Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Gradient , Directional Derivative , Divergence , Curl 

Gradient , Directional Derivative , Divergence , Curl
Similar to Coordinate and unit vector
Similar to Coordinate and unit vector (20)
History,applications,algebra and mathematical form of plane in mathematics (p...

History,applications,algebra and mathematical form of plane in mathematics (p...
Reflection, Scaling, Shear, Translation, and Rotation

Reflection, Scaling, Shear, Translation, and Rotation
Recently uploaded
Call Girls Service Nagpur Tanvi Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts
Booking Contact Details
WhatsApp Chat: +91-7001035870
Nagpur Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus they look fabulously elegant; making an impressionable.
Independent Escorts Nagpur understands the value of confidentiality and discretion - they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together.
We provide -
27-april-2024(v.n)
Call Girls Service Nagpur Tanvi Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts

Call Girls Service Nagpur Tanvi Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur EscortsCall Girls in Nagpur High Profile
High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Meera Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts
Booking Contact Details
WhatsApp Chat: +91-7001035870
Nagpur Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus they look fabulously elegant; making an impressionable.
Independent Escorts Nagpur understands the value of confidentiality and discretion - they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together.
We provide -
27-april-2024(v.n)
High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Meera Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts

High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Meera Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur EscortsCall Girls in Nagpur High Profile
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Pargaon 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Girls Waiting For You To Fuck
Booking Contact Details
WhatsApp Chat: +91-6297143586
pune Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus they look fabulously elegant; making an impressionable.
Independent Escorts pune understands the value of confidentiality and discretion - they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together.
We provide -
01-may-2024(v.n)
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Pargaon 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Gi...

Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Pargaon 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Gi...Call Girls in Nagpur High Profile
Welcome to the April edition of WIPAC Monthly, the magazine brought to you by Water Industry Process Automation & Control.
In this month's edition, along with the latest news from the industry we have articles on:
The use of artificial intelligence and self-service platforms to improve water sustainability
A feature article on measuring wastewater spills
An article on the National Underground Asset Register
Have a good month,
OliverWater Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - April 2024

Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - April 2024Water Industry Process Automation & Control
Recently uploaded (20)
Call Girls Service Nagpur Tanvi Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts

Call Girls Service Nagpur Tanvi Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts
High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Meera Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts

High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Meera Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts
Roadmap to Membership of RICS - Pathways and Routes

Roadmap to Membership of RICS - Pathways and Routes
Processing & Properties of Floor and Wall Tiles.pptx

Processing & Properties of Floor and Wall Tiles.pptx
High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Isha Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts

High Profile Call Girls Nagpur Isha Call 7001035870 Meet With Nagpur Escorts
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Pargaon 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Gi...

Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Pargaon 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Gi...
(SHREYA) Chakan Call Girls Just Call 7001035870 [ Cash on Delivery ] Pune Esc...![(SHREYA) Chakan Call Girls Just Call 7001035870 [ Cash on Delivery ] Pune Esc...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![(SHREYA) Chakan Call Girls Just Call 7001035870 [ Cash on Delivery ] Pune Esc...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
(SHREYA) Chakan Call Girls Just Call 7001035870 [ Cash on Delivery ] Pune Esc...
result management system report for college project

result management system report for college project
Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - April 2024

Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - April 2024
Coordinate and unit vector
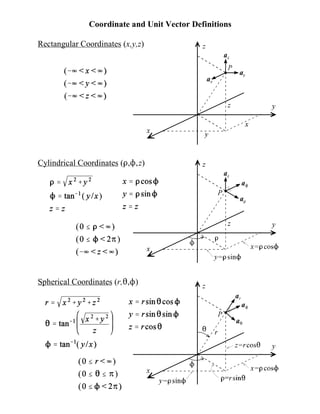
- 1. Coordinate and Unit Vector Definitions Rectangular Coordinates (x,y,z) Cylindrical Coordinates (D,N,z) Spherical Coordinates (r,2,N)
- 2. Vector Definitions and Coordinate Transformations Vector Definitions Vector Magnitudes Rectangular to Cylindrical Coordinate Transformation (Ax, Ay, Az) Y (AD, AN, Az) The transformation of rectangular to cylindrical coordinates requires that we find the components of the rectangular coordinate vector A in the direction of the cylindrical coordinate unit vectors (using the dot product). The required dot products are where the az unit vector is identical in both orthogonal coordinate systems
- 3. such that The four remaining unit vector dot products are determined according to the geometry relationships between the two coordinate systems. The resulting cylindrical coordinate vector is
- 4. In matrix form, the rectangular to cylindrical transformation is Cylindrical to Rectangular Coordinate Transformation (AD, AN, Az) Y (Ax, Ay, Az) The transformation from cylindrical to rectangular coordinates can be determined as the inverse of the rectangular to cylindrical transformation. The cylindrical coordinate variables in the transformation matrix must be expressed in terms of rectangular coordinates.
- 5. The resulting transformation is The cylindrical to rectangular transformation can be written as Rectangular to Spherical Coordinate Transformation (Ax, Ay, Az ) Y (Ar, A2, AN) The dot products necessary to determine the transformation from rectangular coordinates to spherical coordinates are
- 6. The geometry relationships between the rectangular and spherical unit vectors are illustrated below. The dot products are then and the rectangular to spherical transformation may be written as
- 7. Spherical to Rectangular Coordinate Transformation (Ar, A2, AN) Y (Ax, Ay, Az ) The spherical to rectangular coordinate transformation is the inverse of the rectangular to spherical coordinate transformation so that The spherical coordinate variables in terms of the rectangular coordinate variables are
- 8. The complete spherical to rectangular coordinate transformation is
- 11. Coordinate Transformation Procedure (1) Transform the component scalars into the new coordinate system. (2) Insert the component scalarsintothecoordinatetransformation matrix and evaluate. Steps (1) and (2) can be performed in either order. Example (Coordinate Transformations) Given the rectangular coordinate vector (a.) transform the vector A into cylindrical and spherical coordinates. (b.) transform the rectangular coordinate point P (1,3,5) into cylindrical and spherical coordinates. (c.) evaluate the vector A at P in rectangular, cylindrical and spherical coordinates. (a.)
- 13. (b.) P (1, 3, 5) Y x = 1, y = 3, z = 5 P (1, 3, 5) Y P (3.16, 71.6o , 5) Y P (5.92, 32.3o , 71.6 o ) (c.)
- 14. Separation Distances Given a vector r1 locating the point P1 and a vector r2 locating the point P2, the distance d between the points is found by determining the magnitude of the vector pointing from P1 to P2, or vice versa.
- 15. Volumes, Surfaces and Lines in Rectangular, Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates We may define particular three-dimensional volumes in rectangular, cylindrical and spherical coordinates by specifying ranges for each of the three coordinate variables. Rectangular volume (2×2×5 box) (1#x#3) (2#y#4) (0#z#5) Cylindrical volume (cylinder of length = 5, diameter = 2) (0#D#1) (0#N#2B) (0#z#5)
- 16. Spherical volume (sphere of diameter = 4) (0#r#2) (0#2#B) (0#N#2B) Specific lines and surfaces can be generated in a given coordinate system according to which coordinate variable(s) is(are) held constant. A surface results when one of the coordinate variables is held constant while a line results when two of the coordinate variables are held constant. Surface on the Rectangular volume (front face of the box) x=3 (x!constant) (2#y#4) (0#z#5) Surface on the Cylindrical volume (upper surface of the cylinder) (0#D#1) (0#N#2B) z=5 (z!constant)
- 17. Surface on the Spherical volume (outer surface of the sphere) r=2 (r!constant) (0#2#B) (0#N#2B) Line on the Rectangular volume (upper edge of the front face) x=3 (x!constant) (2#y#4) z=5 (z!constant) Line on the Cylindrical volume (outer edge of the upper surface) D=1 (D!constant) (0#N#2B) z=5 (z!constant) Line on the Spherical volume (equator of the sphere) r=2 (r!constant) 2=B/2 (2!constant) (0#N#2B)