IB Chemistry on Ionization energy and electron configuration
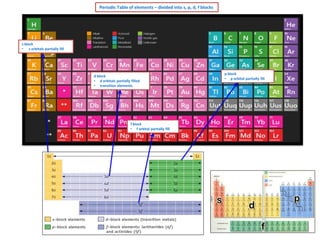
- 1. Periodic Table of elements – divided into s, p, d, f blocks s block • s orbitals partially fill d block • d orbitals partially filled • transition elements f block • f orbital partially fill p block • p orbital partially fill
- 2. s block elements • s orbitals partially fill 1 H He p block elements • p orbital partially fill 5 1s2 n = 2 period 2 B [He] 2s2 2p1 6 1s1 2 Periodic Table – s, p d, f blocks elements C [He] 2s2 2p2 7 N [He] 2s2 2p3 3 Li [He] 2s1 8 O [He] 2s2 2p4 4 Be [He] 2s2 9 F [He] 2s2 2p5 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 10 Ne [He] 2s2 2p6 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 14 20 K Ca [Ne] 3s2 3p2 [Ar] 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 [Ar] 4s2 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 17 19 Si 4s1 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 18 Ar [Ne] 3s2 3p6 d block elements • d orbitals partially fill • transition elements 21 Sc [Ar] 4s2 3d1 22 Ti [Ar] 4s2 3d2 23 V [Ar] 4s2 3d13 24 Cr [Ar] 4s1 3d5 25 Mn [Ar] 4s2 3d5 26 Fe [Ar] 4s2 3d6 27 Co [Ar] 4s2 3d7 28 Ni [Ar] 4s2 3d8 29 Cu [Ar] 4s1 3d10 30 Zn [Ar] 4s2 3d10 f block elements • f orbitals partially fill Video on electron configuration Click here electron structure Click here video on s,p,d,f notation Click here video s,p,d,f blocks,
- 3. Periodic Table – s, p d, f blocks elements Electron structure Chromium d block (Period 4) Electron structure Germanium p block, Gp 4 (Period 4) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 [Ar] 4s1 3d5 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2 [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p2 d block – d partially filled Electron structure Iodine p block, Gp 7 (Period 5) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p5 [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p5 Gp 4 -4 valence electron Gp 7 - 7 valence electron Ge Cr I Cd Hg Electron structure Cadmium d block (Period 5) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 [Kr] 5s2 4d10 d block – d partially filled Pb Electron structure Mercury d block (Period 6) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 d block – d partially filled Electron structure Lead p block, Gp 4 (Period 6) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d106p2 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p2 Gp 4 -4 valence electron
- 4. Electron filled according to 3 Principles 1 Aufbau Principle • electron occupy orbitals of lower energy first • building up, construction from bottom up 4Be High energy - 1s2 2s2 5B - 1s2 2s2 2p1 2p 2p 2s 2s Click here to view simulation 1s 1s lower energy 2 Hund’s Principle • electron occupy orbitals singly first before pairing up 7N High energy - 1s2 2s2 2p3 8O - 1s2 2s2 2p4 2p 2s Click here to view simulation 1s 3 lower energy Pauli Exclusion Principle • each orbital occupy by 2 electron opposite spin 4Be - 1s2 2s2 High energy 10Ne - 1s2 2s2 2p6 Click here to view simulation lower energy
- 5. Electron Notation Atom Positive/Negative Ion s, p, d, f notation Complete configuration Noble gas notation Condensed configuration Noble gas notation Complete configuration 10 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 10 Ne [Ne] 10 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 /[Ne] 11 Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 11 Na+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 12 Mg 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 12 Mg2+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 13 Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 13 Al3+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 14 Si 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 14 Si [Ne] 3s2 3p2 14 Si4+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 15 P 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 15 P3- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 /[Ar] 16 S 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 16 