Electronic renal dialysis patient management network - vision document
- 1. Georgia State University Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Vision Version 3.0
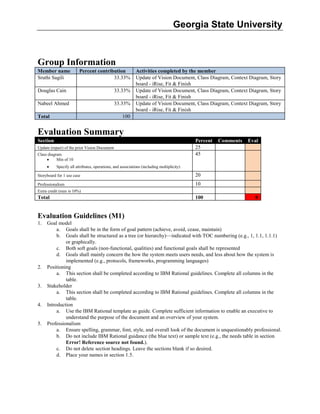
- 2. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 2 Revision History Date Version Description Author <28/Jan/13> <1.0> Creating a new electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Sruthi Sagili, Douglas Cain, Nabeel Ahmed <20/Feb/13> <2.0> Creating a new electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Sruthi Sagili, Douglas Cain, Nabeel Ahmed <2/Mar/13> <3.0> Creating a new electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Sruthi Sagili, Douglas Cain, Nabeel Ahmed
- 3. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction 5 1.1 Purpose 5 1.2 Scope 5 1.3 Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations 5 1.4 References 5 1.5 Analyst Certifications 5 1.6 Overview 5 2. Positioning 6 2.1 Business Opportunity 6 2.2 Problem Statement 6 2.3 Product Position Statement 6 3. Stakeholder and User Descriptions 7 3.1 Stakeholder Summary 7 3.2 User Summary 7 3.3 User Environment 8 4. Product Overview 9 4.1 Assumptions and Dependencies 9 4.2 Licensing and Installation 9 5. Goal Model 9 6. Constraints 10 7. Precedence and Priority 10 8. Overall Diagrams 11 8.1 StoryBoard - Staff dashboard 11 8.2 Business Process Modeling 15 9. Use-case Models 16 9.1 Use-case Diagram 16 9.2 Goal Use-case Traceability 17 9.3 UseCase_1_Create Virtual Chart 17 9.4 UseCase_2_Enter pre-assessment data 18 9.5 UseCase_3_Verify e-flowsheet 18 9.6 UseCase_4_Administer Dialysis 19 9.7 UseCase_5_Enter post-assessment data 20 9.8 UseCase_6_Prescribe drugs 20 9.9 UseCase_7_Triage Patient 21 9.10 UseCase_8_Discharge patient 21 9.11 UseCase_9_Bill Patient 22 10. Class Model 23 11. Context Model 24
- 4. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 4 12. Story Board using iRise 25
- 5. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 5 Vision 1. Introduction The purpose of this document is to collect, define, and analyze high-level needs and features of the electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management System. It focuses on the capabilities needed by the stakeholders and the target users, and why these needs exist. The details of how the electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management System fulfills these needs are detailed in the use-case and supplementary specifications. 1.1 Purpose The purpose of this document is to accurately document goals and requirements for the electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management network as expressed by various stakeholders for creation of a virtual chart. Relationships and expectations will be drawn from these goals and requirements and used as the foundation for creating the electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management network. Stakeholders, users and use cases will define exactly how the system is used. 1.2 Scope This document will outline in detail how a virtual chart will be created, its primary uses and how the stakeholders and users will interface with the system. 1.3 Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations HIPAA - The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act protect the privacy of an individual health information and also governs how the health care providers collect, use, maintain and misuse the protected health information HIS- Hospital Information System are designed to manage all the medical, financial, administrative and legal aspects of health providers DU- Dialysis Unit which includes the dialysis ward and its staff CMS- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is an agency within the US Department of Health & Human Services who are responsible for administration of federal health care programs. ARRA- American Recovery & Reinvestment Act provides investments needed to increase economic efficiency by technological advances in science and health HITECH - The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act was created to stimulate the adoption of electronic health records and supporting technology in the US GUI - Graphical user Interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic images using icons and images rather than text commands HIN - Hospital Identification Number, which is a unique number given to the each patient by the hospital. 1.4 References http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphical_user_interface http://hipaa.stanford.edu/ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/ARRA-American-Recovery-and-Reinvestment-Act-of-2009 http://searchhealthit.techtarget.com/definition/HITECH-Act http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hospital_information_system http://searchhealthit.techtarget.com/definition/Centers-for-Medicare-Medicaid-Services-CMS 1.5 Analyst Certifications We, Douglas Cain, Sruthi Sagili and Nabeel Ahmed analyzed these documents and believe that they: Comply with current UML syntax and best practices Are internally consistent Meet the stakeholder needs as we understand them 1.6 Overview The remaining sections of this document will outline the positioning statement, product positioning,
