More Related Content Similar to Diabetes A Synopsis By Aneek Gupta (20) More from Dr Aneek Gupta (20) 1. ee
k
Diabetes is a disorder of metabolism—the way our bodies use digested food for growth and
energy. Most of the food we eat is broken down into glucose, the form of sugar in the blood.
Glucose is the main source of fuel for the body.
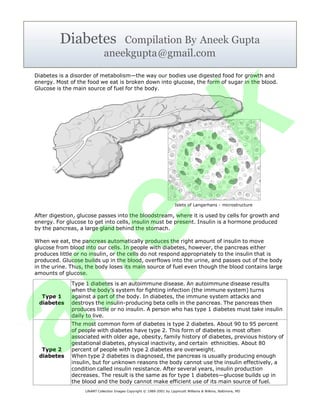
Islets of Langerhans - microstructure
After digestion, glucose passes into the bloodstream, where it is used by cells for growth and
energy. For glucose to get into cells, insulin must be present. Insulin is a hormone produced
by the pancreas, a large gland behind the stomach.
an
When we eat, the pancreas automatically produces the right amount of insulin to move
glucose from blood into our cells. In people with diabetes, however, the pancreas either
produces little or no insulin, or the cells do not respond appropriately to the insulin that is
produced. Glucose builds up in the blood, overflows into the urine, and passes out of the body
in the urine. Thus, the body loses its main source of fuel even though the blood contains large
amounts of glucose.
Type 1
diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. An autoimmune disease results
when the body’s system for fighting infection (the immune system) turns
against a part of the body. In diabetes, the immune system attacks and
destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The pancreas then
produces little or no insulin. A person who has type 1 diabetes must take insulin
daily to live.
Type 2
diabetes
The most common form of diabetes is type 2 diabetes. About 90 to 95 percent
of people with diabetes have type 2. This form of diabetes is most often
associated with older age, obesity, family history of diabetes, previous history of
gestational diabetes, physical inactivity, and certain ethnicities. About 80
percent of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight.
When type 2 diabetes is diagnosed, the pancreas is usually producing enough
insulin, but for unknown reasons the body cannot use the insulin effectively, a
condition called insulin resistance. After several years, insulin production
decreases. The result is the same as for type 1 diabetes—glucose builds up in
the blood and the body cannot make efficient use of its main source of fuel.
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
2. k
Plasma Glucose Result
(mg/dL)
Diagnosis
99 and below
Normal
Pre-diabetes
(impaired fasting glucose)
126 and above
Diabetes*
2-Hour Plasma Glucose
Result (mg/dL)
Diagnosis
139 and below
Normal
140 to 199
Pre-diabetes
(impaired glucose
tolerance)
200 and above
Diabetes*
When
Plasma Glucose Result
(mg/dL)
Fasting
95 or higher
At 1 hour
180 or higher
At 2 hours
155 or higher
At 3 hours
140 or higher
an
ee
100 to 125
*Confirmed by repeating the test on a different day.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institute of Health.
diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
3. k
ee
an
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institute of Health.
diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
4. k
ee
an
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institute of Health.
diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
5. Insulin resistance is a silent condition that increases the chances of developing diabetes
and heart disease.
What does insulin do?
Common
bile duct
Pancreatic
duct
Tail of
pancreas
ee
k
Duodenum
After you eat, the food is broken
down into glucose, the simple sugar
that is the main source of energy for
the body's cells. But your cells cannot
use glucose without insulin, a
hormone produced by the pancreas.
Insulin helps the cells take in glucose
and convert it to energy. When the
pancreas does not make enough
insulin or the body is unable to use
the insulin that is present, the cells
cannot use glucose. Excess glucose
builds up in the bloodstream, setting
the stage for diabetes.
Body of
pancreas
Head of
pancreas
Small intestine
If you have insulin resistance, your muscle, fat, and liver cells do not use insulin properly. The pancreas
tries to keep up with the demand for insulin by producing more. Eventually, the pancreas cannot keep
up with the body's need for insulin, and excess glucose builds up in the bloodstream. Many people with
insulin resistance have high levels of blood glucose and high levels of insulin circulating in their blood at
the same time.
