Cell membrane and transport
- 1. CELL MEMBRANE AND TRANSPORT PRESENTER – Amit kumar Ram MODERATOR- Dr. Nivedita Nanda 1
- 2. Contents : Introduction Cell membrane structure Classification of Transport system Associated disorders Summary 2
- 3. Cell Membrane “Possibly the decisive step [in the origin of life] was the formation of the first cell, in which chain molecules were enclosed by a semi- permeable membrane which kept them together but let their food in.” James Danielli (1911-1984) 3
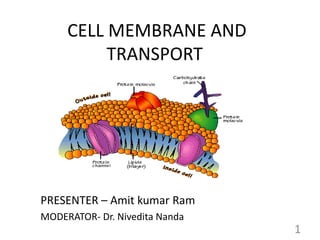
- 4. Cell Membrane Defined as a biological membrane or an outer membrane of a cell. Divide the internal space of eukaryotic cells into discrete compartments to segregate processes and components 4
- 5. Cell Membrane functions • Mechanical structure – maintain the physical integrity of cell and hold the cytoskeleton in place. • Selective permeability – Gases, hydrophibic and small non polar molecules can easily pass through it. • Transport – certain molecules pass through passively other need various transporters. • Markers and signalling – some surface proteins act as cell marker and helps in cell signalling. 5
- 6. COMPOSITION OF CELL MEMBRANE 1. Lipids Phosopholipids Sterols 2. Proteins Integral Peripheral 3. Carbohydrates Glycolipids Glycoproteins 6
- 7. Fluid Mosaic model • Proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972 • Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with a collage of many different proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. • A membrane is a mosaic – Proteins and other molecules are embedded in a framework of phospholipids. • A membrane is fluid – Most protein and phospholipid molecules can move laterally. – Flip-Flop movement is restricted and is catalysed by an enzyme “Flippase”- important during membrane lipid synthesis 7
- 9. Lipid composition varies across the two leaflets of the same membrane. 9 Changes in distribution have biological consequences Platelet is able to play its role in clot formation only when phosphatidylserine moves to outer leaflet. Phosphatidylserine exposure also act as marker for programmed cell death
- 10. Membrane proteins • Classified depending on type of interaction with bilayer. i. Integral membrane proteins- pass through bilayer ii. Peripheral membrane proteins- associate with bilayer by non-covalent interactions iii. Lipid-anchored proteins. 10
- 11. Peripheral membrane proteins Attached to membrane through electrostatic interaction and H-bond. Extracted by treating membrane with high salt or alkaline pH Serve as regulator for membrane bound enzymes, also may limit the mobility of integral proteins. Examples – Ankyrin, spectrin 11
- 12. Integral membrane proteins • Held in the membrane by hydrophobic interaction with lipids • Need detergent to remove. • Types – a) Single Transmembrane -Glycophorin a) Multiple Transmembrane - Bacteriorhodopsin 12
- 13. Certain Integral Proteins Mediate Cell-Cell Interactions and Adhesion 13 • Intigrin serve as binding site for extracellular proteins like Collagen and Fibronectin • It also regulate platelet aggregation at the site of wound. • Mutation in intigrin gene encoding CD18 cause Leukocyte adhesion deficiency in humans
- 14. Lipid-anchored membrane proteins • Covalently linked to membrane by short oligosachharide linked to a molecule of GPI embedded on outer leaflet. • Example –Scrapie protein PrPc • Some linked to inner leaflet like Ras and Src proteins have been implicated in transformation of normal cell to malignant cell. 14
- 15. Lipid-anchored membrane proteins • One of protein is responsible for sleeping sickness. • Protozoan parasite carried by tsetse flies survives in blood by virtue of dense cell surface coat made of a GPI anchored glycoprotein.(Eg- Transamidase complex) • Several hundreds of glycoprotein variants to invade host immune system. 15 Trypanosome brucie
- 16. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) to Visualize Membrane Proteins 16 Purified E.coli aquaporin F0-chloroplast ATP synthase
- 17. Six major functions of membrane proteins Transport Enzymatic activity Signal transduction Cell-cell recognition Intercellular joining Attachment to the cytoskeleton ECM 17
- 18. Transport through cell membrane 18
- 19. Transport through cell membrane Classification based on function Membrane transport Active Via mainly by ATP-driven transporters (pumps) Passive Simple diffusion Facilitated Via various transporters Via Ion channels 19 Primary Active transport Secondary active transport
- 20. Transporters Can Be Grouped into Super families Based on Their Structures A. α Helix type channels 1. Voltage gated ion channel VIC superfamily - Voltage-gated k+ channels 2. Major intrinsic protein family - Aquaporins 3. Ligand gated ion channel - Acetylcholine receptor B. β barrel porins - General bacterial porin (GBP) family 20
- 21. Transporters Can Be Grouped into Super families Based on Their Structures C. Pore forming toxins - Diptheria toxin family D. Porters : Uniports, symports, and antiporters 1. Sugar porter family -GLUT1 glucose transporter of erythrocyte 2. Solute-Na+ transporter - Na+ –glucose symporter in epithelial cells 3. HCO - transporters - HCO - –Cl - antiporter 21