- 6. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 6 stakeholder and user descriptions, user summary, user environment, key stakeholder and user needs, product overview, the goal model, constraints, precedence and priority, the use case and design model and stakeholder requests in increasing order of specificity. 2. Positioning 2.1 Business Opportunity The opportunity to move outpatient dialysis centers onto a competing and complementary platform as the core HIS. The system will significantly bridge logistical divides between auxiliary systems. Safety and privacy are the main concerns of the health organization. Physicians, nurses, nutritionists and technicians will only be allowed to see patient data in relation to assigned roles. This virtual chart addresses lack of redundancy and immediately provides a comprehensive solution for erroneous flow sheets. 2.2 Problem Statement The problem of A single non-redundant paper chart updated by all caregivers Affects Hospitals, physicians, nurses, technicians, patients the impact of which is The loss of patient records due to theft or destruction. Medical Codes and medicines entered erroneously and a lack of security of the patient data between physicians, nurses, nutritionists and technicians a successful solution would be Provide online access to all caregivers. Facilitation of patient care, safety and privacy. The new system interfaces with main hospital HIS and various auxiliary systems 2.3 Product Position Statement For Outpatient Dialysis Unit Who Need an online virtual chart for caregiver staff for the patient's safety and privacy The Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Uses a virtual chart over the enterprise intranet That Maintains a virtual chart for vitals, pre- and post-assessments, labs, orders and results Unlike The current paper based system that lacks privacy, security and back-up Our product Provide online access to a comprehensive virtual chart for inserts and updates of patient data real time. Our product alleviates the data entry mistakes, unreadable manuscript and auto corrects common codes, procedures and medicines entered. Caregivers are assigned to groups to enforce HIPPA regulations and company policies. It interfaces with the Billing system and HIS.
- 7. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 7 3. Stakeholder and User Descriptions 3.1 Stakeholder Summary Name Description Responsibilities Care-A-Lot The company overseeing the entire DU They will ensure that the new system meets the main goals of the DU and complies with its requirements Hospital Management The management of the hospital overseeing the entire facility Will ensure that the new system complies with hospital standards and requirements Other providers Health care providers Healthcare providers responsible for the patients care, such as hospitals, clinics, pharmacies etc who compete with the current DU. Federal Regulators The government bodies/individuals responsible for enforcing standards, such as HIPPA They will be keen to make sure that the new system complies with regulatory practices, such as HIPPAA regulations, ARRA & HITECH federal standards of patient safety, care, and confidentiality Patients The individuals receiving treatment in the DU They are a main beneficiary, as the system will allow providers to deliver optimal and confidential patient care CMS (Center for Medicaid services) Government entity for uninsured and the elderly patients The companies reimburse care providers for uninsured services 3.2 User Summary Name Description Responsibilities Stakeholder Physicians They are the primary users, who manage and update the patient's records in the system Enter the patient information like diagnosis, drug administration, etc. into the new system Update any new additions or changes to the patient's records. Check for any discrepancies in the patient records Operational Stakeholder Nurses They are the primary users, who administer the drugs to the patient based on physician's instruction updated in the system Access the system to monitor the drug administration and test results. Update any new additions or changes to the patient's records. Check for any discrepancies in the patient records Operational Stakeholders
- 8. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 8 Administrators They are the primary users, who manage all the technical problems in the system Manage the technical problems in the new system Set and manage the access privileges to the system Manage the security and maintenance of the system Interfacing Stakeholder Nutritionists They are the primary users, who recommend the diet plans based on the current health conditions of the patient Update the recommended diet plan of the patient into the new system Operational stakeholders Technicians They are the secondary users, who manage the maintenance of the dialysis machines and handle the lab equipment. Update the lab results into the new system Send an alert to the assigned Physician or Nurse in case of any