Hint for transmission media
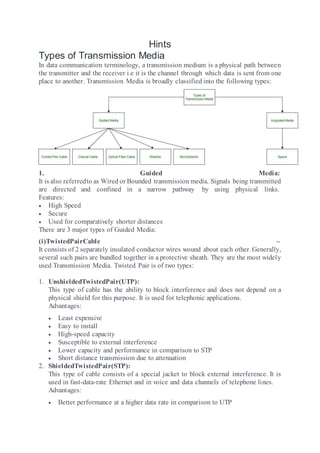
- 1. Hints Types of Transmission Media In data communication terminology, a transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e it is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types: 1. Guided Media: It is also referredto as Wired or Bounded transmission media. Signals being transmitted are directed and confined in a narrow pathway by using physical links. Features: High Speed Secure Used for comparatively shorter distances There are 3 major types of Guided Media: (i)TwistedPairCable – It consists of 2 separately insulated conductor wires wound about each other. Generally, several such pairs are bundled together in a protective sheath. They are the most widely used Transmission Media. Twisted Pair is of two types: 1. UnshieldedTwistedPair(UTP): This type of cable has the ability to block interference and does not depend on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for telephonic applications. Advantages: Least expensive Easy to install High-speed capacity Susceptible to external interference Lower capacity and performance in comparison to STP Short distance transmission due to attenuation 2. ShieldedTwistedPair(STP): This type of cable consists of a special jacket to block external interference. It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and in voice and data channels of telephone lines. Advantages: Better performance at a higher data rate in comparison to UTP
- 2. Eliminates crosstalk Comparatively faster Comparatively difficult to install and manufacture More expensive Bulky (ii)CoaxialCable – It has an outer plastic covering containing 2 parallel conductors each having a separate insulated protection cover. The coaxial cable transmits information in two modes: Baseband mode(dedicated cable bandwidth) and Broadband mode(cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges). Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use Coaxial cables. Advantages: High Bandwidth Better noise Immunity Easy to install and expand Inexpensive Disadvantages: Single cable failure can disrupt the entire network (iii)OpticalFibreCable – It uses the concept of reflectionof light through a core made up of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding. It is used for the transmission of large volumes of data. The cable can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer) supports two modes, namely unidirectional and bidirectional mode. Advantages: Increased capacity and bandwidth Lightweight Less signal attenuation Immunity to electromagnetic interference Resistance to corrosive materials Disadvantages: Difficult to install and maintain High cost Fragile (iv) Stripline
- 3. Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of the planar transmission line. It uses a conducting material to transmit high-frequency waves it is also called a waveguide. This conducting material is sandwiched between two layers of the ground plane which are usually shorted to provide EMI immunity. (v) Microstripline In this, the conducting material is separated from the ground plane by a layer of dielectric. 2.UnguidedMedia: It is also referredto as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media.No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals. Features: The signal is broadcasted through air Less Secure Used for larger distances There are 3 types of Signals transmitted through unguided media: (i)Radiowaves – These are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. The sending and receiving antennas need not be aligned. Frequency Range:3KHz – 1GHz. AM and FM radios and cordless phones use Radiowaves for transmission. Further Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite. (ii)Microwaves – It is a line of sight transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas need to be properly aligned with each other. The distance covered by the signal is directly proportional to the height of the antenna. Frequency Range:1GHz – 300GHz. These are majorly used for mobile phone communication and television distribution. (iii)Infrared – Infrared waves are used for very short distance communication. They cannot penetrate through obstacles. This prevents interference between systems. Frequency Range:300GHz – 400THz. It is used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc.
- 4. 1). What is transmission media? Transmission media is a path that transmits the data from a transmitter to the receiver. 2). What are the types of transmission media? The two types of transmission media are guided and unguided. 3). What are twisted pair cables? Unshielded twisted pair & shielded twisted pair 4). What are the examples of transmission media? They are coaxial cable, twisted-pair cable, and fiber optic cable 5). Mention the most commonly used transmission media in homes? They are coaxial cable, twisted-pair, satellite, fiber optics & microwave,
- 5. Detail Description 1) Unguided Transmission Media It is also called wireless communication or unbounded transmission, they transmit electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. In this medium signals are radiated through the air (or, in a few cases, water) and therefore, are reaching to anyone with a device capable of accepting them. We can categorize wireless transmission into the following groups, a. Radio waves b. Micro waves c. Infrared waves a) Radio Waves Radio waves are electromagnetic waves and are omnidirectional. When an antenna transports radio waves they are propagated in all directions in free space which means the sending and receiving antennas do not have to be aligned that is any receiving antenna can receive that transmitted wave. The frequency of radio waves about 30 hertz (Hz) to 300 gigahertz (GHz) and like all other electromagnetic waves radio waves travel at the speed of light in vacuum. Applications of Radio waves These waves are omnidirectional so they are useful for multicasting in which one sender but many receivers. Examples of radio waves are television, AM and FM radio, cordless phones, and paging. Advantages and disadvantages Radio waves are easy to generate and penetrate buildings also can travel long distances. Radio waves cover a large area and can penetrate the buildings. By this, an AM radio can receive signals inside a building. This can also be disadvantageous because we cannot isolate a communication just inside or outside a building. Cause of this, governments strictly legislate the use of radio transmitters.