- 22. Transporters Can Be Grouped into Super families Based on Their Structures E. Non Ribosomal Synthesized porters -Valinomycin carrier family F. Diphosphate bond hydrolysis-driven transporters (use PPi not ATP) • ATP binding cassette superfamily • A type ATPase superfamily • P-type ATPase superfamily 22
- 23. Simple diffusion Polar molecules (ex. Glucose, water) ions (ex. H+, Na+, K+) small, nonpolar molecules (ex. O2, CO2) LIPID-SOLUBLE 23
- 24. Facilitated diffusion • Carrier mediated and involves transporter protein. • A transporter protein reduces the ∆G€ for transmembrane diffusion of the solute. • It does this by forming non- covalent interactions with the dehydrated solute to replace the H-bonding with water and by providing hydrophilic transmembrane passageway. • Example – Glucose transporters. 24
- 26. The Glucose Transporter of Erythrocytes Mediates Passive Transport Proposed structure of GLUT1 – Type III Transmembrane protein • Contains 12 transmembrane α-helices of which 9 contains three or more polar or charged amino acid residues often separated by several hydrophobic residues. 26
- 27. Proposed structure of GLUT1 Fig : A helical wheel- distribution of polar and non polar residues on surface of helical segment Fig: Side by side association of five or six amphipathic helices, each with its polar face oriented towards central cavity, can produce a transmembrane channel lined with polar and charged residues. 27
- 28. Model of glucose transport into erythrocytes by GLUT1 The transporter exist in two conformation T1, with the glucose-binding site exposed on the outer surface of the plasma membrane, and T2, with its binding site exposed on the inner surface. 28
- 29. Regulation by insulin of glucose transport by GLUT4 into a myocyte 29 Type I (juvenile onset) diabetes mellitus
- 30. Active Transport • Transport against electrochemical gradient. • Thermodynamically unfavorable – coupled with exergonic process • ATP hydrolysis occurs. • Two types- primary and secondary 30
- 31. Primary Active transport • Directly utilizes metabolic energy for the transport process. • Includes ion pumps • Na + K + ATPase - maintenance of intracellular cations and thus cell volume - Protein synthesis by maintaining high concn. of k + - Maintains resting membrane potential - Mediates action of hormones like thyroxine, aldosterone, and insulin 31
- 32. Primary Active transport • Ca + + ATPase - Maintain high concn. Of Ca+ in ECF - helps in storage of Ca+ in SR needed for instant muscle contraction • H + K + ATPase – pumps H+ ion for HCL secretion - Secrets H + ion into tubular fluid – urine acidification Types Examples Location in cell P-Type (phosphorylation type) Na+K+ ATPase Ca++ ATPase Plasmamembrane Sarcoplasmic reticulum V-type(Vacuolar type H+K+ ATPase Plasma membrane F-type(Energy coupling factor) ATP synthase Inner Mitochondrial membrane ABC transporter CFTR proteins MDR-1 protein Plasma membrane Plasma membrane 32 Classification of ATPase
- 33. Postulated mechanism of Na+ and K+ transport by the Na+K+ ATPase Component of Digitalis used to treat congestive Heart Failure 33
- 34. ABC Transporters Pumps Amino-acids, metal ion many hydrophobic compounds including drugs, out of cells against concentration gradients. Multi-drug transporters(MDR1) • responsible for resistance of certain tumors to some generally effective antitumor drugs. • Has broad substrate specificity including chemotherapeutic drugs adriamycin, doxorubicin, and vinablastin. ABC transporter 34 • ABCB4- Familial intrahepatic cholestasis type3 • ABCC2- Dublin-Jhonson’s Syndrome • ABCD1- Adenoleukodystophy • ATP7A- Menkes disease • ATP7B- Wilson’s disease
- 35. Secondary active Transport • Transport of one solute against its concentration gradient by using the energy generated by gradient of another solute transport. • Example – reabsorption of glucose from kidney tubule or intestine. 35
- 36. Channels • Ion channels • Ionophores • Water channels(Aquaporins) • Gap junction 36
- 37. Ion channels Salient features • They are transmembrane proteins and may exist in α- helical or β-barrel structure. • Selective for one particular ion • Different channels are available for Na+ k+, Ca++and Cl- • Well regulated by presence of “gates” • Two main types – Ligand-gated and Voltage-gated • Activities are affected by certain drugs. • Mutation of genes encoding them cause specific disease. 37
- 38. Ligand-gated channels • Specific molecule binds to receptor and opens the channel. • Example – Acetylcholine receptor in post synaptic membrane. It is a complex of five subunits having binding site for acetylcholine. Structure of Acetylcholine receptor 38
- 39. Voltage gated channels • Opens or close in response to change in membrane potential 39 Voltage-gated Na+ channel of neurons- The voltage-sensing mechanism involves movement of helix 4 perpendicular to the plane of the membrane in response to a change in potential