discrepancies in the lab results Check the proper working of the lab equipment and the dialysis machines Operational stakeholders Developers They perform the coding for the application software Understand the Functional Requirements in the System design and build the application software based on it Testing the application software to check the proper working of the system Surrogate stakeholders Project Managers They manage the resources, schedule, cost and scope of the project Manage the schedule, cost & scope of the project Allocate the resources Track all the change requests and approvals Surrogates stakeholders Business Analysts They convert the High level Business needs to the Product or Functional Requirements Understand the requirements of the DU and convert them into the functional requirements that can be understood and converted into working software by the developers. Track any high level changes to the system Surrogate stakeholders 3.3 User Environment The current system follows paper-based patient records. It is handled by lot of staff and there is a probability of the patient chart getting lost or misplaced or misused. Since all the charts are placed in the open cart, there is no security for these charts and any one can access them. There is also a frequent problem of patient records being
- 9. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 9 stolen by the staff or by an intruder. To overcome all these problems, the new Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management system keeps track of the patient records by maintaining a virtual copy of the records rather than a paper based copy. The system maintains a standard format for the records that comply with the HIPAA standards and regulations. This system allows access to the authorized personnel to update or make any changes to the patient records. The new system interfaces with the current billing system and the HIS so that changes made to any patient records will be reflected in billing system and HIS. 4. Product Overview Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management system keeps track of all the patient records in the DU. This system allows the physicians , nurses, Nutritionists, lab technicians to record and update the health records of the patient. Following are some of the important functions performed by the system: The system allows the assigned physician to update or make changes to the patient information The system has a user-friendly GUI, which is self-descriptive enough to be understood by the non-technical staff The patient records will contain all the information of the patient like medical history, drug administration, lab tests and their results and other basic information like allergies, blood group, weight, height etc The Physician can track the progress of the patient The system interfaces with the billing system and the HIS. Any changes to the patient's records will be reflected in the system that are interfaced with it The access privileges for the system are set for the DU staff so that only assigned physician can access and modify a patient's information The new system replaces all the existing paper based patient records The emergency alerts or lab results alert can be sent by any nurse or the lab technician to the patient's assigned physician 4.1 Assumptions and Dependencies N/A 4.2 Licensing and Installation N/A 5. Goal Model 5.1 The system shall ensure optimal patient care 5.2 Maintain: The system features and functions shall always comply with the most current federal HIPPA regulations 5.3 The system shall have a user-friendly GUI 5.4 Maintain: The system shall always maintain back-ups of all patient records 5.5 Convert all the existing paper-based patient charts to patient virtual charts 5.5.1 Avoid: The system shall never require paper-based records 5.6 The system shall ensure patient confidentiality 5.6.1 Avoid: The system shall never allow access to an unauthorized individual 5.6.2 Cease: If the system is inactive for a certain period of time on any machine, it should automatically log off the user account
- 10. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 10 5.7 The system should be able to accept access privilege changes 5.7.1 Maintain: They system shall allow the administrators to change access privileges for staff/users even after initial initiation and launch. 5.8 The system shall allow authorized users to create and update virtual charts. 