People with blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not yet in the diabetic range have
“pre-diabetes.” Doctors sometimes call this condition impaired fasting glucose ( IFG) or impaired glucose
tolerance ( IGT), depending on the test used to diagnose it.
an
If you have pre-diabetes, you have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, formerly called
adult-onset diabetes or noninsulin -dependent diabetes. People with pre-diabetes also have a higher risk
of heart disease.
Insulin resistance can also occur in people who have type 1 diabetes, especially if they are overweight.
Points to Remember:
Glucose is the simple sugar that is the main source of energy for the body's cells.
Insulin helps cells take in blood glucose and convert it to energy
If you have insulin resistance, your body's cells do not respond well to insulin.
Insulin resistance is a stepping-stone to type 2 diabetes.
Lack of exercise and excess weight contribute to insulin resistance.
Engaging in moderate physical activity and maintaining proper weight can help prevent insulin
resistance.
Insulin resistance plays a role in the development of cardiovascular disease, which damages the heart
and blood vessels.
Controlling blood pressure and LDL cholesterol and not smoking can also help prevent cardiovascular
problems.
The Diabetes Prevention Program confirmed that exercise and a low-calorie, low-fat diet are the best
ways to prevent type 2 diabetes.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases,
National Institute of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
6. ee
k
Eyes
High blood sugars can
cause blurred vision,
and poorly-controlled
diabetes can lead to
blindness.
Stroke
People with diabetes are 2 to 4 times
more likely to suffer a stroke than
people without diabetes.
Lungs
People with diabetes are
more likely to die with
pneumonia or influenza
than people who do not
have diabetes.
an
Kidneys
High blood sugars,
especially if combined
with high blood
pressure, can cause
kidney damage and lead
to dialysis.
Nerves
High blood sugars
can damage nerves
in any part of the
body.
Teeth
High blood sugars can cause gum
disease (periodontal disease) and
gum disease can cause high blood
sugars.
Heart
Diabetes, especially in people with
high blood pressure and high
cholesterol, causes heart disease.
Heart disease is the #1 killer of
people with diabetes.
Stomach
Poorly-controlled diabetes can cause
nerve damage to the stomach leading
to nausea, poor digestion, and
bloating.
Reproductive Health
and Pregnancy
Diabetes can also
complicate pregnancy.
Feet
Diabetes can damage both the
nerves and the blood vessels to the
feet leading to numbness, burning
“pins and needles” feeling, poor
circulation and possibly amputation.
Source: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion . www.cdc.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
7. k
ee
The diabetes food pyramid can help you make wise food
choices. It divides foods into groups, based on what they
contain. Eat more from the groups at the bottom of the
pyramid, and less from the groups at the top. Foods from the
starches, fruits, vegetables, and milk groups are highest in
carbohydrate. They affect your blood glucose levels the most.
How much should I eat each day?
Talk with your diabetes teacher about how to make a meal
plan that fits the way you usually eat, your daily routine, and
your diabetes medicines. Then make your own plan.
Have about 1,600 to 2,000 calories a
day if you are a
large woman who wants to lose weight
small man at a healthy weight
medium-sized man who does not
exercise much
medium-sized or large man who wants
to lose weight
an
Have about 1,200 to 1,600 calories a
day if you are a
small woman who exercises
small or medium-sized woman who
wants to lose weight
medium-sized woman who does not
exercise much
Have about 2,000 to 2,400 calories a
day if you are a
medium-sized or large man who
exercises a lot or has a physically active
job
large man at a healthy weight
medium-sized or large woman who
exercises a lot or has a physically active
job
Choose this many servings from these food groups to meet your calories a day:
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institute of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
8. k
When the kidneys are working well, the tiny
filters in your kidneys, the glomeruli, keep
protein inside your body. You need the
protein to stay healthy.
ee
High blood glucose and high blood pressure
damage the kidneys’ filters. When the kidneys
are damaged, the protein leaks out of the
kidneys into the urine. Damaged kidneys do
not do a good job of cleaning out wastes and
extra fluid. Wastes and fluid build up in your
blood instead of leaving the body in urine.
an
Kidney damage begins long before you notice
any symptoms. An early sign of kidney
damage is when your kidneys leak small
amounts of a protein called albumin into the
urine. But the only way to know about this
leakage is to have your urine tested.
