People from endemic regions - Babies of mothers with chronic HBV - Intravenous drug abusers - People with multiple sex partners - Hemophiliacs and other patients requiring blood and blood product treatments - Health care personnel who have contact with blood v Patients who are immunocompromised. c) Humoral and cellular response: - HBV has 3 distinct antigen: i. HBSAG, also known as "Australian antigen, ii. HBCAG antigen (core antigen) iii. HBeAg envelope antigen They stimulate production of corresponding antibody. * Incubation Period 45-180 days (usually 60-90 days) Mode of Transmission 90% resolve by themselves; <1% develop fulminant hepatic failure. - occurs in approx 2-10% progress to chronic state. -occur in approx. Perinatal - 1% - Perinatal -95% Childhood - 10% (1-5 yr. Age) - Childhood -80% Late infection - 30% (> 5 yr. Age) - After 5 yr. of age -5-10%
- 12. 12 - Parenteral- IV drug abusers, health workers are at increased risk. - Sexual- sex workers and homosexuals are particular at risk. - Perinatal (Vertical) mother (HBEA9 +) -infant. Mothers who are HBeAg positive are much more likely to transmit to their offspring than those who are not. Perinatal transmission is the main means of transmission in high prevalence populations Diagnosis : - Serology ; -Liver Chemistry tests AST, ALT, ALP, and total Bilirubin -Histology : Immunoperoxidase staining -HBV Viral DNA : Most accurate marker of viral DNA and detected by PCR - Liver Biopsy - to determine grade (Inflammation) and stage (Fibrosis) in chronic Hepatitis Prevention ➢ Vaccination - highly effective recombinant vaccines ➢ Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG) -exposed within 48 hours of the incident / neonates whose mothers are HBSAg and HBeAg positive. ➢ Other measures -screening of blood donors, blood and body fluid precautions. Treatment I Interferon Alfa (Intron A) Response rate is 30 to 40%. Lamivudine (Epivir HBV) (relapse, drug resistance) Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera) Hepatitis C V ➢ Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). V ➢ The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years.
- 13. 13 ➢ It is estimated that 150-200 million people, or -3% of the world's population, are living with chronic hepatitis C. Incubation Period: 40-120 days Mode of Transmission • Intravenous Drug Use • Healthcare Exposure: Blood Transfusion, transfusion of Blood products, Organ Transplant without HCV screening carry significant risk of infection. • Hemodialysis • Accidental injuries with needles / sharps • Sexual / household exposure to anti-HCV-positive contact • Multiple sex partners • Vertical Transmission: Vertical transmission of hepatitis C from an infected mother to her child Diagnosis • HCV antibody - ELISA used to diagnose hepatitis C infection. Not useful in the acute phase as it takes at least 4 weeks after infection before antibody appears. • HCV-RNA - various techniques are available eg PCR and branched DNA. May be used to diagnose HCV infection in the acute phase. However, its main use is in monitoring the response to antiviral therapy. • HCV-antigen - an EIA for HCV antigen is available. It is used in the same capacity as HCV-RNA tests but is much easier to carry out. Prevention: Only General Prophylaxis, such as blood, tissue, organ screening, is possible. No specific active or passive immuntizing agent is available. Treatment: Interferon may be considered for patients with chronic active hepatitis. The response rate is around 50% but 50% of responders will relapse upon withdrawal of treatment. Ribavirin - there is less experience with ribavirin than interferon. However, recent studies suggest that a combination of interferon and ribavirin is more effective than interferon alone.
- 14. 14 Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a disease that goes through the hepatic manifestations of alcohol, fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis. In other words it is cirrhosis. Symptoms: General symptoms include: R Abdominal pain and tendemess ,Dry mouth and increased thirst ,Loss of appetite (food),Swelling or fluid buildup in the legs and in the abdomen when cirrhosis is present ,Weight loss Pathology: Alcohol can produces a wide spectrum of liver disease from fatty change to hepatitis and cirrhosis. Treatment Abstinence: 1) Leads to reversal of liver disease and improvement in survival. 2)Less than 20% of patients will demonstrate progression of liver disease after abstinence. 3) 5 years survival improves from 34% to 60% for those with decompensated liver disease. 4)Patients with chronic HCV infection should abstain from any alcohol intake due to the risk for rapid acceleration of liver disease. Nutrition: A) Alcoholism is associated with nutritional deficiencies. B) Enteral as well as tube feeding found to be associated with decreased mortality. C)Continued entral nutrition support after hospitalization also improves long tem morbidity. Corticosteroids: A) Only five studies have shown benefit in survival mostly in rural populations the remaining studies have been wrong. B) Corticosteroid therapy is beneficial in improving 30 and 60 days mortality only in patients with severe acute alcoholic hepatitis and an MDF> 32 in the absence of acute GI bleeding, renal failure, acute infection or pancreatitis. C) 2months survival is about 80% but up to 40% of patients still die in 6 months. D) Significant improvement in LFTS is evident at 7 day after initiation of therapy and may be present up to 1 year.
- 15. 15 E) Patients with a score> 0.45 using lille model had a mortality rate of 76% at 6 months. F) Prednisolone given at a dose of 40mg daily for 4 wks followed by rapid 4 wks taper.