S2- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 /[Ar] 17 CI 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 17 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 17 CI- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6/ [Ar] 18 Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 18 Ar [Ar] 19 [Ne] 18 Ar [Ar] K [Ar] 4s1 19 K+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 /[Ar] 20 Ca [Ar] 4s2 20 Ca2+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 / [Ar] 21 Sc [Ar] 4s2 3d1 22 Ti [Ar] 4s2 3d2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 23 V [Ar] 4s2 3d3 Cr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 24 Cr [Ar] 4s1 3d5 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 25 Mn [Ar] 4s2 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 26 Fe [Ar] 4s2 3d6 27 Co 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 27 Co [Ar] 4s2 3d7 28 Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 28 Ni [Ar] 4s2 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 29 Cu [Ar] 4s1 3d10 30 Zn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 30 Zn [Ar] 4s2 3d10 K 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 19 20 Ca 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 22 Ti 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 23 V 24 [Ar]
- 6. Electron configuration 5 B 1s2 2s2 2p1 6 C 1s2 2s2 2p2 7 N 1s2 2s2 2p3 8 O 1s2 2s2 2p4 9 F 1s2 2s2 2p5 10 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 11 Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 12 Mg 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 13 Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 14 Si 1s2 15 P 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 16 S 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 17 CI 1s2 18 Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 19 K 1s2 20 Ca 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 22 Ti 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 23 V 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 24 Cr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 27 Co 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 28 Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 30 Zn Electron occupy 4s first then 3d Energy level and sublevels 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 2s2 2s2 2s2 2p6 2p6 2p6 4s energy level lower than 3d 3s2 3s2 3s2 4s 3d 3p 3p2 3s 18Ar – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 2p 2s 3p5 3p6 4s1 Electrons fill 4s first 3d 4s 1s 3p 19K – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3s 4s then 3d is fill 2p 3d 2s 4s 1s 21Sc 3p 3s – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 2p 2s 1s
- 7. d block Exception to d block elements 4s energy level lower than 3d 3d 4s 3p Electron configuration d block 3s 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 22 Ti V 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 24 Cr 1s2 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 27 Co Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 30 Zn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 4s energy level lower than 3d 2p 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 28 – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 23 21Sc 2s 1s 24Cr – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s13d5 24Cr – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d4 3d ✔ 4s 3p 3s ✗ Half fill energetically more stable 2p 2s 1s 29Cu 29Cu –1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 –1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 ✔ ✗ 4s 3p 3s Half fill energetically more stable 2p 2s 1s 3d