The kidneys act as filters to clean the blood. They get rid of wastes and
send along filtered fluid. The tiny filters in the kidneys are called glomeruli.
When kidneys are healthy, the artery brings blood and wastes from the
bloodstream into the kidneys. The glomeruli clean the blood. Then wastes
and extra fluid go out into the urine through the ureter. Clean blood leaves
the kidneys and goes back into the bloodstream through the vein.
With more damage, the kidneys leak more
and more protein. This problem is called
proteinuria. More and more wastes build up in
the blood. This damage gets worse until the
kidneys fail.
Diabetic nephropathy is the medical term for
kidney problems caused by diabetes.
Nephropathy affects both kidneys at the same
time.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health.
diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
9. What if I don’t get treated for
gestational diabetes?
ee
Why do some women get
gestational diabetes?
k
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes, or high blood sugar, that only pregnant women get. In fact, the word
gestational means pregnant. If a woman gets high blood sugar when she’s pregnant, but she never had high blood sugar
before, she has gestational diabetes. Nearly 200,000* pregnant women get the condition every year, making it one of
the top health concerns related to pregnancy.
If not treated, gestational diabetes can cause problems for mothers and babies. Some of these problems can be serious.
an
Usually, the body breaks down
much of the food you eat into
a type of sugar, called
glucose. Because glucose
moves from the stomach into
the blood, some people use
the term blood sugar, instead
of glucose. Your body makes a
hormone called insulin that
moves glucose out of the
blood and into the cells of the
body. In women with
gestational diabetes, the
glucose can’t get into the
cells, so the amount of
glucose in the blood gets
higher and higher. This is
called high blood sugar or
diabetes.
Most women with gestational diabetes have
healthy pregnancies and healthy babies
because they control their condition. Without
treatment, these women are at risk for: high
blood pressure, preeclampsia (a sudden,
dangerous increase in blood pressure), and
fetal death during the last 4 to 8 weeks of
pregnancy. These women may also have very
large babies. Some women need surgery to
deliver their bigger babies, which can
increase the risk of infection and prolong
recovery time.
As babies, children whose mothers had
gestational diabetes are at higher risk for
breathing problems. As they get older, these
children are also at higher risk for obesity,
abnormal glucose tolerance, and diabetes.
These women and their children also have a
higher lifetime risk for type 2 diabetes. It
may be possible to prevent type 2 diabetes
through lifestyle changes. Talk to your health
care provider about diabetes and risk from
gestational diabetes.
Source: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health. www.nichd.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
10. ee
k
High blood glucose levels before and during
pregnancy can:
worsen your long-term diabetes complications,
such as vision problems, heart disease, and
kidney disease
increase the chance of problems for your baby,
such as being born too early, weighing too much
or too little, and having low blood glucose or
other health problems at birth
increase the risk of your baby having birth
defects
increase the risk of losing your baby through
miscarriage or stillbirth
However, research has shown that when women
with diabetes keep blood glucose levels under
control before and during pregnancy, the risk of
birth defects is about the same as in babies born
to women who don’t have diabetes.
an
However, research has shown that when women
with diabetes keep blood glucose levels under
control before and during pregnancy, the risk of
birth defects is about the same as in babies born to
women who don’t have diabetes.
Glucose
Glucose in a pregnant woman’s blood passes through to the baby. If your blood
glucose level is too high during pregnancy, so is your baby’s glucose level before
birth.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases,
National Institutes of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
11. k
ee
Most women with gestational diabetes can make it to their due dates safely and begin labor naturally. In some cases, though,
gestational diabetes could change the way you feel or how your baby is delivered. Again, keep in mind that just because you have
gestational diabetes does not mean that you will have any change in delivery. Talk to your health care provider about ANY
concerns you have about labor or delivery.
an
Keeping your blood sugar level under control during labor and
delivery is vital to your own health and to your baby's health. If
you do not take insulin during your pregnancy, you probably
won't need it during labor or delivery. If you do take insulin
during your pregnancy, you may receive an insulin shot when
labor begins, or you may get insulin through a thin, plastic tube
in your arm that goes into your bloodstream during labor.