- 6. b) Micro Waves Micro Waves includes a line of sight transmission that is the sending and receiving antennas that need to be properly aligned with each other. The distance is directly proportional to the height of the antenna which is covered by the signal. In mobile phone communication and television distribution, these are majorly used. Applications of Micro Waves Due to the unidirectional properties of Micro Waves, they are very useful when unicast (one-to-one) communication is needed between the sender and the receiver. Cellular phones, satellite networks, and wireless LANs are using Micro Waves. Microwave Transmission Two types of Microwave Transmission are as follows, i. Terrestrial Microwave ii. Satellite Microwave (i) Terrestrial Microwave The frequency of Electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 300 GHz are called microwaves. These waves are unidirectional. Whenever through an antenna microwave are transmitting, they can be narrowly focused. That is the sending and receiving antennas need to be aligned. Characteristics of microwaves It is inexpensive for short distance expensive as it requires a higher tower for a longer distance. Due to environmental conditions and antenna size attenuation (loss of signal) occurs. There is a capacity in very high-frequency microwaves that they cannot penetrate walls. This characteristic can be a disadvantage of microwaves if the receiver is inside the buildings. Advantages
- 7. Microwave transmission is cheaper than using cables. It does not require any land for the installation of cables that is free from land acquisition. Microwave transmission provides easy communication. Disadvantages Bandwidth is limited in microwave transmission. A signal can be moved out of phase and any environmental change such as rain, wind can distort the signal so these signals are susceptible to weather conditions. Cause of eavesdropping insecure communication occurs in which any user can catch the signal in the air by using its antenna. (ii) Satellite Microwave A satellite is an entity that revolves around the earth at a certain height. Satellite communication offers more flexibility than fiber optic and cable systems. We can transmit signals from any point on the globe by using satellite transmission. How does a Satellite work? The satellite receives the signal that is transmitted from the earth station, and it amplifies these signals. It is retransmitted the amplified signal to another earth station. Satellite transmission is much like the line-of-sight transmission in which one of the stations is a satellite orbiting the earth. The principle is the same as the terrestrial microwave. Signals still travel in straight lines in satellite transmission. Features of Satellite Microwave It provides transmission capability to and from any location on earth. Deployment of Satellite microwaves for orbiting satellites is difficult. Advantages of Satellite Microwave High-quality communication available to undeveloped parts of the world without requiring a huge investment in the ground-based infrastructure. It is used in a variety of applications such as radio/TV signal broadcasting, weather forecasting, radio/TV signal broadcasting, mobile communication and mobile, and wireless communication applications. The coverage area of a terrestrial microwave is less than the terrestrial microwave. Disadvantages of Satellite Microwave The manufacturing cost is very high of satellite and very expensive to launch a satellite.
- 8. Transmission can go down in bad weather. c) Infrared Waves The frequency of Infrared waves is about 300 GHz to 430 THz, which can be used for short- range communication. Infrared waves of high frequencies cannot penetrate walls. This characteristic of Infrared waves prevents interference between one system and another. This means a short-range communication system in a room cannot be affected by another system in the adjacent room. If we are using the infrared remote control, we do not interfere with the use of the remote by our neighbors. However, by this characteristic, infrared signals become useless for long- range communication. Also, we cannot use infrared waves outside a building because the sun's rays contain infrared waves that can interfere with communication. Characteristics of infrared waves This type of wide bandwidth can be used to transmit digital data with a very high data rate. The Infrared Data Association (IrDA) has established standards for using these signals for communication between devices such as keyboards, mouse, PCs, and printers and it is also responsible for sponsoring the use of infrared waves. This type of communication provides better security with minimum interference.