Cellular-Respiration-student-copy...pptx
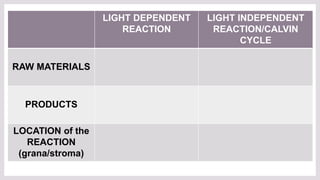
- 1. LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION LIGHT INDEPENDENT REACTION/CALVIN CYCLE RAW MATERIALS PRODUCTS LOCATION of the REACTION (grana/stroma)
- 2. How do plants and other organisms used up the chemical energy stored in sugar?
- 4. Cellular Respiration Occurs in the mitochondrion The outer membrane encloses the mitochondrion The inner membrane folds back and forth across the interior is known as cristae
- 5. • The function of the mitochondrion may be compared to a • . Both are machines that release energy from fuel. • In the mitochondrion, the energy lost as heat is less. Here, the combination of sugar with oxygen is slow and occurs in several steps. • The sugar molecules breaks down little by little and the energy released is trapped at once in the ATP molecule. Thus, not much energy is lost or jeepney engine
- 6. Three major reactions of the complex process of respiration • 1. Glycolysis ( occurs in the cytoplasm) • 2. Krebs Cycle ( occurs in the liquid part of the mitochondrion) • 3. Electron flow along the respiratory chain (occurs in the
- 8. Glycolysis • Takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. • In a series of reactions, glucose is broken down into pyruvate (C3- a molecule with Carbon atoms) • Energy is released and trapped in 2 molecules of ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation • NAD+ is reduced to NADH which carries the electrons to electron transport chain at the cristae
- 9. •Pyruvate moves into the mitochondrion •Glycolysis occurs whether O2 is present or not.
- 10. Krebs Cycle – by Hans Krebs in 1930
- 11. Krebs Cycle •Takes place in the liquid part of the mitochondrion. •Acetyl coenzyme A ( acetyl coA) which is formed from pyruvate enters the cycle and performs a series of reactions to produce 2 molecules of CO2 •Carbon dioxide leaves the cell, and 2 molecules of ATP is also released again by substrate level-phosphorylation
- 12. Krebs Cycle • A pair of electrons is transferred from the remaining two-carbon fragment to NAD+ to form NADH and the FAD to FADH2 • NADH and FADH the Hydrogen carrier molecules passes into the cristae where the third major reactions occurs. • Each cycle produces 2CO2, 2ATP, 3NADH, and FADH2 (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) by substrate-level phosphorylation, per acetyl CoA.
- 13. Electron flow along the respiratory chain • FADH and NADH ( hydrogen carrier molecules) breaks down into hydrogen and electrons. • The electrons flow from one electron acceptor to another. • The movement of electrons along the electron transport chain does contribute to chemiosmosis (coupling of the redox reactions of the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis) and ATP synthesis. • As the electrons flow, energy is released forming a total of 34 ATP molecules. • The last electron acceptor is oxygen which finally forms water with hydrogen
- 15. Differences between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration • Photosynthesis utilizes sunlight to produce food molecules. • Cellular respiration utilizes glucose molecules to obtain energy- storing ATP molecules. • Photosynthesis takes place in plant leaves containing the chlorophyll pigment. • Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell. • Photosynthesis uses water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to create glucose molecules, and releases oxygen as a by-product. • Cellular respiration uses glucose molecules and oxygen to produce ATP molecules, water and carbon dioxide as the by- product.
- 16. • Photosynthesis takes place only when there is sunlight. • Cellular respiration always occurs. • Photosynthesis involves conversion of one type of energy into another: light energy into chemical energy. • Cellular respiration involves using that chemical energy and breaking it down to release energy. • Photosynthesis takes place in two stages of light reactions and dark reactions. • Cellular respiration involves aerobic and anaerobic respiration. • Photosynthesis occurs only in plants and some bacteria. • Cellular respiration takes place in all types of living organisms.