Gestational diabetes puts women at higher risk than women
without the condition for developing preeclampsia, late in their
pregnancies. Preeclampsia is a condition related to a sudden
blood pressure increase; it can be a serious. (For more
information on preeclampsia, go to the Your health care
provider might also tell you to: Have your blood pressure
checked as indicated section of this booklet.) The only way to
cure preeclampsia is to deliver the baby; but delivery may not
be the best option for your health or for the health of the baby.
Your health care provider will keep you under close watch,
possibly at the hospital, and will run multiple tests to determine
whether early delivery is safe and needed. Your health care
provider will give you more information about early delivery,
should it be necessary.
This is a type of surgery used to deliver the baby, instead of
natural delivery through the vagina. Cesarean delivery is also
called a cesarean section, or "C" section. Simply having
gestational diabetes is not a reason to have a C section, but your
health care provider may have other reasons for choosing a
cesarean delivery, such as changes in your health or your baby's
health during labor.
Source: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health. www.nichd.nih.gov
12. k
an
ee
Most women who have gestational diabetes give birth to healthy babies, especially when they keep their blood sugar under
control, eat a healthy diet, get regular, moderate physical activity, and maintain a healthy weight. In some cases, though, the
condition can affect the pregnancy.
Keeping glucose levels under control may prevent certain problems related to gestational diabetes.
Below are some conditions that can result from your having gestational diabetes. Keep in mind that just because you have
gestational diabetes does not mean that these problems will occur.
Source: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health. www.nichd.nih.gov
13. k
Tooth and gum problems can happen to anyone. A sticky film full of
germs, called plaque, builds up on your teeth. High blood glucose
helps germs, also called bacteria, grow. Then you can get red, sore,
and swollen gums that bleed when you brush your teeth.
ee
People with diabetes can have tooth and gum problems more often
if their blood glucose stays high. High blood glucose can make tooth
and gum problems worse. You can even lose your teeth.
Smoking makes it more likely for you to get a bad case of gum
disease, especially if you have diabetes and are age 45 or older.
Formation of plaque on the teeth
Red, sore, and bleeding gums are the first sign of gum disease.
These problems can lead to periodontitis. Periodontitis is an
infection in the gums and the bone that holds the teeth in place. If
the infection gets worse, your gums may pull away from your teeth,
making your teeth look long.
an
If you have one or more of these problems, you may have tooth
and gum damage from diabetes:
red, sore, swollen gums
bleeding gums
gums pulling away from your teeth so your teeth look long
loose or sensitive teeth
bad breath
a bite that feels different
dentures—false teeth—that do not fit well
Anterior view of teeth and gums
afflicted with periodontitis.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health.
diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
14. ee
k
Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with
diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe
vision loss or even blindness.
Diabetic eye disease may include:
Cornea
Pupil
Lens
Iris
Cataract:
clouding of the eye's lens.
Cataracts develop at an
earlier age in people with
diabetes.
Vitreous gel
Macula
an
Retina
Optic nerve
Diabetic
Retinopathy:
damage to the
blood vessels in
the retina.
Glaucoma:
increase in fluid
pressure inside the
eye that leads to optic
nerve damage and
loss of vision. A
person with diabetes
is nearly twice as
likely to get glaucoma
as other adults.
Source: National Eye Institute, U.S. National Institute of Health. www.nei.nih.gov
15. The lens lies behind the iris and the pupil (see diagram). It works much like a
camera lens. It focuses light onto the retina at the back of the eye, where an image
is recorded. The lens also adjusts the eye's focus, letting us see things clearly both
up close and far away. The lens is made of mostly water and protein. The protein is
arranged in a precise way that keeps the lens clear and lets light pass through it.
ee
k
But as we age, some of the protein may clump together and start to cloud a small
area of the lens. This is a cataract. Over time, the cataract may grow larger and
cloud more of the lens, making it harder to see.
Researchers suspect that there are several causes of cataract, such as smoking and
diabetes. Or, it may be that the protein in the lens just changes from the wear and
tear it takes over the years.
an
Symptoms of Cataract
includes:
Cloudy or blurry vision.
Colors seem faded.
Glare.
Poor night vision.
Double vision or multiple
images in one eye.
Frequent prescription
changes in your
eyeglasses or contact
lenses.