- 8. d block Exception to d block elements 4s energy level lower than 3d Noble gas notation Condensed configuration Electron configuration d block Positive Ions 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 21 Sc [Ar] 3d1 4s2 21 Sc3+ [Ar] 22 Ti 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 22 Ti [Ar] 3d2 4s2 22 Ti4+ [Ar] 23 V 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 23 V [Ar] 3d3 4s2 23 V3+ [Ar] 3d2 24 Cr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 24 Cr [Ar] 3d5 4s1 24 Cr3+ [Ar] 3d3 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 25 Mn [Ar] 3d5 4s2 25 Mn2+ [Ar] 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 26 Fe [Ar] 3d6 4s2 26 Fe2+ [Ar] 3d6 27 Co 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 27 Co [Ar] 3d7 4s2 27 Co2+ [Ar] 3d7 28 Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 28 Ni [Ar] 3d8 4s2 28 Ni2+ [Ar] 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 29 Cu [Ar] 3d10 4s1 29 Cu2+ [Ar] 3d9 30 Zn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 30 Zn [Ar] 3d10 4s2 30 Zn2+ [Ar] 3d10 Why electron fill 4s first? 1 Why electrons lost from 4s first 4s fill first – 4s2 4s – greater penetration/closer to nucleus 4s – lower in energy 3d 2 3d – filled 3d – higher energy 3 4 4s – higher in energy 4s – e lost first 4s 4s 4s – [Ar] 4s2 3d0 4S – FIRST IN – FIRST OUT 3d once filled 3d e attracted by increasing nuclear charge 3d orbitals lower in energy - shield 4s e 3d 20Ca Electrons lost from 4s then 3d 21Sc – [Ar] 4s2 3d1 3d 3d 21Sc – [Ar] 3d2 4s2 lose 2 electron 21Sc2+ – [Ar] 3d2 4s0
- 9. d block d block elements and ions 4s energy level lower than 3d Electron configuration d block Electron lost from 4s then 3d 21 Sc 22 Ti [Ar] 3d2 4s2 23 V Cr 25 Mn [Ar] 3d5 4s2 26 Fe [Ar] 3d6 4s2 27 Co 28 Ni [Ar] 3d8 4s2 29 Cu [Ar] 3d10 4s1 30 Zn [Ar] 3d10 4s2 3d 3d 4s 4s lose 2 e 3d 3d V3+ [Ar] 3d2 24 Cr3+ [Ar] 3d3 Mn2+ [Ar] 3d5 Fe2+ [Ar] 3d6 Co2+ [Ar] 3d7 28 Ni2+ [Ar] 3d8 29 Cu2+ [Ar] 3d9 30 [Ar] 3d7 4s2 lose 3 e [Ar] 26 4s Ti4+ 25 4s [Ar] 27 [Ar] 3d5 4s1 3d Sc3+ 23 3d 21 22 lose 3 e [Ar] 3d3 4s2 24 4s 4s [Ar] 3d1 4s2 Positive Ions Zn2+ [Ar] 3d10 Video on Ionization energy Click here to view IE Click here to view IE Click here to view IE
- 10. Why IE increases across the period? Why IE decreases down a group ? Ionization energy (IE) 1st Ionization energy Min energy to remove 1 mole e from 1 mole of element in gaseous state M(g) M+ (g) + e 2nd Ionization energy Min energy to remove 1 mole e from 1 mole of +1 ion to form +2 ion M+(g) M2+ (g) + e Ionization energy Factors affecting ionization energy 1 2 Distance from nucleus 3 Nuclear charge electron +3 +4 +5 +6 Effective Nuclear Charge (ENC)/(Zeff) • Screening effect/shielding • Effective nuclear charge (ENC)/(Zeff) (Zeff) = Nuclear charge (Z) – shielding effect • Net positive charge felt by valence electrons. Nuclear charge increase Distance near to nucleus – IE High Distance far away nucleus – IE Low Nuclear charge high (more proton) – IE High Nuclear charge low (less proton) – IE Low +6 Inner electron – shield valence e from positive charge Distance near Nuclear charge Higher electron/electron repulsion Strong electrostatic forces attraction bet nucleus and e Strong electrostatic forces attraction bet nucleus and e Easier valence e to leave IE – High IE – High IE – Low
- 11. IE drop from Be to B and N to O Ionization Energy- Period 2 Why IE increases across the period 2? IE increases across period 2 Nuclear charge increase Strong electrostatic forces attraction bet nucleus and e IE – High Li Be B C N O F Ne 2p 2s 1s 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p1 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p4 IE drop from Be to B IE drop from N to O Electron in p sublevel of B – further away from nucleus 2 electrons in same p orbital - Greater e/e repulsion Weak electrostatic force attraction between nucleus and electron Easier to remove e IE - Low IE - Low period 2 1s2 2s2 2p5 1s2 2s2 2p6
- 12. IE drop from Mg to AI and P to S Ionization Energy- Period 3 Why IE increases across the period 3? IE increases across period 3 Nuclear charge increase Strong electrostatic forces attraction bet nucleus and e IE – High Na Mg AI Si P S CI Ar 3p 3s [Ne] 3s1 [Ne] 3s2 [Ne] 3s2 3p1 [Ne] 3s2 3p2 IE drop from Mg to AI [Ne] 3s2 3p3 [Ne] 3s2 3p4 IE drop from P to S Electron in p sublevel of AI – further away from nucleus 2 electrons in same p orbital - Greater e/e repulsion Weak electrostatic force attraction between nucleus and electron Easier to remove e IE - Low IE - Low Period 3 [Ne] 3s2 3p5 [Ne] 3s2 3p6