- 17. Equation of Aerobic Cellular Respiration Glucose + Oxygen ➜ Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy Released (ATP) C6H12O6 + 6O2 ➜ 6H2O + 6CO2 + 38 ATP
- 18. Difference between a Chloroplast and Mitochondrion
- 19. Assessment: 1. Name the starting materials of respiration 2. Which major reactions uses each of these starting materials? 3. Name the end products of respiration 4. Which major reactions forms each of these end products? 5. In which reaction are ATP molecules produced? 6. Which reaction produces the greatest number of
- 20. The energy source of the Cell • The ATP molecule is the energy source of the cell consisting of Adenosine and three Phosphates • Energy is stored in food molecules such as sugars, starch and fats. • Everytime the cell needs energy, it “withdraws” the energy from the food molecules through the process of respiration done in the mitochondrion. • The process of respiration which produces 38 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule can supply the cell with 252 kilocalories of energy
- 21. Our Body needs • Those who want to lose weight are advised to watch their calories. Calories is a unit of heat. It is a measure of the amount of energy in food. • The main source of energy for man are carbohydrates and fats. • Excess food is stored as fat. • Some people who do not have anything to eat use the stored energy in their bodies such as the liver , muscles and various organs. • When all the stored energy is used up the body starts breaking down the proteins of the muscles which is the last food reserve.
- 22. • Respiration is the process through which energy is released by breaking down glucose in the body. • The energy produced is used by the body for various purposes including working the muscles, keeping body temperature constant, allowing chemical reactions to take place, sending messages throughout the body, etc. • There are two types of respiration that happen within all living things: Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration.
- 23. • Aerobic respiration is the process of breaking down glucose using oxygen. • The cells use glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water and energy. • This energy produced is then reserved until required by the body.
- 24. • The released energy is used to make a special energy molecule called Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is where the energy is stored for use later by the body. • The process is pretty much the same for almost all living things but is reversed in plants because in plants it uses carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and
- 25. Anaerobic Respiration • At rest, our body works with aerobic respiration, but there are many times where oxygen is not available and yet the cell needs to survive. • In this case the cell performs Anaerobic Respiration( breaking down glucose without Oxygen) • In humans, this event occurs when a person performs extraneous exercises. • When doing an intense workout, the lungs and heart cannot pump blood and oxygen fast enough to keep up with the requirements of the cells. When this happens, the body cannot simply stop making energy.
- 26. In such an event during anaerobic respiration: • The body breakdown glucose by using catalysts such as nitrate. • These release a by product of lactic acid and energy. • glucose lactic acid + energy • The lactic acid causes the muscles to tire quickly producing fatigue in the body and can even cause cramps. Hence, the vigorous exercise cannot be maintained for more than a few minutes. nitrate
- 27. • The body needs to consume more oxygen in order to breakdown the lactic acid inside the body; this is known as oxygen debt. • In plants, the process is a little different. When glucose is broken down in plants using anaerobic respiration, it produces a by product of ethanol, carbon dioxide and energy.
- 28. Difference between Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Definition Uses oxygen to breakdown glucose in the body Uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. Cells that use it Aerobic respiration occurs in plant and animal cells Anaerobic respiration occurs in bacteria, yeasts, some prokaryotes, erythrocytes (red blood cells), and in muscle cells. Lactic Acid Does not produce lactic acid Produces lactic acid
- 29. Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration By Product s Carbon dioxide, water, energy • Lactic acid + energy in animals • Ethanol + carbon dioxide + energy in Plants Equatio n C6H12O6+ O2 CO2 + H2O • C6H12O6 2C3H6O3 + energy • C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2+energy Locatio n Begins in cytoplasm and continues to mitochondria In cytoplasm
Notas do Editor
- Fart contains odorless gases such as NITROGEN, OXYGEN, HYGROGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE AND METHANE. It has a small portion of Hydrogen sulfide which causes it to smell like a rotten egg.