Project Management
- 1. An Overview of Project Management 6e. 1–1
- 2. Project Management Framework In this Unit, you would have a broader understanding of what is a project Need for Project Management Project Life Cycle Project Stake Holders
- 3. 3 What is a Project - Examples Research work to identify specific needs of a customer, say preference of clove salt in a toothpaste Devising strategies for eliminating or reducing Drug Abuse or society related offences
- 4. 4
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 7. 7
- 8. 8 Characteristics of Project Management 1. An Established objective 2. A defined Life span with a beginning and an End. 3. Usually the involvement of several departments and professionals. 4. Typically trying to do something that has never been done before. 5. Specific in nature and includes a specific timing, cost and performance requirements.
- 9. 9 Characteristics of Project Management 6. Is measured and Accounted with results and Learning/s. 7. Enables an Individual or a Professional to learn and practice the systematic approach of a project and process to make it more workable and successful. 8. A Project manager learns the art of “On Field and Off Field” management practices that can enable and nurture success of a project.
- 10. 10 What is NOT a Project A repetitive or a routine daily work . Eg., a research to find a new derivative product or service. Program Vs Project . – Synomously used with each other Program -- A group of related projects designed to accomplish a common goal over an extended period of time. Under each project within a program -- Project manager …. Project Executives
- 11. 11 What is NOT a Project Program Management – Is a process of managing a group of ongoing, inter- dependent, related projects in a co-ordinated way to achieve strategic objectives. For example - A company would participate in a promotional campaign as part of Awareness drive of the brand or the product or service, it provides. Example -- Cancer Awareness Campaign.
- 12. Need and Importance of Project Management 1. Defines a plan and organises chaos – Projects are naturally chaotic. The primary business function of project management is organizing and planning projects to tame this chaos. A clear path mapped out from start to finish ensures the outcome meets the goals of your project. 12
- 13. Need and Importance of Project Management 2. Establishes a schedule and plan – Without a schedule, a project has a higher probability of delays and cost overruns. A sound schedule is key to a successful project. 13
- 14. Need and Importance of Project Management 3. Enforces and encourages teamwork – A project brings people together to share ideas and provide inspiration. Collaboration is the cornerstone to effective project planning and management. 14
- 15. Need and Importance of Project Management 4. Manages Integration – Projects don’t happen in a vacuum. They need to be integrated with business processes, systems and organizations. 15
- 16. Need and Importance of Project Management 5. Controls cost – Some projects can cost a significant amount of money so on budget performance is essential. Using project management strategies greatly reduces the risk of budget overruns. 16
- 17. Need and Importance of Project Management 7. Managing quality – Quality is the value of what you produce. Project management identifies, manages and controls quality. This results in a high quality product or service and a happy client. 17
- 18. Need and Importance of Project Management 8. Manages change – Projects always happen in an environment in which nothing is constant except change. Managing change is a complex and daunting task. It is not optional. Project management manages change. 18
- 19. Need and Importance of Project Management 9. Strategic Alignment – Project management is important because it ensures what is being delivered, is right, and will deliver real value against the business opportunity. 19
- 20. Need and Importance of Project Management 10. Learning from failure – Projects do fail. When they do, it is important to learn from the process. Project management ensures that lessons are learned from project success and failure. 20
- 21. Need and Importance of Project Management 11. Leadership – Project management is important because it brings leadership and direction to projects. 21
- 22. Need and Importance of Project Management 12. Risk Management – Project management is important because it ensures risks are properly managed and mitigated against to avoid becoming issues. 22
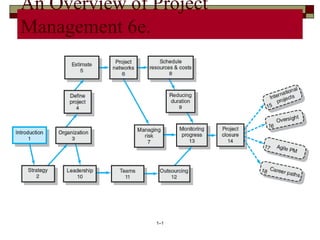
- 23. 23 Project Life Cycle Undergoes 4 stages in a sequential manner. 1. Defining Stage -- Specifications (Specs) of the project are defined, project objectives are established, Teams formed, major responsibilities are assigned. In this stage, a substantial Clarity of the project and Understanding by the Team is established.
- 24. 24 Project Life Cycle 2. Planning Stage -- Increase in the Level of efforts Development of systematic plans. Understanding purpose, beneficiary, objectives, financial implications, ROI, etc.
- 25. 25 Project Life Cycle 3. Executing Stage – Major portion of the project work takes place at this stage of operations. Physical product – report or parameters established – Time, cost and Specs analyzed and used for control. Project Status reviewed as per the forecasting done. Review /Rectification /Changes done wherever necessary.