5.8.1 Achieve: WHEN the patient is a reoccurring patient, THEN the system shall update the virtual chart for the patient 5.8.2 Achieve: WHEN the patient is a new incoming patient, THEN the system shall create a virtual chart for the patient 5.8.3 Achieve: WHEN a new or reoccurring patient arrives, THEN the system shall create a e-flowsheet within the virtual chart of the patient 5.9 Each e-flowsheet should contain the visit information of a patient 5.9.1 Achieve: WHEN an pre-assessment has been conducted, THEN a nurse can update the pre- assessment section of the e-flowsheet 5.9.2 Achieve: WHEN an post-assessment has been conducted, THEN a nurse can update the post- assessment section of the e-flowsheet 5.10 The system shall allow authorized users to have online access to patient information 5.10.1 Achieve: WHEN the e-flowsheet verification has been completed, THEN a physician can accept/reject patient dialysis treatment 5.10.2 Achieve: WHEN the post-assessment of the patient has been completed, THEN a physician can prescribe drugs for the patient 5.10.3 Achieve: WHEN the dialysis treatment has been started, THEN a technician can update the dialysis status in the e-flowsheet of the patient 5.11 The system shall maintain an up-to-date list of dischargeable patients 5.11.1 Maintain: The system shall always allow immediate discharge of patients by clinical staff. 5.12 The system shall interface with the current Hospital Information Systems (HIS) 5.12.1 Achieve: When a patient is transferred to the main hospital, THEN the system shall transfer the virtual chart of the patient to the main hospital 5.12.2 Achieve: When a patient is transferred from the main hospital, THEN the system shall receive the virtual chart of the patient from the main hospital 5.13 The system shall interface with the hospital Billing system 5.13.1 Achieve: WHEN changes are made to diagnosis or services of the patient, THEN the system shall update the changes in the Billing system 6. Constraints N/A 7. Precedence and Priority N/A
- 11. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 11 8. Overall Diagrams 8.1 StoryBoard - Staff dashboard
- 12. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 12
- 13. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 13
- 14. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 14
- 15. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 15 8.2 Business Process Modeling
- 16. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 16 9. Use-case Models 9.1 Use-case Diagram
- 17. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 17 9.2 Goal Use-case Traceability Use Case Goal 5.8 5.9.1 5.9.2 5.10.1 5.10.3 5.11.1 5.12 5.13 5.10.2 Create Virtual Chart Enter pre- assessment data Verify e-flowsheet Enter post- assessment data Prescribe Drugs Triage Patient Discharge patient Bill patient Administer Dialysis 9.3 UseCase_1_Create Virtual Chart Goal: The system shall allow authorized users to create and update virtual charts. Actors: Clinical Staff Brief Description: This use-case describes creating a virtual chart for a new patient Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: The referred patient is a new patient and clinical staff is logged into the system. Post-conditions: An online virtual chart is created for new patients to record longitudinal and visit-specific data. Basic Flow of Events: Clinical Staff System Response 1. Authenticated staff member clicks on virtual chart tab 2. System displays empty virtual chart containing new patient fields 3. Staff records patient longitudinal data in the fields 4. Staff clicks on “Save” button 5. System saves virtual chart in the database 6. System displays message "virtual chart successfully created" Alternatives: a) System recognizes erroneous data format 5. System re-displays form along with an error message
- 18. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 18 and appropriate field format (back to step 3 in main flow) 9.4 UseCase_2_Enter pre-assessment data Goal: WHEN an pre-assessment has been conducted, THEN a nurse can update the pre-assessment section of the e- flowsheet Actors: Nurse Brief Description: This use-case describes patient pre-assessment data being recorded in the e-flowsheet Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized nurse is logged into the system and virtual chart has been created for the patient Post-conditions: Pre-assessment data is recorded in the electronic flowsheet Basic Flow of Events: Nurse System Response 1. Nurse clicks on “create e-flowsheet” tab 2. System creates a new e-flowsheet form within virtual chart 3. System displays the pre-assessment form having fields such as blood pressure, blood type, height and weight 4. Nurse records pre-assessment data in the pre assessment form within the e-flowsheet 5. Nurse clicks on “Save” button 6. System saves e-flowsheet in the database 7. System displays message "patient data saved" and displays the patient data for confirmation 8. Nurse verifies patient data and clicks "submit" 9. System displays message "e-flowsheet successfully created" Alternatives: a) System recognizes erroneous data format 6. System re-displays the form along with an error message and appropriate field format (back to step 4 in main flow) 9.5 UseCase_3_Verify e-flowsheet Goal: WHEN the e-flowsheet verification has been completed, THEN a physician can accept/reject patient dialysis treatment Actors: Physician Brief Description: This use-case describes the patient e-flowsheet verification process by the physician Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized physician is logged into the system and pre-assessment data in the e-flow sheet has been entered for the patient Post-conditions: Physician has given approval or rejection of the dialysis process for the current patient Basic Flow of Events: Physician System Response 1. Physician selects the "verify e-flowsheet" tab 2. System displays the pending patient e-flow sheets for approval 3. User selects the current patient's e-flow sheet 4. System displays the content of the selected e-flow