- 13. IE for Period 2 and 3 Ionization Energy- Period 2 and 3 Why IE period 3 lower than 2? Period 3 – 3 shells/energy level period 2 Period 3 Valence e further from nucleus High shielding effect – more inner e Weaker electrostatic forces attraction bet nucleus and e IE – Lower period 2 Li Be B C N O F Ne 2p 2s 1s 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p1 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p4 1s2 2s2 2p5 1s2 2s2 2p6 Period 3 Na Mg AI Si P S [Ne] 3s2 3p1 [Ne] 3s2 3p2 [Ne] 3s2 3p3 [Ne] 3s2 3p4 CI Ar 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s [Ne] 3s1 [Ne] 3s2 [Ne] 3s2 3p5 [Ne] 3s2 3p6
- 14. IE for Ne and Ar Ionization Energy- Period 2 and 3 Why Ne and Ar have HIGH IE ? Full electron configuration, 2.8/2.8.8 neon argon Most energetically stable structure Difficult to lose electron IE – High period 2 Li Be B C N O F Ne 2p 2s 1s 1s2 2s1 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p1 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p4 1s2 2s2 2p5 1s2 2s2 2p6 Period 3 Na Mg AI Si P S [Ne] 3s2 3p1 [Ne] 3s2 3p2 [Ne] 3s2 3p3 [Ne] 3s2 3p4 CI Ar 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s [Ne] 3s1 [Ne] 3s2 [Ne] 3s2 3p5 [Ne] 3s2 3p6
- 15. Successive Ionization Energy (IE) for Mg ( 2.8.2) Successive Ionization Energy (IE) for magnesium 1st Ionization energy Min energy to remove 1 mole e from 1 mole of element in gaseous state M(g) M+(g) + e 2nd Ionization energy Min energy to remove 1 mole e from 1 mole of +1 ion to form +2 ion M+(g) M2+(g) + e Mg 3rd energy level 1st + 2nd electron 3s 2p 2nd energy level 3rd to 8th electron 9th to 10th electron 2s 1st energy level 11th to 12th electron 1s 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 1 Successive (IE) Mg (2.8.2) show • IE increase when e removed 2 Successive (IE) Mg (2.8.2) show • High jump in 2nd to 3rd IE • High jump in 10th to 11th IE 3 Successive (IE) Mg (2.8.2) show • Presence of 3 energy level • • Ion become increasingly more positive as more e are removed Electron-electron repulsion decrease as more e removed High jump in IE – presence of new inner shell 1st + 2nd e – outmost shell (3rd level) High electrostatic forces attraction Electron nearer to nucleus – High electrostatic forces attraction 3rd to 10th e – 2nd shell (2nd level) IE – High IE – High 11th to 12th e – innermost shell (1st level)
- 16. Successive Ionization Energy (IE) for Mg ( 2.8.2) Successive Ionization Energy (IE) for magnesium 1st Ionization energy Min energy to remove 1 mole e from 1 mole of element in gaseous state M(g) M+(g) + e 2nd Ionization energy Min energy to remove 1 mole e from 1 mole of +1 ion to form +2 ion M+(g) M2+(g) + e Mg 3rd energy level 1st + 2nd electron 3s 2p 2nd energy level 3rd to 8th electron 9th to 10th electron 2s 1st energy level 11th to 12th electron 1s 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 • Slow gradual increase in IE from 3rd to 10th e 4 Successive (IE) Mg (2.8.2) show • Presence of sublevel, 2s + 2p 5 Successive (IE) Mg (2.8.2) show • Succesive IE increasing Species form increase in proton/e ratio by losing e 6 Successive (IE) Mg (2.8.2) show • More difficult to lose e M(g) M+(g) + e M+ M2++ e 3rd to 8th e in 2p orbital 9th to 10th e inner 2s orbital Species becomes more positively charged M2+ M3++ e More energy need to lose e IE – High IE – High
- 17. IB Questions on IE s block elements • s orbitals partially fill 1 H He 5 1s2 n = 2 period 2 B [He] 2s2 2p1 6 1s1 2 p block elements • p orbital partially fill C [He] 2s2 2p2 7 N [He] 2s2 2p3 3 Li [He] 2s1 8 O [He] 2s2 2p4 4 Be [He] 2s2 9 F [He] 2s2 2p5 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 10 Ne [He] 2s2 2p6 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 14 Si [Ne] 3s2 3p2 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 17 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 18 Ar [Ne] 3s2 3p6 19 K 20 1 Ca [Ar] [Ar] 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d106p2 