- 26. 26 Project Life Cycle 3. Closing Stage -- Involves three activities ** a, Delivery of project/service product to the customer ** b, Redeploying Project resources for other Live Projects by the company / team. ** c, Post Project Review.
- 28. 28
- 29. Role of Project Management Helps to sustain Economic Growth of the Country. Helps to derive competitive advantage through Innovation and continuous Real Time Improvements. Helps to drive an Institution or an Organization “Result Oriented”. Helps in development in every step of the society 29
- 30. Role of Project Management A extra-ordinary tool for both Private and Public sector. Demand for Project Management courses have tremendously Increased and gained wider recognition. Approximately in many developed and fast growing economy, PM contributes to the tune ranging from 30 to 70% in the country’s development. Professionals excel in project works eg. CA, Lawyer, Scientists, PHO, Contractors, etc. 30
- 31. Role of Project Management PMI provides certification as Project Management Professional (PMP). Currently around 5 Lac PMP in the country. Ever Green Professional, as each endeavor or service is a Project by itself. 31
- 32. Current Drivers of Project Management 1. Compression or Quickening of the Product Life Cycle (PLC) One of Significant driving forces behind the demand for PM is shortening of PLC. New products with shortest PLC is a reality For example – Digital Mobiles, Electronic products. 32
- 33. Current Drivers of Project Management 2. Knowledge Explosion New Technology, new explosion of knowledge has increased the complexity of many projects. Digital Age and Digital Intervention has made man to harness his knowledge quickly to the need of the hour. Need for Integrating divergent Technologies for survival. 33
- 34. Current Drivers of Project Management 3. Triple Bottom Line (Planet, People, Profit) Customer Awareness Common Benefit – son’s of the soil theory Ecology conservation, CSA, Reducing Carbon footprint, using Renewable resources Genuine efforts to be in Green Line 34
- 35. Current Drivers of Project Management 4. Corporate Downsizing :: Downsizing Dramatic restructuring based on core competency of the company and employee. Middle management getting replaced by Corporate Management. Increased responsibility of PM in also managing external Teams from various orgn. 35
- 36. Current Drivers of Project Management 5. Increased Customer Focus:: Customers are highly educated in their specific needs. Companies addressing them through increased interactions and relationships PM – vital for both development of customized products and sustaining relationships with customers. 36
- 37. Current Drivers of Project Management 6. Small Projects Represent Big Problems : Several small projects, allocation of limited resources Inefficient management of small projects Wrong estimation of small projects and its relevance to company’s growth/profitability Accountability, flexibility, Speed and continuous improvements at stake. 37
- 38. Alignment of Projects with Organizational Strategy and its Impact Projects – Modus Operandi for Implementing Strategy… Strategic Alignment / Plan by Leadership Portfolio management by Middle Level Managers Project Management by one set of Managers This leads to gaps in communication, decision making and delivery of projects within time frame and with quality and precision. 38
- 39. Socio Technical Approach to Project Management The focus of Senior management is only selections of projects, not implementation Hence Implementation is always a challenge. Two dimensions within the actual execution of Projects. 1. The Technical Dimensions 2. The Socio Cultural Dimensions 39
- 40. Socio Technical Approach to Project Management 1. The Technical Dimensions :: a. Scope b. WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) c. Schedule d. Resource Allocation e. Baseline Budgets f. Status Reports 40
- 41. Socio Technical Approach to Project Management 2. The Socio Cultural Dimensions :: a. Leadership b. Problem Solving c. Teamwork d. Negotiation e. Politics f. Customer Expectations. 41
- 42. 42
- 43. 43
- 45. SPONSOR An Undisputable Champion An Effective Communicator and Leader. Have definitely Accountability in the Success of the Project. 45
- 46. Project Manager Provide a framework for the project’s activities Identify needed resources Negotiate with higher authorities Recruit effective participants Set milestones Coordinate activities 46
- 47. Project Management Team Keep the vision clear and the work on track Make sure everyone on the team contributes and benefits Mediate conflicts Make sure project goals are delivered on time and on budget 47
- 48. Team Leader 1. Initiator 2. Role Model 3. Negotiator 4. Listener 5. Coach 6. Working Member. 48
- 49. Team Player / Members 1. Technical Skill 2. Problem Solving Skill 3. Interpersonal Skill 4. organizational Skills (Including Networking Skills) 49
- 50. Project Steering Committee A Steering Committee, which takes wide accountability and Immense level of Commitment and Leadership. Decision making is quick and realistic Continuous monitoring of the wellness of the projects. Help sought out complexities between and in the Team and its members. 50