Types of cataract surgery:
Phacoemulsification, or phaco. A small incision is made on the side of the cornea,
the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Your doctor
inserts a tiny probe into the eye. This device emits ultrasound waves that soften
and break up the lens so that it can be removed by suction. Most cataract surgery
today is done by phacoemulsification, also called "small incision cataract surgery."
Extracapsular surgery. Your doctor makes a longer incision on the side of the
cornea and removes the cloudy core of the lens in one piece. The rest of the lens
is removed by suction.
Source: National Eye Institute, U.S. National Institute of Health. www.nei.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
16. k
Anterior chamber
Pupil
Fluid exits here
ee
Fluid exits here
In the front of the eye is a space called the anterior chamber. A clear
fluid flows continuously in and out of the chamber and nourishes
nearby tissues. The fluid leaves the chamber at the open angle where
the cornea and iris meet. (See diagram.) When the fluid reaches the
angle, it flows through a spongy meshwork, like a drain, and leaves
the eye.
Sometimes, when the fluid reaches the angle, it passes too slowly
through the meshwork drain. As the fluid builds up, the pressure
inside the eye rises to a level that may damage the optic nerve. When
the optic nerve is damaged from increased pressure, open-angle
glaucoma--and vision loss--may result. That's why controlling
pressure inside the eye is important.
Iris
Iris
Lens
Angle
Fluid forms here
an
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form. Some people have other types of the disease.
Low-tension or normal-tension glaucoma. Optic nerve damage and narrowed side vision occur in people with normal eye
pressure. Lowering eye pressure at least 30 percent through medicines slows the disease in some people. Glaucoma may worsen
in others despite low pressures.
Angle-closure glaucoma. The fluid at the front of the eye cannot reach the angle and leave the eye. The angle gets blocked by
part of the iris. People with this type of glaucoma have a sudden increase in eye pressure. Symptoms include severe pain and
nausea, as well as redness of the eye and blurred vision. If you have these symptoms, you need to seek treatment immediately.
Congenital glaucoma. Children are born with a defect in the angle of the eye that slows the normal drainage of fluid. These
children usually have obvious symptoms, such as cloudy eyes, sensitivity to light, and excessive tearing. Conventional surgery
typically is the suggested treatment, because medicines may have unknown effects in infants and be difficult to administer.
Surgery is safe and effective. If surgery is done promptly, these children usually have an excellent chance of having good vision.
Secondary glaucomas. These can develop as complications of other medical conditions. These types of glaucomas are
sometimes associated with eye surgery or advanced cataracts, eye injuries, certain eye tumors, or uveitis (eye inflammation).
Pigmentary glaucoma occurs when pigment from the iris flakes off and blocks the meshwork, slowing fluid drainage. A severe
form, called neovascular glaucoma, is linked to diabetes. Corticosteroid drugs used to treat eye inflammations and other diseases
can trigger glaucoma in some people. Treatment includes medicines, laser surgery, or conventional surgery.
Source: National Eye Institute, U.S. National Institute of Health. www.nei.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
17. k
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease and a leading cause of blindness in American adults. It is
caused by changes in the blood vessels of the retina.
In some people with diabetic retinopathy, blood vessels may swell and leak fluid. In other people, abnormal new blood
vessels grow on the surface of the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. A healthy retina
is necessary for good vision.
ee
If you have diabetic retinopathy, at first you may not notice
changes to your vision. But over time, diabetic retinopathy can
get worse and cause vision loss. Diabetic retinopathy usually
affects both eyes.
How does diabetic retinopathy cause vision loss?
Blood vessels damaged from diabetic retinopathy can cause
vision loss in two ways:
an
Fragile, abnormal blood vessels can develop and leak blood
into the center of the eye, blurring vision. This is proliferative
retinopathy and is the fourth and most advanced stage of the
disease.
Fluid can leak into the center of the macula, the part of the
eye where sharp, straight-ahead vision occurs. The fluid
makes the macula swell, blurring vision. This condition is
called macular edema. It can occur at any stage of diabetic
retinopathy, although it is more likely to occur as the disease
progresses. About half of the people with proliferative
retinopathy also have macular edema.
Image of the retina afflicted
with proliferative diabetic
retinopathy as seen through
an opthalmoscope.
Source: National Eye Institute, U.S. National Institute of Health. www.nei.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
18. an
ee
k
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease and a
leading cause of blindness in American adults. It is caused by changes in
the blood vessels of the retina.