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p2 4s1 4s2 Identify position elements P, Q, R, S and T Electron configuration : P – 3s2 3p6 Q – 4s2 4p5 R – 3s2 3p6 4s2 S – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 T – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 Answer 2 Write electron configuration for X, Y and Z Element Group Period X 2 3 Y 15 2 Z 18 3 Answer Element Group Period Classification P 8/18 3 Noble gas Q 7/17 4 p block R 2 4 s block S 5 4 d block T 8/18 4 Noble gas X – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 Y – 1s2 2s2 2p3 Z – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3 Write electron structure for ions: • • • • • • O - 1s2 2s2 2p4 O2- V - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 V3+ Cu - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 Cu2+ - Answer Write electron structure for ions: • • • • • • O - 1s2 2s2 2p4 O2- -1s2 2s2 2p6 V - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 V 3+ - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s0 3d2 Cu - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 Cu 2+ - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s0 3d9
- 18. IB Questions on IE s block elements • s orbitals partially fill 1 H He 5 1s2 n = 2 period 2 B [He] 2s2 2p1 6 1s1 2 p block elements • p orbital partially fill C [He] 2s2 2p2 7 N [He] 2s2 2p3 3 Li [He] 2s1 8 O [He] 2s2 2p4 4 Be [He] 2s2 9 F [He] 2s2 2p5 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 10 Ne [He] 2s2 2p6 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 14 Si [Ne] 3s2 3p2 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 17 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 18 Ar [Ne] 3s2 3p6 19 20 4 K Ca [Ar] [Ar] 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d106p2 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p2 4s1 4s2 Successive IE of X is shown below Predict the group and arrange in order of increasing proton number Element 1st IE 2nd IE 3rd IE 4th IE P 746 1423 7689 10456 Q 920 1768 14578 21343 R 587 1134 4890 6453 S 542 1045 4121 5412 Answer All in Gp 2 – 2 valence electron Order increasing proton number Q, P, R, S ReasonGp 2, cause 1st and 2nd IE low Q – Highest IE (less shell/energy level) S – Lowest IE (more shell/energy level) 5 Successive IE of X is shown below Determine electron structure of X Successive IE (kJ/mol) 1314 3302 5436 Answer: X = 6 outermost electron, Gp 6, 2.6 Reason - 1st IE to 6th IE are low. 7436 10647 13768 71564 84736
- 19. IB Questions on IE 6 Successive IE of sodium is shown below: State full electron structure and explain how the successive IE are related to Its electron configuration. Answer: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Reason: • 1st electron easiest to remove, or 1st e in outmost shell/n= 3 energy level • Large increase in IE bet 1st and 2nd as 2nd electron located in inner level, n=2 • Next 8 electrons more difficult to remove as the ion now is positively charged • Large increase in IE between 9th and 10th , two innermost electron 10th/11th in n=1 (close to nucleus) 8 Successive IE for 4 element shown below a) Which element form charge +1 b) Predict C in periodic table c) Which element requires least amt energy to charge a gaseous ion which carry charge +3 d) Which element belong to same group? Element 1st IE 2nd IE 3rd IE 4th IE A 423 3021 4657 5867 B 754 1431 7741 10432 C 557 1814 2735 11843 D 597 1104 4942 6342 7 Successive IE of magnesium is shown below: Explain the large increase in 10th and 11th IE and the general trend of Increasing successive IE for Mg. Answer: Reason: • 10th electron comes from 2nd energy level, (n=2) and 11th electron from n=1 • Electron in 1st energy level (n=1) closer to nucleus/ not shielded by inner electrons • Successive IE high as it is more difficult to remove e from a positively charged ion. Answer: A – Gp 1, B - Gp 2, C – Gp 3, D – Gp 2 a) A- Gp 1 – lose 1 electron foming +1 b) C – Gp 3 c) Total IE = 1st IE + 2nd IE + 3rd IE A = 8101 B= 9926 C = 5106 D = 6643 C requires least – Gp 3 – lose 3 e easily d) B and D