- 40. Many naturally occuring toxins act as Ion Channels Produced by Puffer fish, an ingredient of Japanese delicacy Fugu act by binding to the voltage gated Na+ channels of neurons and preventing normal action potential. Concentrated in shellfish which become highly poisonous to organism higher up the food chain The active component of crurae block the acetylcholine receptor or k+ channels 40
- 41. Ionophores • They are membrane shuttle for specific ions. • Produced by microorganisms and used as antibiotics. • Increase the permeability of membranes by acting channel formers, thus ion gradient is dissipated. • Two types – Mobile ion carriers(Valinomycin) and channel formers(Gramicidin) Valinomycin, a peptide ionophore that binds K+ 41
- 42. Water channel (Aquaporin) • Family of Integral membrane proteins. • Provide channels for rapid movement of water molecules across all plasma membrane. • Ten aquaporins are known in humans. • RBC contain 2x105 copies of AQP-1 per cell. • Plasma membrane of PCT cells contain five different aquaporin types. Structure of Aquaporin 42
- 43. Permeability characteristics and predominant distribution of known mammalian Aquaporins 43
- 44. Gap junction • Structure that permits direct transfer of small molecule(upto 1200Da). • Composed of family of protein called connexins. • Mutations in genes encoding connexins are associated with cardiovascular diseases and X-linked form of charcot- Marrie-tooth disease. 44
- 45. CELLS TRANSPORT CERTAIN MACROMOLECULES ACROSS THE MEMBRANE BY ENDOCYTOSIS AND EXOCYTOSIS 45
- 46. Vesicle Fluid outside cell Protein Cytoplasm Exocytosis Cytoplasmic vesicles merge with PM and release its content Example – release of neurotransmitters 46
- 47. Vesicle forming Endocytosis Endocytosis can occur in three ways • Phagocytosis ("cell eating") • Pinocytosis ("cell drinking") • Receptor-mediated endocytosis 47
- 49. Receptor Mediated Endocytosis • Phosphatidylinositol 4.5 bisphosphate(PIP2) and the protein dynamin are necessary for the pinching off clathrin-coated vesicles from the cell surface. • Low density lipoprotein(LDL) molecule and its receptor are internalized by means of coated pits containing the LDL receptors. • There is dark side to receptor-mediated endocytosis in that viruses which cause such disease as hepatitis, poliomyelitis, and AIDS initiate their damage by this mechanism. • Iron toxicity also begins with excessive uptake due to endocytosis. 49
- 50. Disorders Some disease resulting from or attributed to abnormalities of Membranes 50
- 51. Disorder due to defect in ion channels 51
- 52. Cystic Fibrosis • Defect in CFTR gene. • CFTR is basically an ion channel for Cl- ion. 52
- 53. Cystic Fibrosis • Common in Caucasian population and are carriers. • Obstruction of GIT & Respiratory tract leading to bacterial infection of airway & death due to respiratory insufficiency before the age of 30. 53
- 54. Myasthenia Gravis • Auto immune disease • Decrease in Ach receptors on motor end plate. • The anti-AchR antibodies compete with Ach to bind to AchR, producing receptor blockade. 54
- 55. Myasthenia Gravis • Womens are more affected. • The extraocular muscles and eyelids are often involved in early course of disease. • Weakness increases during prolonged use of muscle and improves after rest or sleep. • Treated by AchE inhibitors - Pyridostigmine bromide - Neostigmine bromide 55
- 56. Summary • Membranes are complex structure composed of phospholipid bilayer, proteins and carbohydrates. • The Fluid –mosaic models forms a useful basis for thinking about membrane structure. • Integral proteins firmly embed the bilayer while peripheral proteins are attached to the inner or outer surface. • Certain hydrophobic molecules freely diffuse across membranes but the movement of other is restricted because of their size or charge. 56
- 57. Summary • Passive and active (usually ATP-dependent) mechanisms maintain gradient of various ions across membrane. • Glucose enter cells by facilitated diffusion via different transporters. • Na+ K+ ATPase is the key enzyme in regulating intracellular concentration of Na+ and K+. • Ligand or voltage gated ion channels transport charged molecules(Na +, K+, Ca+ + etc.) 57
- 58. Summary • Ionophores carries specific ions dissipating the energy of electrochemical ion gradients. • Water moves across membranes through aquaporins. Defective aquaporins leads to certain disease like Nephrogenic DI. • Large molecules enter or leave cells through endocytosis or exocytosis. • Mutation that affect to structure of membrane proteins(receptor, transporter, ion channels, enzymes, & structural proteins) may cause disease. • Examples include cystic fibrosis, Myesthenia Gravis. 58
- 59. References • Cox. MM, Nelson. DL; Lehninger Principle of Biochemistry; 5th edition. • G.M. Cooper; The cell-A molecular approach; 5th edition. • Gerald Karp; Cell and Molecular Biology 6th edition. • Murray RK, Bender DA, Botham KM, Kennelly PJ et al; Harper Illustrated Biochemistry; 28th edition. • Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 17th edition. • Lodish H; Molecular Biology of Cell; 6th edition. • Yeagle PL; The structure of Biological Membranes 2nd edition. • Clapham DE; Symmetry, selectivity and the 2003 Nobel prize cell 2003; 115:641 59
- 60. 60
Editor's Notes
- Carbonate.
- Alpha and beta conformation.