Source: National Eye Institute, U.S. National Institute of Health. www.nei.nih.gov
19. k
ee
Diabetic neuropathies are a family of nerve disorders caused by diabetes.
People with diabetes can, over time, develop nerve damage throughout the
body. Some people with nerve damage have no symptoms. Others may have
symptoms such as pain, tingling, or numbness—loss of feeling—in the hands,
arms, feet, and legs. Nerve problems can occur in every organ system,
including the digestive tract, heart, and sex organs.
About 60 to 70 percent of people with diabetes have some form of
neuropathy. People with diabetes can develop nerve problems at any time,
but risk rises with age and longer duration of diabetes. The highest rates of
neuropathy are among people who have had diabetes for at least 25 years.
Diabetic neuropathies also appear to be more common in people who have
problems controlling their blood glucose, also called blood sugar, as well as
those with high levels of blood fat and blood pressure and those who are
overweight.
an
The causes are probably different for different types of diabetic neuropathy.
Researchers are studying how prolonged exposure to high blood glucose
causes nerve damage. Nerve damage is likely due to a combination of
factors:
metabolic factors, such as high blood glucose, long duration of diabetes,
abnormal blood fat levels, and possibly low levels of insulin
neurovascular factors, leading to damage to the blood vessels that carry
oxygen and nutrients to nerves
autoimmune factors that cause inflammation in nerves
mechanical injury to nerves, such as carpal tunnel syndrome
inherited traits that increase susceptibility to nerve disease
lifestyle factors, such as smoking or alcohol use
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
20. k
Focal Neuropathy
Autonomic Neuropathy
appears suddenly and affects specific nerves,
most often in the head, torso, or leg. Focal
neuropathy may cause
inability to focus the eye
double vision
aching behind one eye
paralysis on one side of the face, called Bell’s
palsy
severe pain in the lower back or pelvis
pain in the front of a thigh
pain in the chest, stomach, or side
pain on the outside of the shin or inside of the
foot
chest or abdominal pain that is sometimes
mistaken for heart disease, a heart attack, or
appendicitis
ee
affects the nerves that control the heart,
regulate blood pressure, and control blood
glucose levels. Autonomic neuropathy also
affects other internal organs, causing
problems with digestion, respiratory function,
urination, sexual response, and vision. In
addition, the system that restores blood
glucose levels to normal after a hypoglycemic
episode may be affected, resulting in loss of
the warning symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Proximal Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy
an
(Lumbosacral Plexus Neuropathy,
Femoral Neuropathy, or Diabetic
Amyotrophy ) starts with pain in the
thighs, hips, buttocks, or legs, usually
on one side of the body. This type of
neuropathy is more common in those
with type 2 diabetes and in older adults
with diabetes. Proximal neuropathy
causes weakness in the legs and the
inability to go from a sitting to a
standing position without help.
Treatment for weakness or pain is
usually needed. The length of the
recovery period varies, depending on
the type of nerve damage.
(Distal Symmetric Neuropathy or Sensorimotor
Neuropathy) is nerve damage in the arms and
legs. Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may
include:
numbness or insensitivity to pain or
temperature
a tingling, burning, or prickling sensation
sharp pains or cramps
extreme sensitivity to touch, even light touch
loss of balance and coordination
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
21. an
ee
k
Diabetic neuropathy can be classified as peripheral, autonomic, proximal, or focal. Each affects different parts of the body
in various ways.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases,
National Institutes of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
22. k
Too much glucose in the blood for a long time can
cause diabetes problems. This high blood glucose,
also called blood sugar, can damage many parts of
the body.
ee
Saphenous nerve
High blood glucose from diabetes causes two
problems that can hurt your feet:
Nerve damage:
One problem is damage to nerves in your legs and
feet. With damaged nerves, you might not feel pain,
heat, or cold in your legs and feet. A sore or cut on
your foot may get worse because you do not know it
is there. This lack of feeling is caused by nerve
damage, also called diabetic neuropathy. Nerve
damage can lead to a sore or an infection.
an
Poor blood flow:
The second problem happens when not enough
blood flows to your legs and feet. Poor blood flow
makes it hard for a sore or infection to heal. This
problem is called peripheral vascular disease, also
called PVD. Smoking when you have diabetes makes
blood flow problems much worse.