- 19. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 19 sheet 5. Physician reviews the e-flow sheet data for any medical issues 6. Physician clicks on the "Approve" button 7. System updates the approval status of the e-flow sheet in the database 8. System displays the message " Patient is approved for Dialysis" Alternatives: a) When medical issues are found in the patient e- flow sheet 6. Physician selects the "Reject" button 7. System updates the approval status in the e-flow sheet into the database 8. System displays the message " Patient is rejected for Dialysis" 9.6 UseCase_4_Administer Dialysis Goal: WHEN the dialysis treatment has been started, THEN a technician can update the dialysis status in the e- flowsheet of the patient Actors: Technician Brief Description: This use-case describes the dialysis administration and status update process Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized technician is logged into the system, and e-flow sheet is verified and approved by the physician Post-conditions: Technician has completed the dialysis administration and status update process for the current patient Basic Flow of Events: Technician System Response 1. Technician clicks on the "Pending Patients" tab 2. System displays the list of patients waiting for the dialysis administration 3. User selects the current patient e-flow sheet from the list 4. Technician clicks on "Administer Dialysis" button 5. System updates the patient dialysis status as" in progress" in the e-flowsheet 6. System displays a message " Dialysis Status updated to in progress" 7. When dialysis administration is complete, Technician clicks on "End Dialysis" button 8. System updates the patient dialysis status as" complete" in the e-flowsheet 9. System displays a message " Dialysis Status updated to complete" Alternatives: a) When dialysis administration is cancelled 7. Technician clicks on the "Cancel" button 8. System updates the patient dialysis status as "cancelled" in the e-flowsheet 9. System displays a message "Dialysis Status updated to cancelled"
- 20. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 20 9.7 UseCase_5_Enter post-assessment data Goal: WHEN an post-assessment has been conducted, THEN a nurse can update the post-assessment section of the e-flowsheet Actors: Nurse Brief Description: This use-case describes the recording of post-assessment data in the e-flowsheet Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized Nurse is logged into the system, and dialysis administration is complete for the current patient Post-conditions: Nurse has completed the post-assessment form within the e-flowsheet for the current patient Basic Flow of Events: Nurse System Response 1. .Nurse clicks on "Post-assessment data" option 2. System displays the pending post-assessment list 3. Nurse selects the current patient e-flowsheet from the post-assessment list 4. System displays the post assessment form with blank fields to fill the patient data 5. Nurse records the post assessment data into the respective fields of the post assessment form within the e-flowsheet. 6. Nurse selects the " Submit" button 7. System updates the e-flowsheet in the database 8. System displays the message "post assessment data updated successfully into the e-flowsheet" Alternatives: a) System recognizes erroneous data format 7. System re-displays form along with an error message and appropriate field format (back to step 5 in main flow) 9.8 UseCase_6_Prescribe drugs Goal: The system shall always allow immediate discharge of patients by clinical staff. Actors: Physician Brief Description: This use-case describes the patient drug prescription process Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized Physician is logged into the system and post-assessment process has been completed. Post-conditions: The drug prescription for the current patient is updated in the e-flowsheet Basic Flow of Events: Physician System Response 1. Physician selects the "Formulary" tab 2. System displays a list of patients awaiting drug prescription 3. Physician checks the post assessment form 4. Physician clicks on " Assign Formulary" button 5. Physician selects the current patient from the list 6. The system displays the post assessment form for the current patient 7. Physician checks the post assessment form 8. Physician clicks on " Assign Formulary" button 9. The system provides a list of recommended drugs 10. Physician selects the necessary drugs from the list 11. Physician selects "Confirm" button 12. The system updates the e-flowsheet in the database 13. The system displays a message "e-flowsheet
