Week7 Quiz Help 2009[1]
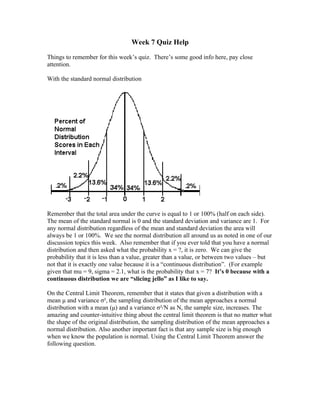
- 1. Week 7 Quiz Help Things to remember for this week’s quiz. There’s some good info here, pay close attention. With the standard normal distribution Remember that the total area under the curve is equal to 1 or 100% (half on each side). The mean of the standard normal is 0 and the standard deviation and variance are 1. For any normal distribution regardless of the mean and standard deviation the area will always be 1 or 100%. We see the normal distribution all around us as noted in one of our discussion topics this week. Also remember that if you ever told that you have a normal distribution and then asked what the probability x = ?, it is zero. We can give the probability that it is less than a value, greater than a value, or between two values – but not that it is exactly one value because it is a “continuous distribution”. (For example given that mu = 9, sigma = 2.1, what is the probability that x = 7? It’s 0 because with a continuous distribution we are “slicing jello” as I like to say. On the Central Limit Theorem, remember that it states that given a distribution with a mean μ and variance σ², the sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution with a mean (μ) and a variance σ²/N as N, the sample size, increases. The amazing and counter-intuitive thing about the central limit theorem is that no matter what the shape of the original distribution, the sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution. Also another important fact is that any sample size is big enough when we know the population is normal. Using the Central Limit Theorem answer the following question.
- 2. Assuming you have a normal distribution for your population and you take 64 samples of size 25 each. Calculate the standard deviation of the sample means if the population’s variance is 16. Since the population is normally distributed with a variance of 16, then the sample means have a variance equal to 16/25 according to the Central Limit Theorem. Hence their standard deviation will be SQRT(16/25) = 4/5 = .800 Be able to use the normal distribution to solve problems. Examples Bob scored a 190 on his entrance exam, where the average was 165 and the standard deviation was 12. Where does he stand in relation to the rest of his class? He scored in the “top 2 %”, see excel attachment. In a normal distribution with mu = 35 and sigma = 6 what is the z score for a value of 41? Z= +1 see excel attachment In a normal distribution with mu = 35 and sigma = 6 what number corresponds to z = -2? 23, see excel attachment We have an area of .4840. What z-score corresponds to this area?
- 3. Using the Standard Normal Table in your book, or the one on the attached excel you can see it is a z score of -0.04 Find P(80 < x < 86) when mu = 82 and sigma = 4. Write your steps in probability notation. I did this in excel (see attachment – fourth tab), but I still need to show my work: The z-score corresponding to x = 86 is z = (86-82)/4 = 4/4 = 1.0. The area corresponding to z = 1.0 is .8413 The z-score corresponding to x = 80 is (80 - 82)/ 4 = -2/4 = -0.5. The area corresponding to z = -0.5 is .3086. Thus, P(80 < x < 86) = P(-0.5 < z < 1.0) = P(z < 1.0) - P(z < -0.5) = 0.8413 – 0.3086 = 0.5327 (my excel calculated it to be 0.5328 so I feel good about it) My excel file will be in a separate post.
- 4. Interpret a 90% confidence interval of (63.3, 83.4). You should note that there here is a 90% probability that the interval (63.3 to 83.4) contains µ, the true population mean. What is the critical value that corresponds to a confidence level of 96% 100 – 96 = 4 Divide 4 by 2 (tails) and get 2 Add 2 to the original 96% and get 98% and find the critical value (z-score that corresponds to . 9800 which is 2.05 (closest to it) Compute the population mean margin of error for a 90% confidence interval when sigma is 7 and the sample size is 81. E = z * sigma / sqrt(n) = 1.645 * 7 / sqrt(81) = 1.279 (remember +/-)
- 5. A Military entrance exam has a mean of 120 and a standard deviation of 9. We want to be 95% certain that we are within 6 points of the true mean. Determine the sample size. n = ( z * sigma / error ) ^ 2 = (1.96*9/6)^2 = 2.94^2 = 8.6436. Round up to 9. A researcher wants to get an estimate of the true mean performance measure of its product. It randomly samples 180 of its machines. The mean performance measure was 900 with a standard deviation of 60. Find a 95% confidence interval for the true mean performance measure of the machines. The population standard deviation is unknown and the sample size is 180. Thus, since the sample size is greater than 30, this confidence interval will use a z-value. For a 95%
- 6. confidence interval, the z-value = 1.96. Sample mean = 900 and sample standard deviation = 60. Population mean = 900 +/- 1.96 * 60/sqrt(180) = 900 +/- 8.765. 891.235 and 908.765 A researcher wants to get an estimate of the true mean performance measure of its product. The researcher needs to be within 15 of the true mean. The researcher estimates the true population standard deviation is around 30. If the confidence level is 95%, find the required sample size in order to meet the desired accuracy. For a 95% confidence level, the z-value = 1.96. The formula for sample size is n = ( z-value * standard deviation / error ) ^ 2 = ( 1.96 * 30/ 15) ^ 2 = ( 3.92 ) ^ 2 = 15.3664. Thus, the researcher must sample at least 16 to obtain the desired accuracy.
- 7. A researcher wants to estimate the mean cost to develop a product. The researcher tests 18 cases and finds the mean cost to be $3000 with a standard deviation of $400. Find a 95% confidence interval for the true mean cost to develop this product. The population standard deviation is unknown and the sample size is 18. Thus, since the population standard deviation is unknown AND the sample is less than 30, we must use the t- value for this confidence interval. For a 95% confidence interval and degrees of freedom = 17 (from 18-1), the t-value = 2.110. Sample mean = 3000 and sample standard deviation = 400. Population mean = 3000 +/- 2.110 * 400/sqrt(18) = 3000 +/- 198.93. So our bounds are 2801.07 and 3198.93
- 8. A researcher wants to estimate what proportion of failures that are due to poor workmanship. The researcher randomly samples 50 failures and finds 18 are due to poor workmanship. Using a 95% confidence interval, estimate the true proportion of poor workmanship for all failures. For a 95% confidence level, the z-value is 1.96. The sample proportion = 18/50 = 0.36, thus p hat = 0.36 and 1-p hat = 0.64 . The sample size = 50. The population proportion is between 0.36 +/- 1.96 * sqrt ( 0.36 * 0.64 / 50 ) = 0.36 +/- .13 So the bounds are .23 and .49 Excel Spreadsheets Separately
- 9. Normal Distribution Me a n S tde v 165 12 P (X<x) x x P (X>x) x1 P (x 1 <X<x 2 ) x2 190 0.0186 Inve rse Ca lcula tions P (<x) x x P (>x) S ymme tric Inte rva ls x1 P (x 1 <X<x 2 ) x2 R e me mbe r the gre e n a re a s re d le tte ring is the re sulting It is importa nt to note tha t th to show you wha t pa rt of the