Principal nerve
Tibial nerve
Deep fibular nerve
Superficial
fibular nerve
Medial plantar nerve
Lateral plantar nerve
Nerves of Leg
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
23. ee
k
Esophagus
Gastroparesis, also called
delayed gastric emptying, is
a disorder in which the
stomach takes too long to
empty its contents. Normally,
the stomach contracts to
move food down into the
small intestine for digestion.
The vagus nerve controls the
movement of food from the
stomach through the
digestive tract. Gastroparesis
occurs when the vagus nerve
is damaged and the muscles
of the stomach and intestines
do not work normally. Food
then moves slowly or stops
moving through the digestive
tract
Stomach
an
Small Intestine
What are the complications ofgastroparesis?
If food lingers too long in the stomach, it can cause bacterial overgrowth from the
fermentation of food. Also, the food can harden into solid masses called bezoars that
may cause nausea, vomiting, and obstruction in the stomach. Bezoars can be
dangerous if they block the passage of food into the small intestine.
Gastroparesis can make diabetes worse by making blood glucose control more difficult.
When food that has been delayed in the stomach finally enters the small intestine and
is absorbed, blood glucose levels rise. Sincegastroparesis makes stomach emptying
unpredictable, a person’s blood glucose levels can be erratic and difficult to control.
Source: National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases,
National Institutes of Health. diabetes.niddk.nih.gov
24. Pneumonia is an infection in one
or both of the lungs. Many small
germs, such as bacteria, viruses,
and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Bronchioles
Oxygenated blood to the heart
Deoxygenated blood
from the heart
ee
k
The infection causes your lungs’
air sacs, called alveoli, to become
inflamed. The air sacs may fill up
with fluid or pus, causing
symptoms such as a cough, fever,
chills, and trouble breathing.
an
Alveoli - site of gas exchange
Pneumonia and its symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Many factors
affect how serious pneumonia is, such as the type of germ causing the
infection and your age and overall health.
Pneumonia tends to be more serious for:
Infants and young children.
Older adults (people 65 years or older).
People who have other health problems like heart failure, diabetes, or
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
People who have weak immune systems as a result of diseases or other
factors. These may include HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy (a treatment for
cancer), or an organ or bone marrow transplant.
Source: National Heart and Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health. www.nhlbi.nih.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
25. k
an
ee
Pneumonia is named for the way in which a person gets the infection or for the germ that causes it.
Source: National Heart and Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health. www.nhlbi.nih.gov
26. k
an
ee
The pneumococcal shot protects you from getting a serious infection in your blood or brain that can
cause dangerous health problems, hospitalization or death.
Source: Center for Disease Control; and Prevention. www.cdc.gov
27. k
ee
Influenza (the flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild to severe illness, and at
times can lead to death. The best way to prevent the flu is by getting a flu vaccination each year. Every year in the United
States, on average 5% to 20% of the population gets the flu; more than 200,000 people are hospitalized from flu
complications, and; about 36,000 people die from flu. Some people, such as older people, young children, and people with
certain health conditions (such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease), are at high risk for serious flu complications.
The single best way to prevent the flu is to get a flu vaccination each
year. There are two types of vaccines:
The "flu shot" – an inactivated vaccine (containing killed virus) that is
given with a needle. The flu shot is approved for use in people 6
months of age and older, including healthy people and people with
chronic medical conditions.
The nasal-spray flu vaccine – a vaccine made with live, weakened flu
viruses that do not cause the flu (sometimes called LAIV for “Live
Attenuated Influenza Vaccine”). LAIV is approved for use in healthy*
people 2-49 years of age who are not pregnant.
an
Some people should not be vaccinated without first consulting a
physician. They include:
People who have a severe allergy to chicken eggs.
People who have had a severe reaction to an influenza vaccination in
the past.
People who developed Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) within 6 weeks
of getting an influenza vaccine previously.
Children less than 6 months of age (influenza vaccine is not approved
for use in this age group).
People who have a moderate or severe illness with a fever should wait
to get vaccinated until their symptoms lessen.
If you have questions about whether you should get a flu vaccine,
consult your health-care provider.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. www.cdc.gov
LifeART Collection Images Copyright © 1989-2001 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD