Soil food web
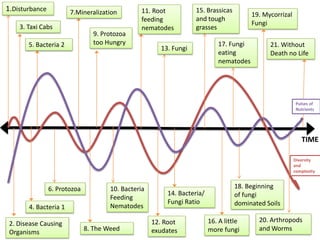
- 1. 1.Disturbance 15. Brassicas and tough grasses 11. Root feeding nematodes 7.Mineralization 19. Mycorrizal Fungi 3. Taxi Cabs 9. Protozoa too Hungry 17. Fungi eating nematodes 5. Bacteria 2 21. Without Death no Life 13. Fungi Pulses of Nutrients TIME Diversity and complexity 18. Beginning of fungi dominated Soils 6. Protozoa 10. Bacteria Feeding Nematodes 14. Bacteria/ Fungi Ratio 4. Bacteria 1 20. Arthropods and Worms 16. A little more fungi 12. Root exudates 2. Disease Causing Organisms 8. The Weed
- 2. Above slide is where we started with this Process (Gautier Gras and Doug Crouch) Below is what myself and Elaine Ingham refined it as Needs more work on making sure succession sequence is correct and the description are accurate (like I have endomychorrizal fungi but not ecto, may combine in the same card)
- 3. 1.Disturbance 11. Endo Mycorrhizal Fungi 15. Fungi 19. EctoMycorrhizal Fungi 7.Mineralization 3. Decomposer bacteria 9. Root exudates 13. Stressed Plants 21. Without death, no life 17. Fungal-feeding nematodes 5. Taxi cabs Diversity and complexity Forest Grasslands Weeds TIME * .8:1 B/F * 1:1 B/F * 2:1 B/F 6. Protozoa 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria 18. Beginning of fungal dominated soils 10. Protozoa over eat 14. Root feeding nematode 2. Photosynthetic bacteria 12. Bacterial-feeding nematode 16. Tough grasses/brassicas 20. Arthropods and worms 8. The Weed *** (B/F) Bacteria/ Fungi ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the availability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). **
- 4. 1.Disturbance Disturbance: Whether from a high heat fire, the iron plough, severe overgrazing, or clear cutting a forest: disturbance will decrease diversity and complexity, and increase the pulses of nutrients. Extreme disturbance will wipe the slate clean like a volcano. Photosynthetic Bacteria: produce sugars from photosynthesis, obtain minerals from acids that they produce, release oxygen, nitrogen fixing, produce organic material Decomposer Bacteria: feed on organic matter (sugars produced by photosynthesis) produced by Photosynthetic bacteria which are simple organic materials, release other waste compounds More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria: feeding on the waste products of the previous two, again creating basic sugars through photosynthesis and the process of breakdown than follows this creation 5. Taxi Cabs: Wind, human movement, birds, snakes, mice or insects transport microbes. Soil organisms are dependant on these taxi cabs which highlights the importance of soil inoculums and compost. 6. Protozoa: When there is enough bacterial biomass, protozoa arrive, grow, reproduce and over time maintain their population. Release nutrients in a plant available form 3. Decomposer bacteria 5. Taxi cabs Weeds * .8:1 B/F 6. Protozoa 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria 2. Photosynthetic bacteria
- 5. 1.Disturbance 11. Endo Mycorrhizal Fungi 7.Mineralization Mineralization (Predator- Prey Relationships) The minerals locked in bacteria are now released by the protozoa. Predator- Prey relationships begins, and now plants can survive in this soil. But not just any plant, the weeds. The Weed: The weed is a plant that requires pulses of high nitrate levels, poor soil structure, and that produces huge number of seeds that disperse far and wide. Root Exudates: Plants put 30-50% of their energy to feed biology both on the leaf surface and contribute to root biomass to the soil. 10. Endo Mychorhyzal fungi: Penetrate root of plants, and help with nutrient cycling while the plant feeds it with carbohydrates explained in #9 11: Protozoa over Eat: Sometimes Protozoa over-eat their food resource, mineralize ( make available) high concentrations of nutrients (Nitrates) and help out the weeds tat require these pulses to germinate. 12.Bacterial Feeding Nematodes: When these organisms arrive, diversity and complexity continues to build. This causes enhanced mineralization, smoothes pulses of nutrients, more consistent concentrations of available nutrients. 3. Decomposer bacteria 9. Root exudates 5. Taxi cabs Grasslands Weeds * .8:1 B/F * 1:1 B/F 6. Protozoa 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria 10. Protozoa over eat 2. Photosynthetic bacteria 12. Bacterial-feeding nematode 8. The Weed *** (B/F) Bacteria/ Fungi ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the availability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). **
- 6. 15. Fungi 19.EctoMycorrhizal Fungi 13. Stressed Plants: Pulses of nutrients are out of sink with plant requirements. Poor soil structure and anaerobic conditions can create stressed plants and set up stage for attack. 14. 14. Root Feeding Nematodes: nematodes may arrive and survive, since weeds are present. Because few competitors of the root feeders are present, if they do arrive they can have a major impact on weeds or food crops if planted in such soils. Fungi: Fungi that arrive now have a food resource to utilize and to begin to build their communities through using celluslose and other complex carbon compounds that the plants provide. This begins the slow building of soil and more nutrient cycling is taking place. 16. Tough Grasses/ brassicas: The early Succession grass species and brassicas begin to grow. These form 10% of plants that do not require mychorrizal fungal association). 13. Stressed Plants 21.Without death, no life 17. Fungal-feeding nematodes Diversity and complexity Forest Grasslands TIME * 1:1 B/F * 2:1 B/F 18. Beginning of fungal dominated soils 14. Root feeding nematode 16. Tough grasses/brassicas 20. Arthropods and worms *** (B/F) Bacteria/ Fungi ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the availability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). **
- 7. 17. Fungal Feeding Nematodes: As the fungi population and diversity grows, fungal feeding nematodes arrive and increase the number of connections in the soil food web. Smoothes out the pulses and makes constant availability of nutrients for plants. 18. Beginning of fungal dominated soils: The plant species put more fungal foods into the soil, and the soil slowly but surely becomes fungal dominated. As the threshold passes, shrubs, bushes, early succession trees win in the competition for soil nutrients. Switch to an ammonium based nutrient input. Mycorrhizal Fungi: Mycorrhizal fungi arrive with the plants that can give their carbohydrates. In exchange they protect the roots from disease causing organisms, by improving nutrient uptake and by producing metabolites that inhibit disease. 20. Arthropods and worms: The top predators of the soil arrive when a strong web is already established. Nutrient pulses calm, diversity and complexity builds, diseases become less common. The forest is on its way. 21. Without death no life: But of course a disturbance will eventually occur again. The process of destruction will yield new opportunities fir life. Diversity and complexity will decrease nutrient pulses will go out of whack. And the cycle continues. 19. EctoMycorrhizal Fungi 21. Without death, no life 17. Fungal-feeding nematodes Diversity and complexity Forest TIME * 2:1 B/F 18. Beginning of fungal dominated soils 20. Arthropods and worms *** (B/F) Bacteria/ Fungi ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the availability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). **
- 8. 1.Disturbance 11. Endo Mycorrhizal Fungi 15. Fungi 19. EctoMycorrhizal Fungi 7.Mineralization 3. Decomposer bacteria 9. Root exudates 13. Stressed Plants 21. Without death, no life 17. Fungal-feeding nematodes 5. Taxi cabs Diversity and complexity Forest Grasslands Weeds TIME * .8:1 B/F * 1:1 B/F * 2:1 B/F 6. Protozoa 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria 18. Beginning of fungal dominated soils 10. Protozoa over eat 14. Root feeding nematode 2. Photosynthetic bacteria 12. Bacterial-feeding nematode 16. Tough grasses/brassicas 20. Arthropods and worms 8. The Weed *** (B/F) Bacteria/ Fungi ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the availability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). **
- 9. Succession Cards 1-6 Disturbance: Whether from a high heat fire, the iron plough, severe overgrazing, or clear cutting a forest: disturbance will decrease diversity and complexity, and increase the pulses of nutrients. Extreme disturbance will wipe the slate clean like a volcano. Photosynthetic Bacteria: produce sugars from photosynthesis, obtain minerals from acids that they produce, release oxygen, nitrogen fixing, produce organic material Decomposer Bacteria: feed on organic matter (sugars produced by photosynthesis) produced by Photosynthetic bacteria which are simple organic materials, release other waste compounds More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria: feeding on the waste products of the previous two, again creating basic sugars through photosynthesis and the process of breakdown than follows this creation 5. Disease Causing Organism: The next organisms to arrive in our soils are disease causing organisms because they are better at dispersing that nay other kind of bacteria and fungi. 6. Taxi Cabs: Wind, human movement, birds, snakes, mice or insects transport microbes. Soil organisms are dependant on these taxi cabs which highlights the importance of soil inoculums and compost.
- 10. Succession Cards 7-12 Mineralization (Predator- Prey Relationships) The minerals locked in bacteria are now released by the protozoa. Predator- Prey relationships begins, and now plants can survive in this soil. But not just any plant, the weeds. The Weed: The weed is a plant that requires pulses of high nitrate levels, poor soil structure, and that produces huge number of seeds that disperse far and wide. Root Exudates: Plants put 30-50% of their energy to feed biology both on the leaf surface and contribute to root biomass to the soil. 10. Endo Mychorhyzal fungi: Penetrate root of plants, and help with nutrient cycling while the plant feeds it with carbohydrates explained in #9 11: Protozoa over Eat: Sometimes Protozoa over-eat their food resource, mineralize ( make available) high concentrations of nutrients (Nitrates) and help out the weeds tat require these pulses to germinate. 12. Bacterial Feeding Nematodes: When these organisms arrive, diversity and complexity continues to build. This causes enhanced mineralization, smoothes pulses of nutrients, more consistent concentrations of available nutrients.
