Cell organele AIMC
- 2. Cell Theory • All living things are made up of cells.Cells are building blocks of our body (as bricks are building blocks of a house). • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division. • All living things have 3 common features: Reproduction,Locomotion n Digestion
- 3. Definition of Cell A Cell is the structural and functional unit of all living organism. The cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions as reproduction,locomotion and digestion.
- 4. DISCOVARY • By Robert Hook in 1665 • He observed boxes in bark of tree(cork) under microscope.He named these boxes Cells • After staining with Eosine/Hematoxyline cytoplasm looks pink and nucleus blue.
- 5. Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Bacteria
- 6. CELLS VARY IN • No. of cells; • Unicellular(Amoeba,bacteria) • Multicellular(Animals-trillions-elepphant) • Size of cells; • 0.1-0.5µm(bacteria) to170x130mm(ostrich) • Shape of cells; • Round(RBC’s),spherical(WBC,s),elongate d(Epithelial),Spindle(muscle),branched(ner ve)
- 7. Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic
- 9. Types of Cells • Eukaryots;Cells having true nucleus(Eu=true,karyo=nucleus • Prokaryots;comprise bacteria which are considered by scientists to have evolved before eukaryotes (pro=before,karyo=nucleus)
- 10. Prokaryotic-Bacteria • Oldest form of life on earth • Outermost capsule-cell wall-cell memb. • Cytoplasm contain free single circular DNA (nucleoid/plasmid) without welldefined nucleous for reproduction. • Ribosomes consist of rRNA n proteins. • External structures-flagella,pili etc
- 12. are the most complex form of life. They have nucleus Contain organelles surrounded by membranes They are multicellular organisms (composed of many cells). Most living organisms Examples: animals and plants. Eukaryotic
- 14. Common Characteristics • All cells are surrounded by a barrier called the cell membrane • They contain the molecule that carries biological information-DNA
- 15. Isolation of cell components • The cellular compt. are obtained by differential centrifugation of cells,after they have been gently broken by one of the following methods; • Grinding,In Hypotonic soln.,Alternative freezing thawing,Ultrasonification,Enzymic treatment. • The homogenized cells can be fractionated by differential centrifugation at various forces of gravity(1000-150,000g for 10min-3hrs).
- 17. Eukaryotic cell
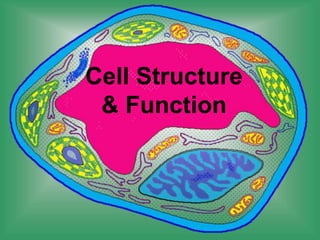
- 20. Cell Parts Cell membrane Cytoplasm- Organeles Nucleous CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
- 22. Cell Structures • The Plasma Membrane—A Cell's Protective Coat • The Cytoskeleton—A Cell's Scaffold • The Cytoplasm—A Cell's Inner Space • Genetic Material Cell Organelles include • The Nucleus—A Cell's Center • The Endoplasmic Reticulum and the Golgi Apparatus Macromolecule Manager • The Ribosome—The Protein Production Machine • Mitochondria and Chloroplasts—The Power Generators • Lysosomes and Peroxisomes—The Cellular Digestive System
- 23. Cytoplasm and Organelles • Cytoplasm lies between the cell membrane and nucleus and contains the organelles. • Cytosol is a gelatin like aqueous fluid that contains salts, minerals and organic molecules
- 24. ORGANELLES
- 25. Nucleus
- 26. Nucleus • Most prominent structure • Maintains its shape with a protein skeleton called the nuclear matrix • Double membrane – nuclear envelope • Inside the envelope – chromatin (DNA & protein) • When the cell is about to divide it forms the chromosomes-made of DNA. • Stores heriditary information in its DNA-transfer by replication. • RNA is copied from DNA-transcription- forming mRNA • m-RNA travels from nucleus to the cytosol through small holes in the envelope – nuclear pores • Contains the nucleolus – the site where ribosomes are synthesized
- 27. Nucleolus • Inside nucleus • Contains RNA to build proteins • Site where ribosome are synthesized
- 29. Endoplasmic Reticulum • System of membranous tubules and sacs • Intracellular Highway – molecules move from one part of the cell to another • 2 types – rough and smooth • Rough ER-studded with ribosomes –synthesis of proteins with posttranslational modifications- to be used by the cell organelles, membrane or secreted from the cell • Smooth ER - no ribosomes-has enzymes for: Synthesis of TAG & Phospholipids in enterocytes Synthesis of steroids in gland cells Has cyto.P450 for detoxification in liver Regulation of calcium in muscle cells
- 30. Ribosomes
- 31. Ribosomes • Most numerous • Not surrounded by a membrane • Synthesized in nucleolus in the nucleous. • Made up of proteins and RNA • RNA is packaged into the ribosomes then transported to the cytosol • Some ribosomes are free • Some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum • Protein is synthesized in the ribosomes • Proteins to be used in the cytosol – free ribosomes • Proteins to be exported or inserted in the cell membrane – ribosomes on the ER
- 32. Golgi Apparatus • System of membranes • Series of flattened sacs with convex shape • Works with the ER to modify proteins Processing, packaging distributing proteins to lysosomes,secretory vesicles and pl.memb.
- 33. CYTOSKELETON • .
- 34. CYTOSKELETON • Network of long flexible fibrous protein strands,maintains the shape and size of cell • Microtubules – largest strands are hollow cyllindrical tubes begin in nu n extend to pl memb. made up of tubulin protein – Help the cell divide by forming spindle - Responsible for positioning of organelles - Participates in the movement of vesicles • Microfilaments – threads made of actin (protein) – smallest strands-control the shape of cell n movement of cell surface to move, divide n engulf. • Intermediate filaments- are composed of fibrous protein polymers-provide structural support to memb n other cellular components.
- 35. Mitochondria They are called the “POWER HOUSE” of the cell
- 36. Mitochondria • Sites of chemical reactions that transfer energy from organic compounds to ATP • ATP- main energy source for cells • Size 1-2 µ,1-1000 in number • Cells with high energy requirements have more mito. e.g.CNS,muscle,liver • Have 2 membranes • Smooth outer membrane serves as a boundary between the mitochondria and the cytosol • Inner membrane has many folds called Cristae – they enlarge the surface area for more chemical reactions • Have their own DNA n RNA(maternal) • Mito has 120 proteins(13 encoded by mito.DNA. Mito can replicate. • Mutations cause muscle n nerve,renal diseases e.g. LHON & MERRF
- 37. LYSOSOMES
- 38. LYSOSOMES • Small spherical organelles of digestion. • Enclose hydrolytic enzymes, within single membranes with ATPase to keep ph 5.5 • Digest proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, DNA and RNA(Endocytosis) • Eliminating unwanted material- old organelles,misfold proteins bacterias,viruses,tissue remodeling after injury • Destroyed compt. are recycled • L.Enz Defficiency leads to storage dis, L-cell disease(T.sachs,Gaucher,Pompaei diseases)
- 40. PEROXYSOMES • Spherical with single emb.,similar to lysosomes in size,involved in oxidative reactions using molecular O2,producing H2O2 degraded by catalase. • Function in oxidation of long chain FA & synth of bile acids from cholestrol • Can replicate by division like mito.
- 41. Label the parts of the cell http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phbio/activities/cbd-3072/simbase.htm http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/cell/cell.htm