- 21. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 21 updated successfully" Alternatives: a) When the necessary drugs are not listed in the recommended list 10. The Physician selects the "Other" option at the end of the recommended list 13. The system displays a search window, which allows to search based on name, brand and class 11. The Physician inputs the values into the search fields 12. The Physician clicks on the " Search" button 14. The system searches for the drug 15. The system displays the matching entries satisfying the search criteria 16. The Physicians selects the valid drug from the matched entries 17. The Physician clicks on the "Add" button 18. The system adds the selected drug to the recommended list 9.9 UseCase_7_Triage Patient Goal: The system shall interface with the current Hospital Information Systems (HIS) Actors: Clinical staff Brief Description: This use-case describes the triage process for the patients who have been rejected for dialysis by the physician Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized clinical staff member is logged into the system, and dialysis administration has been rejected for the current patient by the physician Post-conditions: The current patient has been transferred to the main hospital based on the physician recommendations Basic Flow of Events: Clinical staff System Response 1. Staff member selects the “Transfer patient” tab 2. System displays a transfer form to be completed 3. Staff member enters important information, including patient identifying information and reason(s) for transfer 4. Staff member clicks on “Transfer” button to confirm the transfer 5. System displays message “patient information transferred successfully.” Alternatives: Transfer action fails 6. System displays message “transfer failed – please attempt transfer again” (back to step 5) 9.10 UseCase_8_Discharge patient Goal: The system shall always allow immediate discharge of patients by clinical staff. Actors: Clinical staff
- 22. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 22 Brief Description: This use-case describes the discharge of the patient from the Dialysis unit Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized Clinical staff is logged into the system, and the patient treatment and check-up has ended Post-conditions: The current patient is checked out of the Dialysis unit Basic Flow of Events: Clinical staff System Response 1. The staff selects the "Discharge" tab 2. System displays a list of patients awaiting discharge 3. The staff selects the current patient to be discharged from the list 4. The staff clicks on "Discharge" to confirm the discharge of the patient 5. The system updates the time of discharge into the e-flowsheet in the database 6. The system displays the message "Patient discharged from the clinic" Alternatives: a) When the current patient is not present in the Dischargeable patient's list 3. The Staff clicks on the "Add" button below the dischargeable patient's list to manually add the patient into the list 4. The system displays an “add” dialog box with fields to enter the patient information 5. The staff enters the current patient information in the respective fields 6. The staff selects the "Confirm" button 7. The System adds the patient to the “dischargeable patients” list(back to step 5 in main flow) 9.11 UseCase_9_Bill Patient Goal: The system shall interface with the hospital Billing system Actors: Coder Brief Description: This use-case describes billing the patient for diagnosis and services undergone Type: User-goal Pre-conditions: Authorized coder should be logged into the system and the patient should be discharged from the dialysis unit Post-conditions: The invoice is created for the current patient Basic Flow of Events: Coder System Response 1. The coder selects the "Billing" tab 2. System displays the list of patients waiting for their invoice 3. The coder selects the current patient e-flowsheet from the list 4. The coder clicks on " OK" button 5. The system displays the services and diagnosis of the patient along with the recommended list of codes for each service 6. The coder selects the appropriate code for the services 7. The system generates an invoice for the services 8. The system stores the invoice into the database
- 23. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 23 7. The coder clicks on the "Confirm" button 9. The system displays the message "invoice generated and saved into the database successfully" Alternatives: a) When the necessary codes are not listed in the recommended list 6. The Coder selects the "Add" button, which is next to the recommended list 7. The system displays the “add” dialog box and the respective fields to add the code. 8. The Coder inputs the values into the respective fields 9. The Coder clicks on the "Confirm" button 10. The system adds the code into the recommended list 11. The system displays the message " Code is added to the list successfully" (back to step 7 in main flow) 10. Class Model
- 24. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 24 11. Context Model
- 25. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 25 12. Story Board using iRise
- 26. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 26
- 27. Electronic Renal Dialysis Patient Management Network Version: 3.0 Vision Date: <02/Mar/13> <document identifier> Confidential Georgia State University, 2013 Page 27