- 11. Succession Cards 13-16 13. Stressed Plants: Pulses of nutrients are out of sink with plant requirements. Poor soil structure and anaerobic conditions can create stressed plants and set up stage for attack. Root Feeding Nematodes: nematodes may arrive and survive, since weeds are present. Because few competitors of the root feeders are present, if they do arrive they can have a major impact on weeds or food crops if planted in such soils. 15. Fungi: Fungi that arrive now have a food resource to utilize and to begin to build their communities through using cellulose and other complex carbon compounds that the plants provide. This begins the slow building of soil and more nutrient cycling is taking place. (Bacteria/ Fungi Ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the ability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). ) Tough Grasses/ brassicas: The early Succession grass species and brassicas begin to grow. These form 10% of plants that do not require mychorrizal fungal association).
- 12. Succession Cards 17-21 17. Fungal Feeding Nematodes: As the fungi population and diversity grows, fungal feeding nematodes arrive and increase the number of connections in the soil food web. Smoothes out the pulses and makes constant availability of nutrients for plants. 18. Beginning of fungal dominated soils: The plant species put more fungal foods into the soil, and the soil slowly but surely becomes fungal dominated. As the threshold passes, shrubs, bushes, early succession trees win in the competition for soil nutrients. Switch to an ammonium based nutrient input. 19. Mycorrhizal Fungi: Mycorrhizal fungi arrive with the plants that can give their carbohydrates. In exchange they protect the roots from disease causing organisms, by improving nutrient uptake and by producing metabolites that inhibit disease. Arthropods and worms: The top predators of the soil arrive when a strong web is already established. Nutrient pulses calm, diversity and complexity builds, diseases become less common. The forest is on its way. 21. Without death no life: But of course a disturbance will eventually occur again. The process of destruction will yield new opportunities fir life. Diversity and complexity will decrease nutrient pulses will go out of whack. And the cycle continues.
- 13. Succession Cards 1-4 Disturbance: Whether from a high heat fire, the iron plough, severe overgrazing, or clear cutting a forest: disturbance will decrease diversity and complexity, and increase the pulses of nutrients. Extreme disturbance will wipe the slate clean like a volcano. Photosynthetic Bacteria: produce sugars from photosynthesis, obtain minerals from acids that they produce, release oxygen, nitrogen fixing, produce organic material 3. Decomposer Bacteria: feed on organic matter (sugars produced by photosynthesis) produced by Photosynthetic bacteria which are simple organic materials, release other waste compounds 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria: feeding on the waste products of the previous two, again creating basic sugars through photosynthesis and the process of breakdown than follows this creation
- 14. Disturbance: Whether from a high heat fire, the iron plough, severe overgrazing, or clear cutting a forest: disturbance will decrease diversity and complexity, and increase the pulses of nutrients. Extreme disturbance will wipe the slate clean like a volcano. Photosynthetic Bacteria: produce sugars from photosynthesis, obtain minerals from acids that they produce, release oxygen, nitrogen fixing, produce organic material 3. Decomposer Bacteria: feed on organic matter (sugars produced by photosynthesis) produced by Photosynthetic bacteria which are simple organic materials, release other waste compounds 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria: feeding on the waste products of the previous two, again creating basic sugars through photosynthesis and the process of breakdown than follows this creation
- 15. 1.Disturbance 11. Endo Mycorrhizal Fungi 15. Fungi 19. Beginning of fungal dominated soils 7.Mineralization 3. Decomposer bacteria 9. Root exudates 13. Stressed Plants 21. Arthropods and worms 17. A little more fungi 5. Taxi cabs Diversity and complexity Forest Grasslands Weeds TIME * .8:1 B/F * 1:1 B/F * 2:1 B/F 6. Protozoa 4. More photosynthetic and more decomposer bacteria 18. Fungal-feeding nematodes 10. Protozoa over eat 14. Root feeding nematode 2. Photosynthetic bacteria 12. Bacterial-feeding nematode 16. Tough grasses/brassicas 20. EctoMycorrhizal Fungi 8. The Weed *** (B/F) Bacteria/ Fungi ratio: As the ratio of fungi to bacteria changes, the pulses of nutrients are smoothed out, and true weedy species lack the availability to out compete plants of later succession (the plants we humans like to eat). **
